ETHANOL BLENDING
1. Context

- Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol, is a type of alcohol commonly used as a biofuel and a key ingredient in alcoholic beverages.
- It is a clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic odor and a slightly sweet taste.
- Ethanol has a wide range of applications and is produced through the fermentation of sugars by yeast or other microorganisms.
3. Ethanol Blending
- Ethanol blending refers to the practice of mixing ethanol with gasoline or other fuels to create a blended fuel.
- Ethanol is a biofuel derived from renewable sources such as sugarcane, corn, or other plant materials.
- It is commonly used as an additive to gasoline in various parts of the world to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote cleaner fuel options.
- In the context of transportation, the most common form of ethanol blending is with gasoline, creating a blend known as ethanol-gasoline blend or gasohol.
- The most common ethanol-gasoline blends are E10 and E15, indicating the percentage of ethanol in the mixture. For example, E10 contains 10% ethanol and 90% gasoline, while E15 contains 15% ethanol and 85% gasoline.

4. Benefits of Ethanol blending
- Ethanol is considered a renewable fuel because it is derived from plant materials that absorb carbon dioxide during their growth. When blended with gasoline, ethanol can help reduce the carbon footprint of transportation fuels, as it emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to pure gasoline.
- By blending ethanol with gasoline, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels and promote energy security.
- Ethanol has a higher octane rating than gasoline, which can improve engine performance and increase fuel efficiency.
- Ethanol production often relies on agricultural feedstocks, providing economic benefits to farmers and rural communities.
- Ethanol-gasoline blends can help reduce harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and volatile organic compounds, contributing to improved air quality.
-
Mixing 20 percent ethanol in petrol can potentially reduce the auto fuel import bill by a yearly $4 billion, or Rs 30,000 crore.
-
Another major benefit of ethanol blending is the extra income it gives to farmers. Ethanol is derived from sugarcane and also foodgrains. Hence, farmers can earn extra income by selling their surplus produce to ethanol blend manufacturers.
5. What is E20 Fuel?
- E20 fuel is a type of blended fuel that contains 20% ethanol and 80% gasoline.
- It is an ethanol-gasoline blend, similar to other common blends like E10 (10% ethanol) and E15 (15% ethanol).
- The percentage of ethanol in the blend is denoted by the "E" followed by the percentage of ethanol content.
- E20 fuel is considered a higher ethanol blend compared to E10 and E15, which are more widely available in various countries.
- The use of E20 is part of efforts to promote renewable fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector.
6. Significance of E20 fuel
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Ethanol is derived from renewable plant sources, and blending it with gasoline can help reduce the carbon footprint of transportation fuels, contributing to efforts to combat climate change.
- Energy Security: By using more domestically produced ethanol, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhance energy security.
- Improved Engine Performance: Ethanol's higher octane rating can enhance engine performance and increase fuel efficiency in certain vehicles.
- Support for Agriculture: Ethanol production often relies on agricultural feedstocks, supporting farmers and rural economies.
7. Challenges in Ethanol Blending Programme
While ethanol blending in transportation fuels offers various benefits, there are several challenges that countries may face in implementing and sustaining a successful ethanol blending program. Some of these challenges include:
- Infrastructure and Distribution: Establishing the necessary infrastructure for blending and distributing ethanol-gasoline blends can be a significant challenge. This includes ensuring that fuel stations have the proper storage facilities and compatible pumps to dispense blended fuels.
- Compatibility with Vehicles: Not all vehicles are designed to run on high ethanol blends like E20 or E85. Older vehicles or vehicles from certain manufacturers may not be compatible with these blends, leading to potential engine damage or decreased performance.
- Fuel Quality and Standards: Maintaining consistent fuel quality is essential to prevent engine damage and ensure consumer confidence. Governments and fuel suppliers must adhere to strict quality standards and monitor the blending process to avoid issues with fuel performance.
