3D PRINTING
1. Context
- The emergence of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has transformed industries and innovation.
- The collaboration between multinational company Larsen & Toubro Limited and IIT Madras, guided by Professor Manu Santhanam, has highlighted the potential of this technology.
- While initial flaws hindered its progress, recent developments have propelled 3D printing into various sectors, including aerospace and automotive.
2. What is 3D Printing?
- 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is an innovative technology that has redefined traditional manufacturing processes.
- It involves the creation of three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer, guided by a computer-generated design.
- This method contrasts with subtractive manufacturing, where the material is removed from a solid block to achieve the desired shape.
3. Process Overview:
- Design: The process begins with a digital 3D model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This virtual blueprint guides the printer on how to construct the physical object.
- Layering: The 3D printer interprets the digital model and begins the additive process. It deposits material, often in the form of plastic, metal, or composite, layer by layer to form the final object.
- Building Up: As each layer is added, the object gradually takes shape. The printer's precision ensures the accurate reproduction of intricate details, resulting in a three-dimensional physical replica of the digital model.
4. Key Advantages:
- Complex Geometry: 3D printing enables the creation of highly complex and intricate geometries that might be challenging or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods.
- Customization: It allows for personalized and customizable products, catering to the specific needs and preferences of users.
- Rapid Prototyping: The technology is widely used for rapid prototyping, allowing designers and engineers to quickly iterate and test ideas before committing to full-scale production.
- Reduced Material Waste: Unlike subtractive manufacturing, where excess material is often discarded, 3D printing adds material only where needed, minimizing waste.
- On-Demand Production: 3D printing facilitates on-demand manufacturing, reducing the need for mass production and warehousing.
5. Applications and Challenges
- Aerospace: Used to create lightweight, high-performance components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Healthcare: Utilized for producing patient-specific medical implants, prosthetics, and even human tissue.
- Automotive: Enables rapid prototyping of vehicle components and customization.
- Fashion: Designers employ 3D printing to create unique and avant-garde clothing and accessories.
- Architecture: Used in creating detailed architectural models and prototypes.
Challenges
- Limited material options compared to traditional manufacturing.
- Slower production speed for larger objects.
- Post-processing may be required to achieve desired surface finishes.
6. Conclusion
3D printing has revolutionized the way objects are designed, manufactured, and customized. Its ability to create intricate and unique structures with precision has found applications across diverse industries, promising continued innovation and reshaping the manufacturing landscape.
|
For Prelims: 3D Printing, Architectural models, Prototypes, Computer-aided design (CAD) software. For Mains: 1. Discuss the concept of 3D printing, its technological process, and its transformative impact on traditional manufacturing methods. (250 words) 2. Highlight the advantages of additive manufacturing, including complex geometry, Customisation, rapid prototyping, and reduced material waste. (250 words) |
Previous year Question1. "3D printing" has applications in which of the following? (UPSC 2018) 1. Preparation of confectionery items 2. Manufacture of bionic ears 3. Automotive industry 4. Reconstructive surgeries 5. Data processing technologies Select the correct answer using the code given below: A. 1, 3, and 4 only B. 2, 3, and 5 only C. 1 and 4 only D. 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Answer: D |
UNEMPLOYMENT IN INDIA
Unemployment is a situation where people who are actively seeking employment are unable to find work. The unemployment rate is calculated as the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
The labor force is defined as the number of people who are either employed or unemployed.
2.1. Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate in India is the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed
The unemployment rate in India has been fluctuating in recent years.
In 2020, the unemployment rate was 10.20%, which was the highest it had been in decades.
The unemployment rate then declined to 7.71% in 2021
Where:
- Number of Unemployed Individuals: The total number of people who are able and willing to work but are currently unemployed and actively seeking employment.
- Labor Force: The total number of people who are either employed or actively seeking employment.
The formula to calculate the employment rate is:
Employment Rate = (Number of Employed Individuals / Working-Age Population) x 100
Where:
- Number of Employed Individuals: The total number of people who are currently employed.
- Working-Age Population: The total number of people within a specified age range (typically those considered to be of working age).
Some common types of unemployment include:
-
Structural Unemployment: This type of unemployment occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills possessed by workers and the skills demanded by available job opportunities. It can result from changes in technology, shifts in industries, or changes in consumer preferences.
