INDIANS AND H1-B
- The H-1B visa program for skilled workers was introduced in 1990. These visas are initially issued for three years but can be extended to a maximum of six years.
- Since 2004, the issuance of new H-1B visas has been capped at 85,000 annually, with 20,000 reserved specifically for foreign students who hold master’s degrees or higher from U.S. universities.
- This cap, however, does not apply to certain entities like universities, think tanks, and other non-profit research organizations, allowing additional visas to be issued beyond the limit.
- Applicants for H-1B visas must have a job offer from a U.S.-based sponsor, such as a company or institution. The U.S. government also grants extensions for individuals already working under H-1B visas.
- During the fiscal year 2023 (October 2022 to September 2023), over 386,000 H-1B applications were approved. This figure includes nearly 119,000 new visas and approximately 267,000 extensions.
- The total number of approvals in 2023 reflects a decline from over 474,000 in the previous fiscal year, 2022
- Immigration remains one of the most divisive political topics in the United States. An October YouGov poll revealed that 14.6% of registered voters considered it the most critical issue in the upcoming election, a significant increase from just 2.1% in 2012.
- During election campaigns, much of the anti-immigration discourse centered on low-skilled labor migration. Beyond its inherent racial undertones, this narrative is driven by the perception that such immigration lowers wages and displaces jobs that might otherwise benefit the American working class.
- This demographic has long struggled with challenges like high unemployment, stagnant wages, inflation, a housing crisis, and other economic difficulties.
- Donald Trump effectively leveraged these concerns, pledging to improve conditions for the average American worker by restricting immigration.
- The current debate echoes many of the same themes as Trump’s rhetoric about Mexicans "stealing American jobs," though the focus has shifted to the immigration of skilled workers competing for higher-paying positions
- The H-1B visa program enables U.S. employers to hire foreign workers for roles requiring "a high level of skill" and "at least a bachelor’s degree," as outlined by the U.S. Department of Labor.
- Established in 1990, the program was designed to assist employers in filling roles that demand specialized skills not readily available within the U.S. workforce, allowing qualified foreign individuals to work temporarily in the United States.
- H-1B visas are typically issued for a maximum of six consecutive years. After this period, visa holders must either leave the U.S. for at least 12 months before returning or apply for permanent residency (a Green Card).
- Currently, the program has an annual limit of 65,000 new visas (the regular cap), with an additional 20,000 visas available for applicants holding master’s degrees or higher from U.S. universities. However, not all H-1B applications are subject to this cap, resulting in the total number of approved petitions often exceeding the cap.
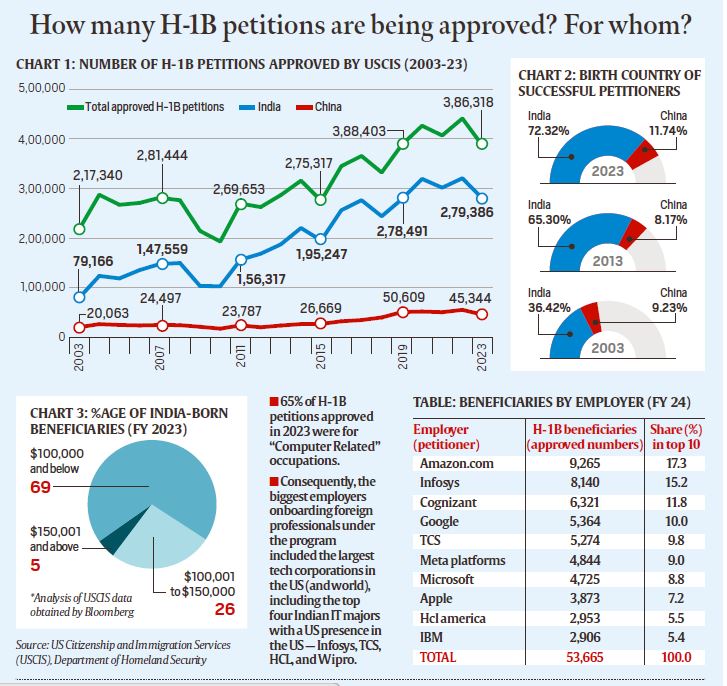
- For example, in the fiscal year 2023, the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), under the Department of Homeland Security, approved 118,948 petitions for initial employment and 267,370 petitions for continuing employment.
- Certain applicants, such as those employed by higher education institutions, nonprofit organizations affiliated with such institutions, nonprofit research organizations, or government research entities, are exempt from the annual cap
- Indian nationals are the primary beneficiaries of the H-1B visa program, consistently accounting for over 70% of all approved H-1B petitions annually since 2015, according to U.S. government data. Chinese nationals rank a distant second, making up 12-13% of approvals since 2018.
- This significant representation of Indian professionals has drawn the attention of nativist MAGA Republicans, who have extended their anti-immigration rhetoric from low-skilled labor migration by Mexicans and Central Americans to include Indian workers in the tech industry.
- Their argument revolves around the claim that the H-1B program, originally designed to attract exceptional global talent, is being exploited by tech companies to fill lower- to mid-level positions at wages much lower than those expected by American workers.
- While proponents like Elon Musk argue that H-1B visas address a "permanent shortage of excellent engineering talent," critics counter that the issue is not a lack of skilled American workers but that they are deemed "too expensive to hire" by tech firms.
- This critique is supported by data. An analysis of 60,000 H-1B approvals from USCIS in the 2023 fiscal year, conducted by Bloomberg, revealed that nearly 70% of Indian H-1B recipients earned annual salaries below $100,000.
- For comparison, the median salary for IT professionals in the U.S. was $104,420 in May 2023, as reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Approximately 25% of H-1B approvals for Indian professionals fell within the $100,000 to $150,000 salary range, while only 5% exceeded $150,000
|
For Prelims: H-1B visa, United States, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, STEM fields, lottery system,
For Mains:
1. What are the implications of the new H-1B visa regime for US-India relations?
Discuss the measures can the Indian government take to support Indian IT workers affected by the new H-1B visa regime. (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2019)
1. Coal sector was nationalized by the Government of India under Indira Gandhi.
2. Now, coal blocks are allocated on lottery basis.
3. Till recently, India imported coal to meet the shortages of domestic supply, but now India is self-sufficient in coal production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 and 3 only C. 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
2. Which of the following statements about town planning in British India in early 19th century is/are correct? (UPSC CAPF 2018)
1. The funds for town improvement were also raised through public lotteries.
2. The threats of epidemics gave an impetus to town planning in the early decades of 19th century.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
A.1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
|
DWARF PLANET
1. Context
2. Dwarf Planet
- A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right.