- Feedstock Availability and Cost: The production of ethanol relies on agricultural feedstocks, such as corn, sugarcane, or other biomass. The availability and cost of these feedstocks can vary, affecting the overall cost of ethanol production and blending.
- Land Use and Food Security Concerns: Utilizing agricultural land for ethanol production can raise concerns about competing with food production and potentially impacting food security in some regions.
- Competing Uses for Ethanol: Ethanol has various applications beyond fuel blending, such as in the production of alcoholic beverages, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals. Competing uses can influence the availability and cost of ethanol for blending.
8. National Biofuel Policy
- India has a National Policy on Biofuels, which was first introduced in 2009 and later revised in 2018. The policy aims to promote the use of biofuels to reduce the country's dependence on fossil fuels, enhance energy security, promote sustainable development, and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
- The policy encourages the blending of biofuels with conventional fossil fuels to create biofuel blends. It focuses on the production and utilization of first-generation biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel, as well as advanced biofuels made from non-food feedstock.
- The policy sets targets for blending biofuels with conventional fuels in the transportation sector. For instance, the policy aimed for a 20% ethanol blending in petrol and a 5% biodiesel blending in diesel by 2030.
- The policy emphasizes the development and promotion of second-generation biofuels, which are produced from non-food feedstock, such as agricultural residues, waste, and non-edible oils. This helps avoid competition with food crops and ensures sustainability.
- The policy supports research and development initiatives in the biofuels sector, aimed at improving production processes, enhancing feedstock availability, and developing cost-effective technologies for biofuel production.
- The policy focuses on creating a robust supply chain for biofuels, from feedstock cultivation and collection to biofuel production, distribution, and marketing. This helps in ensuring a smooth and efficient supply of biofuels across the country.
|
For Prelims: Ethanol Blending, E20 fuel, Greenhouse Gas Emission, National Policy on Biofuels, Food Security, and Gasoline.
For Mains: 1. Discuss the benefits and challenges of ethanol blending in transportation fuels as a strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote renewable energy sources. (250 Words).
|
Previous year Question1. According to India's National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels? (UPSC 2020)
1. Cassava
2. Damaged wheat grains
3. Groundnut seeds
4. Horse gram
5. Rotten potatoes
6. Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2, 5, and 6 only
B. 1, 3, 4, and 6 only
C. 2, 3, 4, and 5 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Answer: A
|
INDIA-US 2+2 MINISTERIAL DIALOGUE
- The annual 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, initiated in 2018, serves as a diplomatic summit aiming to address shared concerns and bolster the relationship between India and the United States.
- This forum facilitates collaboration between key representatives, including India's Minister of External Affairs and Defence Minister, alongside their American counterparts, the Secretary of State and Secretary of Defense, to foster stronger ties between the two nations.
- India engages in 2+2 dialogues with four significant strategic allies: the United States, Australia, Japan, and Russia, all of which are partners in the Quad. The discussions within these dialogues encompass a range of political and defence matters of shared interest.
- For instance, in the fourth annual U.S.-India 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the agenda included discussions on arms control and international security, civilian security, democracy, and human rights, as well as topics related to economic growth, energy, environment, food security, clean energy, waste management, and infrastructure
- The annual 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue serves as a diplomatic event convening the foreign and defense ministers of two nations.
- Its primary objective is to address shared concerns and fortify the relationship between the participating countries.
- This platform facilitates high-level discussions on crucial bilateral and global issues, with a particular emphasis on developments in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Through the dialogue, the partners gain a deeper understanding of each other's strategic concerns, considering political factors on both sides.
- Remarkable progress in defense relations has resulted from the dialogue, including the establishment of a new tri-service military exercise, the deployment of liaison officers in regional commands, and the reduction of U.S. export barriers for military technologies.
- Furthermore, the dialogue has contributed to various outcomes, such as ongoing close consultations on the crisis in Ukraine, including humanitarian assistance efforts.