-
Frictional Unemployment: Frictional unemployment arises due to the natural process of workers moving between jobs or entering the workforce for the first time. It occurs when there is a temporary gap between the end of one job and the start of another.
-
Cyclical Unemployment: Cyclical unemployment is caused by fluctuations in economic activity and demand. It increases during economic downturns or recessions when businesses reduce production and lay off workers due to decreased consumer spending.
-
Seasonal Unemployment: Seasonal unemployment is linked to seasonal changes in demand for specific industries. For example, agricultural or tourism-related jobs might experience temporary unemployment during off-seasons.
-
Long-Term Unemployment: This refers to individuals who have been unemployed for an extended period, often for more than six months. It can lead to skill erosion and decreased employability.
- The deterioration in the employment scenario can be tracked at many levels
- One, over the years, there has been a sharp fall in the labour force participation rate in India
- Data from CMIE suggests that the labour force participation rate has fallen to around 40 per cent. For comparable countries, it is significantly higher.
- This decline suggests that despite India’s young population, many have simply opted out of the labour force, perhaps feeling let down by the absence of remunerative, productive jobs
- The situation is even more dire for women who had a considerably lower participation rate to begin with. India’s female labour force participation is not only lower than the global average, but also lower than countries like Bangladesh
- Two, even as the unemployment rate has declined from the highs observed during the initial phase of the pandemic, it remains elevated, suggesting that among those looking for jobs, those unable to find jobs remains high
- Three, the unemployment rate is higher among the younger and more educated. As per the periodic labour force surveys, the unemployment rate is higher among those in the 15-29 age group (22.5 per cent in September 2019), and those educated up to at least the secondary level (11 per cent).
- Four, while there are signs of increasing formalisation as indicated by the EPFO data, a substantial share of the labour force continues to remain employed in the informal sector, lacking a safety net
CMIE's role is to provide economic data, analysis, and forecasts for India and the world. It does this through a variety of products and services, including:
- Economic data: CMIE collects and publishes economic data on a variety of topics, including GDP, inflation, employment, and trade.
- Economic analysis: CMIE provides analysis of economic data and trends.
- Economic forecasts: CMIE provides forecasts of economic growth, inflation, and other economic indicators.
- Business information: CMIE provides information on businesses in India, including financial data, company profiles, and industry reports.
- Market research: CMIE provides market research on a variety of topics, including consumer behavior, retail trends, and industrial production.
- Training: CMIE provides training on economic data analysis and forecasting.
|
For Prelims: Unemployment, Types of Unemployment, Periodic Labour Force Survey
For Mains: 1.Discuss the different types of unemployment prevalent in India and analyze their causes. How do these types of unemployment impact the country's labor market and overall economic growth?
2.India's demographic dividend has the potential to drive economic growth, but the challenge of youth unemployment persists. Analyze the factors contributing to youth unemployment and propose policy interventions to address this issue effectively.
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Disguised Unemployment generally means
A. Large number of people remain unemployed
B. Alternative Employment is not available
C. Marginal Productivity od Labour is Zero
D. Productivity of Workers is Zero
Answer -C
|
PROJECT 17A AND INS TARAGIRI
Taragiri, the indigenously-designed Nilgiri-class stealth guided-missile frigate constructed by Mazgaon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), was launched in Mumbai Sunday morning.
Taragiri is the third stealth frigate built as part of Project 17A under which a series of such guided-missile frigates are being constructed for the Navy.

2. Project 17A
- Project 17A is an Indian Navy project to build a series of stealth guided-missile frigates. The project is being undertaken by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE)
- The first ship of the class, INS Nilgiri, was launched in 2019. The second ship, INS Himgiri, was launched in 2020.
- The third ship, INS Udaygiri, was launched in 2022. The fourth ship, INS Dunagiri, was launched in July 2022. The fifth ship, INS Taragiri, was launched in August 2022.
- The Project 17A frigates are designed to be more stealthy than the previous Project 17 Shivalik-class frigates.
- They have a low radar cross-section and are equipped with a variety of stealth features, such as radar-absorbent materials and reduced infrared and acoustic signatures.
- The sixth ship, INS Vindhyagiri, was launched by President Ram Nath Kovind on August 17, 2023
- The Project 17A frigates are also equipped with a more advanced weapons and sensor suite than the Shivalik-class frigates.