- The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. Astronomers are in general agreement that at least the nine largest candidates are dwarf planets: Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Sedna, Ceres, and Orcus.
.jpg)
3. A recent discovery about Quora
- Recently, a ring system or a clumpy disc of ice particles was observed around Quaoar, at a distance of 4,100 Km from its center.
- Quaoar is a dwarf planet, about half the size of Pluto, located in the Kuiper belt, which is a region of icy planetesimals beyond Neptune.
- The planet was discovered in 2002 and has been defined as a minor planet, as the International Astronomical Union has yet to formally classify it as a dwarf planet.
4. How was the ring discovered?
- A stellar occultation occurs when, as seen from Earth, a bright star passes behind a planet.
- This allows astronomers or anybody on Earth to observe the sharp silhouette of the planet for a brief period of time.
- This phenomenon, which rarely occurs, is used by researchers to analyze a planet's atmosphere and determine if it has a ring around it in 1977, scientists discovered the Uranium ring system with the help of stellar occultation.
- The team involved in the latest study examined Quaoar for around three years, between 2018 and 2021, through Earth-based and space-based telescopes.
- During these years, the dwarf planet passed in front of four stars, helping researchers observe the shadow of the eclipses.
5. Roche Limit
- The most intriguing part of the findings is the distance between Quaoar and its ring.
- Located 2,500 miles away from the dwarf planet, the ring is around 1,400 miles further away from the Roche limit, as per the calculations of the scientists.
- They suggest that at such a distance, the particles of the ring should have come together to form a moon.
- For a further understanding of the Roche limit, let's look at the Earth and the Moon.
- The Earth's gravity pulls on the moon. However one side of the moon is closer to the planet and hence, the pull is stronger on the side facing the Earth.
- The result is the so-called tidal force, which either stretches or compresses the moon from all sides. What helps the moon keep it together is its own gravity. It essentially counteracts the effect of the tidal force.
- But if you bring the moon closer to the Earth, the tidal force will overcome the satellite's gravity and then disintegrate it, turning the moon into a ring.
- The minimum distance at which this happens is known as the Roche limit. It is named after the French astronomer Edouard Roche, who discovered the limit in 1848.
- The Roche limit does not just exist between just the Earth and the Moon. It is applicable to any planet and the celestial bodies around it.
- For instance, Saturn. The beautiful rings that you see around the planet are within the Roche limit and therefore, there are no moons in that area.
6. What is the reason behind Quaoar’s far-out ring?
- As of now, nobody exactly knows how Quaoar’s ring has managed to remain stable at such a distance from the Roche limit.
- The researchers of the study have said that there can be a variety of possible explanations but they aren’t sure about any one of them.
- It might be possible that Quaoar’s moon, Weywot, or some other unseen moon contributes to gravity that somehow holds the ring stable.
- Another potential explanation can be that the particles of the ring are colliding with each other in such a way that they are avoiding to coalesce into a moon.
- No matter what the reason, astronomers believe the new study points to the possibility of discovering more rings around smaller planets like Quaoar in the outer solar system, which might expand our understanding of planetary ring systems.
For Prelims
| For Prelims: Dwarf planet, Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Sedna, Ceres, and Orcus, Quaoar, Kuiper belt, International Astronomical Union, Uranium ring system, Roche Limit. |
CLOUDBURST
1. Context
2. Cloudburst
- A cloudburst is a sudden and intense weather phenomenon characterized by a heavy and rapid release of precipitation from a cloud.
- This concentrated burst of rainfall can lead to flash floods, landslides, and other forms of water-related disasters in a very short period of time.
- Cloudbursts typically occur in areas with high humidity and convective activity, such as mountainous regions, coastal areas, and places prone to thunderstorms.
3. How do Cloud bursts Occur?
Cloudbursts typically occur in regions with convective activity, such as areas prone to thunderstorms, mountainous terrain, and coastal regions. They are often associated with towering cumulonimbus clouds, which are large and vertically developed clouds capable of generating intense rainfall and thunderstorms. Here's how a cloudburst happens:
- Formation of Cumulonimbus Clouds: Cloudbursts are most commonly associated with cumulonimbus clouds, which are towering clouds formed through the process of convection. Warm air near the Earth's surface rises, cools, and condenses into water droplets as it encounters cooler air at higher altitudes. This process leads to the formation of these large, vertically oriented clouds.
- Updrafts and Water Vapor: Inside a cumulonimbus cloud, strong updrafts of air carry water vapor from lower altitudes to higher altitudes within the cloud. As the air rises, it cools and the water vapor condenses into tiny water droplets or ice crystals.
- Collision and Coalescence: Within the cloud, water droplets and ice crystals collide and combine, forming larger droplets. As these droplets continue to collide and grow in size, they become too heavy for the updrafts to support, causing them to fall.
- Downdrafts: The larger water droplets and ice crystals begin to descend as downdrafts within the cloud. As they fall through the cloud, they can pick up additional moisture, further increasing their size.
- Precipitation Release: Eventually, the water droplets and ice crystals become large enough that the force of gravity overcomes the upward force of the updrafts, and they start to fall rapidly toward the Earth's surface. This is the point at which the cloudburst occurs. The droplets fall in large quantities over a relatively small area, resulting in intense rainfall within a short timeframe.
- Impact and Consequences: The rapid and concentrated release of precipitation from the cloudburst can overwhelm drainage systems, lead to flash floods, and trigger landslides, especially in areas with steep terrain. The intensity of the rainfall can result in immediate and severe flooding, causing damage to property, and infrastructure, and posing risks to human safety.
4. Causes of Cloud Bursts
- Atmospheric Instability: Cloud bursts often occur in regions with convective instability in the atmosphere. Convective instability refers to the situation where warm and moist air near the Earth's surface rises rapidly due to its lower density compared to the surrounding cooler air. This vertical motion can lead to the formation of towering cumulonimbus clouds that are capable of generating intense rainfall.