- It has also seen joint support for an independent investigation into the violence against civilians, along with the acknowledgment of significant events like the inaugural virtual Quad Leaders' Summit in March 2021, the in-person Quad Leaders' Summit in September 2021 in Washington, and the Quad Foreign Ministers' meeting in Melbourne in February 2022. The engagement has been strengthened on shared priorities, including food security, clean energy, waste management, and infrastructure
The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue has become a significant diplomatic mechanism for several countries, bringing together their foreign and defense ministers to discuss strategic and security-related issues. While specific details may have evolved since then, here is a general overview of the history of the 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue:
India-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue (Initiated in 2018):
-
- The concept of a 2+2 dialogue involving the foreign and defense ministers of India and the United States was formalized in 2018.
- The inaugural U.S.-India 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue took place in September 2018 in New Delhi, India.
- The dialogue aimed to enhance diplomatic and defense cooperation between the two countries, covering a range of issues from regional security to defense trade.
Japan-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- The Japan-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue involves the foreign and defense ministers of Japan and the United States.
- This format is designed to strengthen the strategic alliance between Japan and the U.S., addressing regional security challenges and fostering defense collaboration.
Australia-U.S. 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- Australia and the United States hold a 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue involving their foreign and defense ministers.
- The discussions typically encompass a wide range of issues, including defense cooperation, regional security, and shared strategic interests.
India-Japan 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- Apart from the India-U.S. dialogue, India also engages in a 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue with Japan, involving their foreign and defense ministers.
- This platform allows both countries to discuss bilateral and regional security matters, promoting closer diplomatic and defense ties.
India-Australia 2+2 Ministerial (Ongoing):
-
- Similar to its engagements with the U.S. and Japan, India also conducts a 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue with Australia.
- The dialogue aims to strengthen the strategic partnership, addressing common concerns and fostering cooperation in various domains.
COMCASA (Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement) is an agreement between the United States and other countries, primarily aimed at enhancing defense and security cooperation. The agreement focuses on enabling secure and interoperable communication systems between the armed forces of the participating nations. Please note that developments might have occurred since my last update.
Key points about the COMCASA Pact:
Purpose:
-
- The primary purpose of COMCASA is to facilitate secure communication and data sharing between the armed forces of the participating countries, particularly in the context of joint military exercises, operations, and interoperability.
Interoperability:
-
- COMCASA aims to enhance interoperability by ensuring that the communication systems of the signatory nations can work seamlessly with each other. This is crucial for effective coordination during joint military activities.
Secure Communication:
-
- The agreement includes provisions for secure communication systems to protect sensitive information and ensure that the communication channels are not vulnerable to unauthorized access or interference.
Technological Integration:
-
- COMCASA involves the integration of specific technologies and communication equipment to meet the agreed-upon standards, allowing for the secure exchange of military information.
India-U.S. COMCASA Agreement:
-
- India and the United States signed the COMCASA agreement in September 2018. This agreement marked a significant step in the defense and strategic partnership between the two countries.
Implications for India:
-
- For India, the COMCASA agreement with the U.S. has implications for its defense capabilities and interoperability with U.S. military systems. It allows India to access advanced communication technology and equipment, fostering closer collaboration between the two nations' armed forces.
GLACIAL LAKE OUTBURST FLOOD (GLOF)
1. Context
A landslide damaged six houses and a building of the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) at the site of its Teesta-V hydropower station in Gangtok district of Sikkim on Tuesday.The power station, damaged by the glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) in October 2023, has been under construction
2. About glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF)
- A glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) is a type of outburst flood caused by the failure of a dam containing a glacial lake.
- An event similar to a GLOF, where a body of water contained by a glacier melts or overflows the glacier, is called a jokulhlaup.
- The dam can consist of glacier ice or a terminal moraine. Failure can happen due to erosion, a buildup of water pressure, an avalanche of rock or heavy snow, an earthquake or cryoseism, volcanic eruptions under the ice, or massive displacement of water in a glacial lake when a large portion of an adjacent glacier collapses into it.
3. About flash flooding
- Flash flooding is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions.