- They are armed with a 76mm main gun, two 30mm close-in weapon systems, eight Barak 8 surface-to-air missiles, 32 VL-SRSM anti-ship missiles, and two 16-cell vertical launch systems for various missiles. They are also equipped with a towed array sonar and a hull-mounted sonar.
2.1.Objectives of Project 17A
The Project 17A frigates are expected to be commissioned into the Indian Navy between 2024 and 2026. They will play a significant role in the Indian Navy's fleet modernization program
Key features and objectives of Project 17A include:
-
Advanced Technology: Project 17A destroyers are designed to incorporate advanced technology and modern systems to enhance their combat capabilities, survivability, and versatility.
-
Stealth and Survivability: These ships are expected to have reduced radar cross-sections and improved stealth features, making them less detectable by adversaries.
-
Weapon Systems: Project 17A destroyers are equipped with a variety of weapon systems, including advanced anti-ship and anti-air missiles, surface-to-surface missiles, torpedoes, and naval guns.
-
Aegis Combat System: Some reports suggest that these ships may be equipped with an indigenous version of the Aegis combat system, which provides advanced command, control, and communication capabilities along with missile defense capabilities.
-
Multi-Role Capability: The Project 17A destroyers are designed to have multi-role capabilities, allowing them to engage in a range of naval operations, including anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine warfare.
-
Indigenous Construction: The Indian Navy's focus on indigenization is evident in Project 17A, which involves a significant degree of domestic shipbuilding expertise, technology integration, and use of indigenous components.
-
Collaboration: Collaboration with various defense research and development organizations, as well as shipyards, is an integral part of Project 17A's development.
-
Enhancing Naval Power: The addition of Project 17A destroyers to the Indian Navy's fleet is expected to enhance India's naval power projection capabilities and provide a modern and capable platform for a range of maritime operations
- The first ship of Project 17A, Nilgiri, was launched on September 28, 2019 and is expected to undergo sea trials in the first half of 2024
- INS Taragiri is a multi-role warship capable of carrying out a variety of missions, including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, and air defence.
- It is armed with a variety of weapons, including a 76mm main gun, two 30mm close-in weapon systems, eight Barak 8 surface-to-air missiles, 32 VL-SRSM anti-ship missiles, and two 16-cell vertical launch systems for various missiles. The ship is also equipped with a towed array sonar and a hull-mounted sonar
- INS Taragiri (F41) is a Talwar-class frigate in the Indian Navy.
- The Talwar-class frigates are a class of guided-missile frigates developed in Russia for export to various countries, including India. INS Taragiri was the second ship of the Talwar-class and was in service with the Indian Navy
|
For Prelims: INS Taragiri, Project 17A, INS Astradharini For Mains: 1.Discuss the objectives and significance of Project 17A in the context of India's naval modernization efforts. How does Project 17A contribute to enhancing the Indian Navy's capabilities and strategic maritime goals? Analyze the role of indigenous shipbuilding and technology integration in the development of Project 17A destroyers. How does this project reflect India's efforts towards self-reliance in defense production and maritime technology? |
|
Previous Year Questions 1.Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016) (A) Amphibious warfare ship Answer-C |
Source: indianexpress
PUBLIC TECH PLATFORM FOR FRICTIONLESS CREDIT
1. Context
2. Credit Appraisal and Digital Loan Delivery:
- Credit appraisal assesses borrower's ability to repay loans and adhere to agreements.
- Crucial for banks as it affects their interest income and balance sheets.
- Data needed for appraisal spread across different entities, causing delays and issues.
- Separate systems hinder smooth and timely rule-based lending.
3. Centralized Platform Solution:
- New platform integrates data from various sources into a single system.
- Aims to enable seamless and timely loan delivery.
- Addresses hindrances in the current lending process.
4. Pilot Project for Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Digitalization:
- Central banking regulator initiated pia lot in September 2022.
- Focus on digitalizing KCC loans below 1.6 lahks.
- Testing paperless and hassle-free end-to-end lending process.
- Ongoing in selected districts of Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Offers doorstep loan disbursement in assisted or self-service mode without paperwork.
5. Platform Expansion and Development:
- Platform builds on insights from ongoing programs and expands to cover all digital loan types.
- Developed by Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH), a wholly-owned subsidiary.
- Proposed platform features open architecture, APIs, and standards for seamless connections.