- Moisture Availability: The presence of abundant moisture in the atmosphere is essential for the formation of cloud bursts. When warm, moisture-laden air rises and condenses at higher altitudes, it releases latent heat, which further fuels the upward motion of air. This process can lead to the development of strong updrafts within clouds and the rapid accumulation of water droplets.
- Orographic Effects: Cloudbursts are often common in mountainous regions due to orographic lifting. When moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range, it cools and condenses, leading to the formation of clouds and potentially intense rainfall. The combination of orographic lifting and convective instability can enhance the likelihood of cloud bursts in these areas.
- Frontal Boundaries: Cloudbursts can also occur along frontal boundaries, where two air masses of differing temperatures and moisture content meet. The convergence of these air masses can create strong vertical motion and promote the development of thunderstorms and heavy rainfall.
- Cumulonimbus Clouds: Cloud bursts are often associated with cumulonimbus clouds, which are large and vertically developed clouds capable of generating intense weather. These clouds are formed through the process of convection, where warm air rises, cools, and condenses into cloud droplets. The presence of cumulonimbus clouds increases the likelihood of intense rainfall and thunderstorm activity.
5. Consequences of Cloud Bursts
- Flash Floods: One of the most immediate and dangerous consequences of a cloud burst is the occurrence of flash floods. The intense and concentrated rainfall from the cloud burst can overwhelm drainage systems, rivers, and streams, leading to rapid and widespread flooding. Flash floods can occur within minutes of the onset of heavy rainfall and pose a serious threat to lives, property, and infrastructure.
- Landslides and Mudslides: In hilly or mountainous regions, a cloud burst can saturate the soil, making it more susceptible to landslides and mudslides. The additional water weight, coupled with the steep terrain, can trigger the sudden movement of soil and rock, leading to dangerous landslides that can bury homes, roads, and communities.
- Property Damage: The rapid and intense nature of a cloud burst's rainfall can result in significant damage to homes, buildings, and infrastructure. Floodwaters can enter structures, causing structural damage, waterlogging, and destruction of personal belongings. Infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and utility systems can also be severely affected.
- Disruption of Services: Cloud bursts can disrupt essential services, including transportation, communication, and utilities. Flooded roads and bridges can make travel difficult or impossible, hampering emergency response and evacuation efforts. Power outages can occur if the electrical infrastructure is damaged by flooding or landslides.
- Health and Safety Risks: The flooding and contamination of water sources during a cloud burst can pose health risks to the affected population. Contaminated water can lead to the spread of waterborne diseases, and individuals may be at risk of injuries, drowning, or exposure to hazardous materials in floodwaters.
6. Mitigating Measures for Cloud Bursts
- Early Warning Systems: Implement effective early warning systems that can provide timely alerts about impending cloud bursts and heavy rainfall. These systems should be capable of reaching a wide audience through various communication channels, including mobile phones, sirens, and local media.
- Floodplain Zoning and Land Use Planning: Designate floodplain areas where development is restricted or regulated. Proper land use planning can help prevent construction in high-risk flood areas, reducing potential damage to property and infrastructure.
- Improved Drainage Infrastructure: Enhance drainage systems in urban and rural areas to handle sudden and intense rainfall. Well-designed drainage systems can help prevent water accumulation on roads and prevent flash floods.
- Erosion Control Measures: Implement erosion control measures, such as building retaining walls, stabilizing slopes, and using vegetation to prevent soil erosion in hilly and mountainous regions.
- Reservoirs and Dams: Construct reservoirs and dams to store excess water during heavy rainfall and release it gradually to prevent downstream flooding. Proper maintenance of these structures is essential to ensure their effectiveness.
- Green Infrastructure: Incorporate green infrastructure solutions such as permeable pavements, rain gardens, and rooftop gardens in urban planning. These measures can help absorb and manage excess rainwater, reducing the risk of flooding.
7. Conclusion
|
For Prelims: Cloudbursts, flash floods, landslides, Cumulonimbus Clouds, Water Vapour, Floodplain Zoning, Green Infrastructure.
For Mains: 1. What is a cloudburst, and how does it differ from regular rainfall? Explain the causes and meteorological factors that contribute to the occurrence of a cloudburst.
|
Previous year Questions1. Which of the following statements with regard to Cloudburst is/are correct? (UPSC CDS 2017)
1. It is defined as sudden localized very heavy downpour with cloud thunder and lightning.
2. It mostly occurs in the hilly areas.
3. It results in a very high intensity of rainfall, i.e., 250 mm-300 mm in a couple of hours.
4. It occurs only during the daytime.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1, 3 and 4
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 2 only
Answer: A
|
PM SVANIDHI
1. Context
2. Why was this scheme rolled out?
- The COVID-19 pandemic and the nationwide lockdown left daily wage workers and street vendors out of work.
- The scheme aims at aiding the vendors in getting back on their feet financially.
- In the long term, it aims at establishing a credit score for the vendors as well as creating a digital record of their socio-economic status, so that they can avail of the central government schemes later.
- The scheme also attempts to formalize the informal sector of the economy and provide them with safety nets and a means of availing loans in the future.
3. Who is a street vendor?
- Any person engaged in vending of articles, goods, wares, food items, or merchandise of daily use or offering services to the public in a street, footpath, pavement, etc., from a temporary built-up structure or by moving from place to place.
- The goods supplied by them include vegetables, fruits, ready-to-eat street food, tea, pakodas, bread, eggs, textile, apparel, artisan products, books/stationary, etc. and the services include barber shops, cobblers, pan shops, laundry services, etc.
4. What is the rationale of the scheme?
- The COVID-19 pandemic and consequent lockdowns have adversely impacted the livelihoods of street vendors.
- They usually work with a small capital base, which they might have consumed during the lockdown.
- Therefore, credit for working capital to street vendors will be helpful to resume their livelihoods.
5. What are the objectives of the scheme?
- To incentivize regular repayment of loans; and
- to reward digital transactions.
6. What are the salient features of the scheme?
- Initial working capital of up to 10,000/-
- Interest subsidy on timely/early repayment @ 7%.
- Monthly cash-back incentive on digital transactions
- Higher loan eligibility on timely repayment of the first loan
7. Eligibility criteria of the beneficiaries
- The Scheme is available to all street vendors engaged in vending in urban areas *. The eligible vendors will be identified as per the following criteria:
- Street vendors in possession of a Certificate of Vending / Identity Card issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs);
- The vendors, who have been identified in the survey but have not been issued a Certificate of Vending / Identity Card; a Provisional Certificate of Vending would be generated for such vendors through an IT-based Platform. ULBs are encouraged to issue such vendors the permanent Certificate of Vending and Identification Card immediately and positively within one month.
- Street vendors left out of the ULB-led identification survey or who have started vending after completion of the survey and have been issued a Letter of Recommendation (LoR) to that effect by the ULB/ Town Vending Committee (TVC); and
- The vendors of surrounding development/peri-urban/ rural areas vending in the geographical limits of the ULBs have been issued a Letter of Recommendation (LoR) to that effect by the ULB/TVC.
- The list of vendors, prepared by certain States/ UTs, for providing one-time assistance during the period of lockdown; OR
- A system-generated request was sent to ULBs/ TVCs for the issue of LoR based on the recommendation of the Lender after verifying the credentials of the applicant; OR
- The membership details with the vendor's associations including the National Association of Street Vendors of India (NASVI)/ National Hawkers Federation (NHF)/ Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) etc.; OR (iv) The documents in possession of the vendor buttressing his claim of vending; OR (v) Report of local inquiry conducted by ULB/ TVC involving Self-Help Groups (SHGs), Community-Based Organizations (CBOs), etc. ULB shall complete the verification and issuance of LoR within 15 days of the submission of the application.
- Further, ULBs may adopt any other alternate way for identifying such vendors to ensure that all the eligible vendors are positively covered.
- vendors who have gone back to their native places due to COVID-19 Some of the identified/surveyed or other vendors who have been vending/hawking in urban areas have left for their native places before or during the lockdown period because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Such vendors are likely to come back after the situation normalizes and resume their business.
|
Once a LOR is issued by the ULBs, its mandate lasts a month, after which the survey for the issuance of the certificate of vending should be undertaken by the ULBs. But since it is a state subject, the central government can only direct or sensitize the state governments on the importance of doing so, and not evict vendors who have availed of the loan but do not have a certificate.
The scheme is already a hit; so far 25 lakh street vendors have come forward seeking the loan. The next stage being contemplated is to make a first-of-its-kind database of the beneficiaries of this scheme to see who they are, and where they belong vis-à-vis the government’s social security net woven through various welfare schemes on education, housing, food, livelihood, etc.,
|
7. Why is such a study needed?
- The scheme plans to extend the microcredit to over 50 lakh street vendors across India, which is the estimated number of hawkers as per various urban local bodies.
- But, going beyond the mandate of this scheme, the government wants to use the data for comprehensive poverty alleviation.
- However, there is hardly any comprehensive structured data on the socio-economic profile of street vendors and the street vending economy in India, even in government surveys like the National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) and the Economic Survey.
- The NSSO, for instance, has defined street vendors through a category of “enterprises without fixed premises” among “Unincorporated Non-Agricultural Enterprises (excluding construction)”, in its 67-68th round report published in 2011- 12.
- The NSSO data estimated that around 200,000 women and 21,500 children were engaged in street vending. Around 1.18 million households were dependent on this sector as their primary source of income, according to a paper by the think-tank Observer Research Foundation.
- Non-governmental organizations and research by scholars have attempted to put together this kind of data several times in the past in bits and pieces.
8. Will this scheme actually work towards poverty alleviation?
- Becoming formal beneficiaries of various government schemes works as a big step towards entering the policy intervention network.
- Officials say it also helps in financial mainstreaming in the long run.
- For example, several banks, bereft of the prior experience of extending loans as little as Rs. 10,000 to someone like a street vendor, are following processes like checking the CIBIL score for the street vendor and seeking PAN card and IT-return, etc.
- While these cases are dealt with as hurdles on the ground, it is a fact that street vendors hardly have creditworthiness in the eyes of India's formal banking system.
- Therefore, the PMSVANidhi is incentivizing digital transactions by street vendors. They will soon be given QR codes to receive payments through the government’s BHIM UPI app.
- They are given cash back for digital transactions too. The idea is that with a trail of digital transactions against their names, they will create a formal transaction history in banks and will slowly build their creditworthiness for the future.
|
For Prelims: PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme, Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), National Association of Street Vendors of India (NASVI)/ National Hawkers Federation (NHF)/ Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA), Self-Help Groups (SHGs), Letter of Recommendation (LoR), National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) and BHIM UPI.
For Mains:1. What is the PM SVANidhi scheme and explain the rationale of the scheme. Discuss how it will help in the alleviation of poverty(250 words).
|
INDIA-JAPAN RELATIONS
1.Context
2. Historical Background
- Exchange between Japan and India is said to have begun in the 6th century when Buddhism was introduced to Japan. Indian culture, filtered through Buddhism, has had a great impact on Japanese culture, and this is the source of the Japanese people's sense of closeness to India.
- After World War II, in 1949, Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru donated an Indian elephant to the Ueno Zoo in Tokyo. This brought a ray of light into the lives of the Japanese people who still had not recovered from defeat in the war. Japan and India signed a peace treaty and established diplomatic relations on 28th April 1952. This treaty was one of the first peace treaties Japan signed after World War II.
- Ever since the establishment of diplomatic relations, the two countries have enjoyed cordial relations.
- In the post-World War II period, India's iron ore helped a great deal in Japan's recovery from the devastation.
3. Bilateral relations
- India and Japan are committed to working together to promote peace, stability and prosperity, through economic growth and development in the Indo-Pacific, including Africa, by enhancing connectivity through quality infrastructure and capacity building of our partners.
- Both countries are of firm belief that all development cooperation must be carried out in an open, transparent and non-exclusive manner and based on international standards including respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity of nations, responsible debt financing practices, and in alignment with local economic and development strategies and priorities.
- While Japan has been one of the biggest sources of investment flows into India, accounting for $28.16 billion in FDI between April 2000 and June 2018, trade engagements have been below potential. On the list of countries that India exports to, Japan is a lowly 18th; on the list of countries importing into India, Japan ranks 12th.
- Both India and Japan believe that their development cooperation in the Indo-Pacific can contribute to unlocking the potential for an equitable, positive and forward-looking change in the region, and contribute to the socio-economic development of Africa.