- Financial sector participants can easily integrate through a 'plug and play' model.
- Participation of specific banks broadens the platform's focus.
- Encompasses dairy loans, collateral-free MSME loans, personal loans, and home loans.
- Links with various services including Aadhar e-KYC, e-signing, state land records, satellite data, PAN validation, etc.
- Incorporates data from account aggregators, select dairy cooperatives, and property searches.
- Covers farming operations for loan risk assessment and financial profiles.
- Project's insights lead to wider scope and coverage.
- More lenders and information providers to be included based on learning outcomes.
- Aims to create a comprehensive, accessible, and efficient lending ecosystem.
6. Information Access and Credit Assessment:
- Experts, including the World Bank, highlight improved information access for accurate and fast credit assessments.
- Ensures broader credit extension to borrowers with good credit history.
- Borrowers benefit from lower capital access costs, leading to productive investments.
7. Efficiency and Cost Benefits:
- Traditional credit process involves multiple bank visits and complex documentation.
- This results in higher operational costs for lenders, impacting borrowers too.
- RBI survey suggests farm loan processing took 2 to 4 weeks and costs 6% of the loan's value.
- Lending platform aims to reduce costs, expedite disbursement, and enhance scalability.
8. About RBI Innovation Hub (RBIH)
Key Focus Areas: RBIH operates across a spectrum of domains within the financial sector, including but not limited to:
- Payment and Settlement Systems
- Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
- Supervisory Technology (SupTech)
- Financial Inclusion
- Digital Currencies and Blockchain
- Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
Impact and Significance:
- The establishment of the RBI Innovation Hub underscores the RBI's commitment to embracing technological advancements and staying at the forefront of financial innovation.
- By fostering collaboration and experimentation, the hub aims to contribute to India's more robust, inclusive, and technologically-driven financial ecosystem.
- In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, RBIH serves as a catalyst for change, channeling innovation toward solutions that enhance financial services, streamline operations, and strengthen the overall resilience of the financial sector.
- Through its initiatives, partnerships, and research endeavors, the RBI Innovation Hub is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of finance in India and contributing to the global discourse on financial innovation.
|
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India (RBI), RBI Innovation Hub, Kisan Credit Card (KCC), Frictionless Credit, Digital Loan Delivery, Regulatory, and Supervisory Technology.
For Mains: 1. "Discuss the role and significance of the RBI Innovation Hub (RBIH) in fostering financial innovation and driving technological advancements in the Indian financial sector. (250 Words)
|
Previous year Question1. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2019)
The Reserve Bank of India's recent directives relating to 'Storage of Payment System Data', popularly known as data diktat, command the payment system providers that
1. they shall ensure that entire data relating to payment systems operated by them are stored in a system only in India.
2. they shall ensure that the systems are owned and operated by public-sector enterprises
3. they shall submit the consolidated system audit report to the Comptroller and Auditor General of India by the end of the calendar year
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
2. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2018)
1. The Reserve Bank of India manages and services Government of India Securities but not any State Government Securities.
2. Treasury bills are issued by the Government of India and there are no treasury bills issued by the State Governments.
3. Treasury bills offer are issued at a discount from the par value.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
3. Consider the following statements : (UPSC 2021)
1. The Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is appointed by the Central Government.
2. Certain provisions in the Constitution of India give the Central Government the right to issue directions to the RBI in the public interest.
3. The Governor of the RBI draws his natural power from the RBI Act.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
4. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as a bankers' bank. This would imply which of the following? (UPSC 2012)
1. Other banks retain their deposits with the RBI.
2. The RBI lends funds to commercial banks in times of need.
3. The RBI advises commercial banks on monetary matters.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
A. 2 and 3 0nly
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
|
SPECTRO POLARIMETRY OF HABITABLE PLANET EARTH (SHAPE)
- Chandrayaan-3 had been proposed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) as a follow-up mission to the Chandrayaan-2 lunar mission. Chandrayaan-2, launched in July 2019, aimed to study the Moon's south polar region and included an orbiter, a lander (Vikram), and a rover (Pragyan)
- The Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft comprises two parts
- The Lander Module, which also houses the rover component, is designed to travel to the Moon and is expected to land on the lunar surface
- The leftover part, the Propulsion Module, whose job was to transport the Lander to the Moon orbit, will continue to go around the Moon for a few months, possibly even years, in an outer orbit
- The Lander Module is scheduled to make two orbit-reduction manoeuvres over the coming days, first attaining a circular 100 km x 100 km orbit, then coming down further into a 100 km x 30 km orbit
- It is from here that the Lander will begin its final descent to make a touchdown on the Moon
- The Propulsion Module of Chandrayaan-3 has been doing the job of the Orbiter component in Chandrayaan-2.