4. The partnership in the economic domain
- Cooperation on the development of connectivity in the Indo-Pacific region, including in Sri Lanka, Myanmar and Bangladesh as well as in Africa.
- In this regard, the two Prime Ministers welcomed the discussions for establishing the "Platform for Japan-India Business Cooperation in Asia-Africa Region” to further enhance the exchanges between Japanese and Indian businesses toward developing industrial corridors and industrial networks in the region.
- India-Japan Act East Forum identifies and implements projects for enhancing connectivity, sustainable forest and ecological management, disaster risk reduction and people-to-people exchanges. They also highlighted the importance of developing smart islands in India.
- Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail project, which is an important symbol of India-Japan collaboration marked by the 75th anniversary of India’s independence.
- Japan’s role in promoting connectivity through quality infrastructure projects such as the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor and the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor is immense
- India welcomed Japan’s strong support for key transformational initiatives such as "Make in India”, "Skill India” and "Clean India Mission”, through sharing of resources and advanced technologies, and active mobilization of the Japanese public and private sector investments.
- Both countries recognise the close cooperation in Intellectual Property Rights between the Intellectual Property Offices of the two countries
- Japan’s Foreign Direct Investment in India under the "India-Japan Investment Promotion Partnership”, the progress made in Japan Industrial Townships (JIT) and other initiatives included in the Japan-India Roadmap for Investment Promotion.
- Bilateral Swap Arrangement (BSA) of USD 75 billion about External Commercial Borrowing (ECB), no mandatory hedging will be required for infrastructure ECB of more than 5 years minimum average maturity.
- Japan-India Institutes for Manufacturing (Jims) as well as the Japanese Endowed Courses (JEC) in various Indian states.
- Cooperation in human resource development and exchanges, including through utilizing frameworks such as Japan’s "Innovative Asia” initiative, and the Technical Intern Training Program (TITP) will be further promoted, aligning with the emerging demands of the industry.
- India-Japan Digital Partnership with the vision to develop IoT and AI solutions for societal benefits and explore collaboration in emerging technologies by utilizing the "Japan-India Start-Up Hub” having a convergence between India’s flagship programmes such as "Digital India”, "Start-Up India” and "Smart City” with Japan’s "Society 5.0” to promote societal benefits.
- People-to-people exchanges are at the core of the India-Japan partnership and noted with satisfaction the growing cultural, educational, parliamentary, academic and Track 1.5 engagements, including the "Indo-Pacific Forum”.
5. Challenges in India-Japan Relations
- India’s exports to Japan in FY20 were lower than in FY18 in overall value.
- India and Japan have come a long way in their economic cooperation which is appreciable but India needs to take a vital stand as China-Japan economic ties are 30 times more than that of India
- India's access to the Japanese market is limited as India is struggling with various sanitary and phytosanitary measures.
- Exchanges associated with defence equipment are barely seen between the two democracies.
- Though there are common interests in tackling china but common measures associated to replace china are barely seen.
- Concerns regarding China’s intentions in the Indo-Pacific region have led to strengthening bilateral cooperation, but none wish to threaten China with the developing partnership.
6. Need of the Hour
- While the huge economic opportunity in India draws attention from across the world there is a need to attract Japanese companies to invest in India.
- India can aid as a competitive replacement for china.
- Issues of India’s insistence on data localisation and reluctance to accede to global cybersecurity agreements such as the Budapest Convention needs to be discussed.
- Defense ties need to be made for a more dynamic exchange of defence equipment and technologies.
- India-Japan summit should reaffirm Japan’s support for key manufacturing initiatives such as ‘Make in India’ and the Japan Industrial Townships.
|
For Prelims: Current events of national and international importance For Mains: GS II - International relations |
MONEY BILL
Article 110 of the Constitution of India pertains to the definition and procedure of passing a Money Bill in the Parliament. According to this article, a Money Bill exclusively contains provisions dealing with all or any of the following matters:
- The imposition, abolition, remission, alteration, or regulation of any tax.
- The regulation of the borrowing of money by the Government of India, including the giving of any guarantee by the Indian government for the purpose of securing a loan or the repayment of any money borrowed by it.
- The custody of the consolidated Fund or the Contingency Fund of India, the payment of moneys into or the withdrawal of moneys from any such Fund.
- The appropriation of moneys out of the consolidated Fund of India.
- The declaring of any expenditure to be expenditure charged on the Consolidated Fund of India or the increasing of the amount of any such expenditure.
- The receipt of money on account of the Consolidated Fund of India or the public account of India or the custody or issue of such money or the audit of the accounts of the Union or of a State.
A Money Bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha (House of the People), and it cannot be introduced in the Rajya Sabha (Council of States). The Rajya Sabha can only make recommendations on a Money Bill, and the Lok Sabha can either accept or reject these recommendations. The Rajya Sabha cannot amend a Money Bill, and if it is not returned by the Rajya Sabha within 14 days, it is deemed to have been passed by both houses
The decision regarding whether a bill is a Money Bill or not rests with the Speaker of the Lok Sabha (House of the People) in the Indian parliamentary system. As per Article 110 of the Indian Constitution, the Speaker is responsible for certifying whether a bill is a Money Bill or not.
Here is the process involved:
-
Introduction in Lok Sabha: A bill is introduced in either the Lok Sabha or the Rajya Sabha. If it is introduced in the Lok Sabha and the Speaker is of the opinion that it exclusively deals with matters listed in Article 110, it may be certified as a Money Bill.
-
Certification by the Speaker: The Speaker examines the provisions of the bill and determines whether it falls within the definition of a Money Bill as specified in Article 110. If the Speaker certifies it as a Money Bill, the bill is deemed to be so.
-
Presentation to Rajya Sabha: After the Speaker's certification, the Money Bill is sent to the Rajya Sabha for its recommendations. However, the Rajya Sabha's powers regarding a Money Bill are limited. It can only make recommendations, and the Lok Sabha is not bound to accept them.
-
President's Assent: Once the Lok Sabha passes the Money Bill, it is sent to the President for assent. The President's role is mostly formal, and the President cannot withhold assent to a Money Bill. If the President gives assent, the Money Bill becomes law
| Subject | Money Bill | Ordinary Bill |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Can only be introduced in Lok Sabha (LS). | Can be introduced in either Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha. |
| Certification | Requires certification by the Speaker of LS. | Does not require certification by the Speaker. |
| Scope | Deals exclusively with financial matters listed in Article 110. | Covers a wide range of subjects, including non-financial matters. |
| Role of Rajya Sabha | Rajya Sabha can only make recommendations, no power to reject or amend. | Rajya Sabha has the power to suggest amendments and can reject the bill. |
| Timeframe for Rajya Sabha | Rajya Sabha must return it within 14 days; otherwise, it is deemed passed. | Rajya Sabha has the usual time for discussion, amendments, and decision. |
| President's Assent | President cannot withhold assent; mandatory approval. | President can use discretionary powers, and assent is not mandatory. |
| Usage and Importance | Primarily deals with financial matters like taxation and government spending. | Encompasses a wide range of legislative subjects, both financial and non-financial. |
| Examples | Budget-related bills, finance bills, appropriation bills. | Social, economic, or legislative reforms, not necessarily tied to financial matters. |
A Finance Bill is a type of legislation presented in a country's parliament that outlines the government's proposals related to taxation, government spending, and other financial matters for a specific fiscal year. The primary purpose of a Finance Bill is to give legal effect to the fiscal policies announced by the government in the annual budget.
Key features of a Finance Bill include:
-
Taxation Proposals: The Finance Bill contains provisions related to changes in taxes, duties, and levies. It may introduce new taxes, amend existing tax rates, or provide exemptions.
-
Appropriation of Funds: The bill includes details about the allocation and appropriation of funds for various government expenditures. It outlines how the government plans to collect and spend money during the fiscal year.
-
Government Spending: The Finance Bill specifies the government's planned expenditures across different sectors, such as education, healthcare, defense, infrastructure, and more.
-
Economic Policies: It may contain measures to stimulate economic growth, control inflation, or address other macroeconomic concerns.
-
Implementation of Budget Proposals: The Finance Bill is presented in conjunction with the annual budget, and it seeks to implement the financial proposals outlined in the budget speech delivered by the Finance Minister.
-
Parliamentary Approval: In many parliamentary systems, the Finance Bill must be approved by the legislature to become law. It goes through the normal legislative process, including debates, committee scrutiny, and voting.
In some countries, including India, a specific type of Finance Bill is known as the "Money Bill." A Money Bill exclusively deals with matters specified in the constitution, such as taxation, borrowing, and expenditure from the consolidated fund. Money Bills have special procedures for introduction and passage, and they require certification by the Speaker of the lower house (e.g., Lok Sabha in India)
|
For Prelims: Money Bill, Financial Bill, Aadhaar Act, Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, Finance Act, Supreme Court,
For Mains:
1. What are the constitutional safeguards in place to prevent misuse of the Money Bill? Critically assess the mechanisms to ensure that only appropriate bills are categorized as Money Bills. (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Regarding Money Bill, which of the following statements is not correct? (UPSC 2018)
1. A bill shall be deemed to be a money Bill if it contains only provisions relating to imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of any tax.
2. A Money Bill has provisions for the custody of the Consolidated Fund of India or the Contingency Fund of India.
3. A Money Bill is concerned with the appropriation of money out of the Contingency Fund of India.
4. A Money Bill deals with the regulation of borrowing of money or giving of any guarantee by the Government of India.
Answer: 3
2. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2018)
1. Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
2. Once issued, the Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
3. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2015)
1. The Rajya Sabha has no power either to reject or to amend a Money Bill.
2. The Rajya Sabha cannot vote on the Demands for Grants.
3. The Rajya Sabha cannot discuss the Annual Financial Statement.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 1 and 2 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
4. With reference to the Indian judiciary, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2021)
1. Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
2. A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
|
Source: Indianexpress
INDIA-US 2+2 MINISTERIAL DIALOGUE
- The annual 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, initiated in 2018, serves as a diplomatic summit aiming to address shared concerns and bolster the relationship between India and the United States.
- This forum facilitates collaboration between key representatives, including India's Minister of External Affairs and Defence Minister, alongside their American counterparts, the Secretary of State and Secretary of Defense, to foster stronger ties between the two nations.
- India engages in 2+2 dialogues with four significant strategic allies: the United States, Australia, Japan, and Russia, all of which are partners in the Quad. The discussions within these dialogues encompass a range of political and defence matters of shared interest.
- For instance, in the fourth annual U.S.-India 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the agenda included discussions on arms control and international security, civilian security, democracy, and human rights, as well as topics related to economic growth, energy, environment, food security, clean energy, waste management, and infrastructure
- The annual 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue serves as a diplomatic event convening the foreign and defense ministers of two nations.
- Its primary objective is to address shared concerns and fortify the relationship between the participating countries.
- This platform facilitates high-level discussions on crucial bilateral and global issues, with a particular emphasis on developments in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Through the dialogue, the partners gain a deeper understanding of each other's strategic concerns, considering political factors on both sides.
- Remarkable progress in defense relations has resulted from the dialogue, including the establishment of a new tri-service military exercise, the deployment of liaison officers in regional commands, and the reduction of U.S. export barriers for military technologies.
- Furthermore, the dialogue has contributed to various outcomes, such as ongoing close consultations on the crisis in Ukraine, including humanitarian assistance efforts.
- It has also seen joint support for an independent investigation into the violence against civilians, along with the acknowledgment of significant events like the inaugural virtual Quad Leaders' Summit in March 2021, the in-person Quad Leaders' Summit in September 2021 in Washington, and the Quad Foreign Ministers' meeting in Melbourne in February 2022. The engagement has been strengthened on shared priorities, including food security, clean energy, waste management, and infrastructure
The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue has become a significant diplomatic mechanism for several countries, bringing together their foreign and defense ministers to discuss strategic and security-related issues. While specific details may have evolved since then, here is a general overview of the history of the 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue:
India-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue (Initiated in 2018):
-
- The concept of a 2+2 dialogue involving the foreign and defense ministers of India and the United States was formalized in 2018.
- The inaugural U.S.-India 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue took place in September 2018 in New Delhi, India.
- The dialogue aimed to enhance diplomatic and defense cooperation between the two countries, covering a range of issues from regional security to defense trade.
Japan-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- The Japan-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue involves the foreign and defense ministers of Japan and the United States.