- It is equipped with one instrument called SHAPE (Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth) whose job is to make spectroscopic study of the Earth’s atmosphere from that distance, and try to pick up signals that will help scientists understand the markers of life on planets outside our solar system

- The SHAPE mission is a collaborative effort between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (IKI)
- The Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) is an experimental payload onboard the Chandrayaan-3 mission. It is designed to study the spectro-polarimetric signatures of Earth in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range (1.0 – 1.7 μm)
- Polarimetry is a technique that measures the polarization of light. Polarization refers to the direction of the electric field of light waves. Light that is not polarized has its electric field randomly oriented in all directions. Polarized light has its electric field oriented in a specific direction.
- Spectro-polarimetry is a combination of spectroscopy and polarimetry. Spectroscopy is the study of the spectrum of light, which is the distribution of light energy over different wavelengths
The SHAPE instrument will use spectro-polarimetry to study the following aspects of Earth's atmosphere:
- The distribution of water vapor and other gases
- The presence of clouds and aerosols
- The structure of the atmosphere
- The changes in the atmosphere caused by human activity
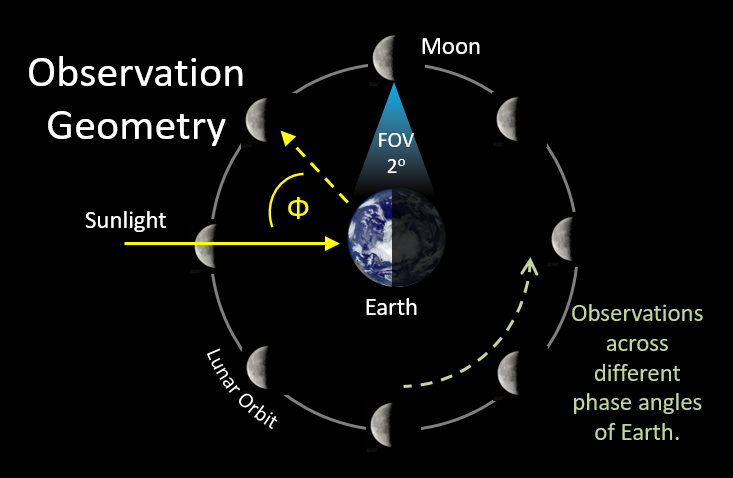
- SHAPE can be used to study the distribution of water vapor in Earth's atmosphere. Water vapor is an important greenhouse gas that plays a role in climate change. SHAPE can be used to map the distribution of water vapor in the atmosphere and to study how it changes over time.
- SHAPE can be used to study the presence of clouds and aerosols in Earth's atmosphere. Clouds and aerosols reflect sunlight, which can affect the amount of heat that is absorbed by Earth. SHAPE can be used to map the distribution of clouds and aerosols in the atmosphere and to study how they change over time.
- SHAPE can be used to study the structure of Earth's atmosphere. The atmosphere is made up of several layers, each with its own unique properties. SHAPE can be used to study the different layers of the atmosphere and to study how they interact with each other.
- SHAPE can be used to study the changes in Earth's atmosphere caused by human activity. Human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels, is releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases are causing the atmosphere to warm, which is leading to changes in the climate. SHAPE can be used to study these changes and to help us understand the impact of human activity on the atmosphere
|
For Prelims: Chandrayan-3, SHAPE, PSLV, GSLV
For Mains: 1.Critically assess the role of Chandrayaan missions in promoting scientific research and technological innovation in India. How have these missions inspired the nation's youth and bolstered India's reputation in the global space community?
2.Discuss the international collaborations and partnerships that ISRO has established for its Chandrayaan missions. How do such collaborations enhance the scientific outcomes of these missions and contribute to global space research?
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Chandrayan-1, India's first mission to the moonwas launched from----- (SSC CPO Tier-1 2019)
A. Srikalahasti
B.Srikakulam
C.Sriharikota
D.Srisailam
Answer- C
|