- This format is designed to strengthen the strategic alliance between Japan and the U.S., addressing regional security challenges and fostering defense collaboration.
Australia-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- Australia and the United States hold a 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue involving their foreign and defense ministers.
- The discussions typically encompass a wide range of issues, including defense cooperation, regional security, and shared strategic interests.
India-Japan 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- Apart from the India-U.S. dialogue, India also engages in a 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue with Japan, involving their foreign and defense ministers.
- This platform allows both countries to discuss bilateral and regional security matters, promoting closer diplomatic and defense ties.
India-Australia 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- Similar to its engagements with the U.S. and Japan, India also conducts a 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue with Australia.
- The dialogue aims to strengthen the strategic partnership, addressing common concerns and fostering cooperation in various domains.
COMCASA (Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement) is an agreement between the United States and other countries, primarily aimed at enhancing defense and security cooperation. The agreement focuses on enabling secure and interoperable communication systems between the armed forces of the participating nations. Please note that developments might have occurred since my last update.
Key points about the COMCASA Pact:
Purpose:
-
- The primary purpose of COMCASA is to facilitate secure communication and data sharing between the armed forces of the participating countries, particularly in the context of joint military exercises, operations, and interoperability.
Interoperability:
-
- COMCASA aims to enhance interoperability by ensuring that the communication systems of the signatory nations can work seamlessly with each other. This is crucial for effective coordination during joint military activities.
Secure Communication:
-
- The agreement includes provisions for secure communication systems to protect sensitive information and ensure that the communication channels are not vulnerable to unauthorized access or interference.
Technological Integration:
-
- COMCASA involves the integration of specific technologies and communication equipment to meet the agreed-upon standards, allowing for the secure exchange of military information.
India-U.S. COMCASA Agreement:
-
- India and the United States signed the COMCASA agreement in September 2018. This agreement marked a significant step in the defense and strategic partnership between the two countries.
Implications for India:
-
- For India, the COMCASA agreement with the U.S. has implications for its defense capabilities and interoperability with U.S. military systems. It allows India to access advanced communication technology and equipment, fostering closer collaboration between the two nations' armed forces.
|
Previous Year Questions
1.What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (UPSC CSE 2020) 2.‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. UPSC CSE 2019) |
INTEGRATED AIR DROP TEST (IADT-1)

- The Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT) is meant to assess the parachute-based braking system that ensures the Gaganyaan crew module lands safely after reentry. In the first trial, IADT-1, the parachutes were expected to open in a fixed sequence once the module was dropped from nearly 3 km altitude.
- Even though the capsule carried no crew and was released from a helicopter, the experiment replicated the final stages of an actual mission.
- In a real operation, the capsule would first decelerate due to atmospheric drag and its heat shield, then be stabilized by small drogue parachutes, and finally slowed by three large main parachutes, each 25 meters in diameter.
- The objective was to bring down the descent speed to about 8 m/s before it hit the sea surface
3. How was the test conducted?
- During IADT-1, a Chinook helicopter of the Indian Air Force airlifted a 4.8-ton dummy crew module and released it from the set altitude. Once released, the automated systems activated and deployed the parachutes in the planned sequence.
- According to ISRO, the landing parameters matched predictions, confirming the system’s effectiveness under real-world conditions.
- The trial required extensive simulations, instrumentation, and collaboration across several organisations. While the Air Force handled the airlift, the DRDO provided inputs on materials and safety mechanisms.
- The Indian Navy and Coast Guard were tasked with recovery preparations after splashdown. A. Rajarajan, Director of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, noted that his centre carried out nearly 90% of the activities for IADT-1.
- In human spaceflight, ascent, descent, and recovery are considered the most critical stages. Even with a successful launch and stay in orbit, astronauts’ safety ultimately depends on the capsule’s ability to slow down safely for re-entry and landing. Any malfunction in parachute deployment could have disastrous consequences, making ground trials essential
- The Gaganyaan mission ultimately aims to place Indian astronauts in low-Earth orbit using a human-rated LVM3 launch vehicle. Before this goal can be realized, ISRO must complete a series of rigorous trials to verify all safety mechanisms.
- Unlike satellite or planetary launches, crewed missions require human-rating of every system, which means building in redundancies, fault-detection features, and life-support capabilities.
- As part of this process, Crew Escape System demonstrations are carried out to ensure astronauts can be safely separated from the rocket if a launch failure occurs. The first test vehicle mission, TV-D1, was conducted in October 2023, while the upcoming TV-D2 will simulate a more advanced abort scenario.
- The first uncrewed mission, Gaganyaan-1 (G1), will send a crew module into orbit atop the LVM3. Inside it will be ‘Vyommitra’, a humanoid robot created to replicate astronaut tasks. The recent success of IADT-1 has laid the groundwork for TV-D2 and G1.
- Additional drop tests, subsystem validations, and multiple IADTs will continue simultaneously to fine-tune the systems before human spaceflight is approved. By the time the inaugural human mission (H1) is attempted, ISRO would have completed thousands of individual tests.
- Key technologies being developed include the Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) to manage oxygen supply, temperature, waste, and fire protection; the Integrated Vehicle Health Management System (IVHMS) for autonomous fault detection and abort activation; and an upgraded LVM3 rocket, strengthened to meet human-rating reliability standards.
- Since many of these critical technologies were unavailable internationally, India has had to indigenously develop components such as escape motors and specialized composites. Every subsystem must undergo hundreds of trials before certification for crewed use
- The Gaganyaan programme is not the final goal but rather the stepping stone for India’s long-term human spaceflight ambitions. The government has outlined plans to set up the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and to attempt a crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- Achieving these milestones will require multiple missions, longer stays in orbit, and the development of advanced deep-space technologies. Timelines may shift — for instance, IADT-1 was initially slated for April 2024 — but each test contributes to building the expertise needed for larger objectives.
- As per ISRO, the upcoming TV-D2 flight will validate the Crew Escape System by simulating an emergency abort: the crew module will detach, slow down using thrusters and parachutes, and land in the sea for recovery operations.
- Parallel to this, ISRO is extending the SpaDeX mission, after its twin satellites successfully carried out an in-orbit docking demonstration in May 2025. This capability will play a vital role in future projects such as Gaganyaan, Chandrayaan-4, and the BAS.
- The first human mission (H1) is officially targeted for 2027, though further delays are anticipated
- The Gaganyaan Mission is India’s first human spaceflight programme, designed and developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) with the goal of sending Indian astronauts into low-Earth orbit.
- Unlike previous satellite or planetary missions, Gaganyaan involves the challenge of carrying humans to space and bringing them back safely, which requires an entirely different level of engineering, testing, and safety validation.
- At its core, the mission seeks to launch a crew of astronauts, often referred to as vyomnauts, aboard a specially human-rated version of the LVM3 rocket. Human-rating means that every system of the launch vehicle and crew module must be designed with additional redundancies, fault detection mechanisms, and life-support provisions so that the astronauts remain safe even if some components fail.
- This involves building systems such as the Crew Escape System, which can rapidly pull astronauts away from the rocket if a launch emergency occurs, and the Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS), which maintains oxygen supply, temperature regulation, waste management, and fire safety inside the module.
- The programme is being executed in carefully planned stages. ISRO has been conducting a series of uncrewed test flights to validate technologies before astronauts are actually sent to space.
- These include drop tests of the crew module, where parachute systems are evaluated to ensure a safe splashdown; abort tests, where the crew escape system is triggered under different scenarios; and orbital missions that will carry an uncrewed module into space with a humanoid robot called Vyommitra, designed to simulate astronaut functions.
- These tests are crucial because the riskiest parts of any human mission are the ascent, re-entry, and landing phases, and a failure in deceleration or parachute deployment could prove catastrophic.
- The mission is not just about a single flight but about laying the foundation for India’s long-term human space exploration programme. The government has already announced ambitious future goals: establishing the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), an indigenous space station, by 2035, and sending Indian astronauts to the Moon by 2040.
- Achieving these milestones will require mastering technologies like in-orbit docking, long-duration orbital habitation, and deep-space travel.
- ISRO’s SpaDeX mission, which successfully demonstrated satellite docking in 2025, is an example of the technology that will directly contribute to Gaganyaan’s evolution and future missions.
- As of now, the first human spaceflight under Gaganyaan, referred to as H1, is officially targeted for 2027, though delays are expected due to the complexity of testing and validation.
- By the time astronauts are launched, ISRO would have carried out thousands of subsystem trials, multiple abort demonstrations, and several uncrewed missions to ensure that the risks are minimized.
- In essence, Gaganyaan is a landmark project for India—not just for sending astronauts into space for the first time, but for creating the technological base for much larger and more ambitious human spaceflight missions in the decades to come
|
For Prelims: Gaganyaan programme, TV-D1 mission, Low Earth Orbit, Isro, LVM3, GSLV Mk III,
For Mains:
1. Discuss the key objectives of the TV-D1 mission within the Gaganyaan program. How does this mission contribute to astronaut safety and the overall success of Gaganyaan? (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. With reference to India's satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2018)
1. PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
2. Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
3. GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3
C. 1 and 2
D. 3 only
Answer: A
2. India's first human space mission "Gaganyaan" will be launched in which year? (ESIC UDC 2022)
A. 2022 B. 2023 C. 2024 D. 2025 E. 2026
Answer: B
3. Find the incorrect statements, about the Gaganyaan Mission of India. (MPSC 2020)
1. Four pilots from Indian Air Force were shortlisted to be astronauts of Gaganyaan.
2. They will be trained at Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Centre in Russia.
3. This mission was announced by Prime Minister in 2014.
4. It is scheduled for 2022 with a team of 5 crew members and a month-long stay in space.
A. 1, 2, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 4 C. 3, 4 D. 2, 3
Answer: C
4. ISRO is related to: (SSC JE EE 2020)
A. space research B. agricultural research C. seed research D. marine research Answer: A
5. Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched? (UPSC 2014) Spacecraft Purpose
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B 6. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2016) The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO 1. is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
2. made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
3. made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: C |
Source: The Hindu
PRADHAN MANTRI JAN DHAN YOJANA (PMJDY)
- The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is a national financial inclusion scheme launched by the Government of India in 2014.
- The objective of this scheme is to ensure access to financial services at affordable cost to all the families in the country
- The primary objective of the scheme is to ensure that every household in India has access to basic banking services, such as a savings account, insurance, and pension.
- The program aims to bring the marginalized and economically weaker sections of society into the formal financial system and promote financial literacy
- Ensure access of financial products & services at an affordable cost
- Use of technology to lower cost & widen reach
- Opening of basic savings bank deposit (BSBD) account with minimal paperwork, relaxed KYC, e-KYC, account opening in camp mode, zero balance & zero charges
- Issuance of Indigenous Debit cards for cash withdrawals & payments at merchant locations, with free accident insurance coverage of Rs. 2 lakhs
- Other financial products like micro-insurance, overdraft for consumption, micro-pension & micro-credit
Key features of Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY):
-
No Minimum Balance Requirement: Under this scheme, individuals can open a bank account with zero minimum balance requirements. This is particularly beneficial for those who were unable to open bank accounts due to financial constraints.
-
Access to Banking Facilities: Account holders are provided with a basic savings account that allows them to deposit and withdraw money, and it also comes with a RuPay debit card which enables access to ATMs and facilitates cashless transactions.
-
Accidental Insurance Cover: Account holders are eligible for accidental insurance coverage. Initially, the insurance coverage was Rs. 1 lakh, but it was increased to Rs. 2 lakh.
-
Overdraft Facility: After a certain period of satisfactory operation of the account, account holders are eligible for an overdraft facility of up to Rs. 10,000, which helps them during emergencies.
-
Financial Literacy Programs: The scheme also emphasizes financial literacy and aims to educate account holders about the benefits of formal financial services, proper money management, and the importance of saving.
-
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): PMJDY accounts are often linked to various government welfare schemes, allowing beneficiaries to receive subsidies and benefits directly into their bank accounts, reducing leakages and ensuring efficient delivery of services.
-
Pension Schemes: Account holders can also access pension schemes like Atal Pension Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana, which provide social security and retirement benefits.
-
Mobile Banking: The scheme promotes the use of mobile banking through USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service Data) codes, allowing account holders to access banking services using basic mobile phones.
|
Previous Year Questions
1.‘Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana’ has been launched for (UPSC CSE 2015) (a) providing housing loan to poor people at cheaper interest rates Answer: (c)
1.Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. (2016) |