- It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields.
- Flash floods may also occur after the collapse of a natural ice or debris dam, or a human structure such as a man-made dam, as occurred before the Johnstown Flood of 1889.
- Flash floods are distinguished from regular floods by having a timescale of fewer than six hours between rainfall and the onset of flooding.
3.1. The reason for flash floods
There are several reasons why flash floods can occur, but the most common cause is heavy rainfall. When rain falls too quickly for the ground to absorb it, the water can run off and cause flooding. Flash floods can also be caused by:
- Thunderstorms can produce heavy rainfall, especially slow-moving or stationary thunderstorms.
- Hurricanes and tropical storms can produce heavy rainfall and storm surge, which can lead to flash flooding.
- If a dam or levee fails, it can release a large amount of water that can cause flash flooding downstream.
- Ice jams can form when large chunks of ice break off from a glacier or river and jam together. This can block the flow of water and cause flooding upstream.
- Landslides can block rivers and streams, causing flash flooding downstream.
- Vegetation helps slow the water flow and allows it to infiltrate the ground more easily. Areas with little or no vegetation are more likely to experience flash flooding.
- Urban areas are more likely to experience flash flooding than rural areas. This is because pavement and other impervious surfaces prevent water from infiltrating the ground.
4. How did South Lhonak Lake become susceptible to GLOF?
- Climate change is causing glaciers in the Himalayas to melt at an accelerated rate. This is leading to the formation of new glacial lakes and the expansion of existing ones, such as South Lhonak Lake.
- South Lhonak Lake is located in a steep-sided valley with a narrow outlet. This makes it difficult for water to drain from the lake, increasing the risk of a GLOF.
- South Lhonak Lake is dammed by a moraine, which is a pile of loose rocks and debris.
- Moraines are naturally unstable and can be easily breached by heavy rainfall, earthquakes, or other triggers.
- South Lhonak Lake is a relatively deep lake, with a maximum depth of over 100 meters.
- This means that a large volume of water could be released quickly if the lake dam were to breach.
- South Lhonak Lake is also located in a seismically active region. Earthquakes can destabilize the moraine dam and trigger a GLOF.
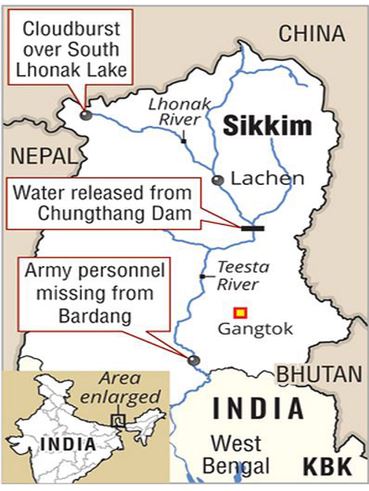
Image Source: Research Gate
|
For Prelims: South Lhonak Lake, Flash Flooding, Glaciers, Glacial Lake Outburst Flood, Sikkam, Climate Change, Teesta River,
For Mains:
1. Describe the environmental and socio-economic impacts of flash floods. How can early warning systems and disaster preparedness help mitigate the risks associated with flash floods? (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. On the planet earth, most of the freshwater exists as ice caps and glaciers. Out of the remaining freshwater, the largest proportion (UPSC 2013) (a) is found in the atmosphere as moisture and clouds (b) is found in freshwater lakes and rivers (c) exists as groundwater (d) exists as soil moisture Answer: C 2. Consider the following pairs: (UPSC CSE 2019)
Glacier River
1. Bandarpunch Yamuna
2. Bara Shigri Chenab
3. Milam Mandakini
4. Siachen Nubra
5. Zemu Manas
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
A. 1, 2 and 4 B. 1, 3 and 4 C. 2 and 5 D. 3 and 5
Answer: A
3. Consider the following features related to a glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF): (UGC NET Geography 2019)
a. Involves sudden release of meltwater
b. Failure of moraine and ice dam
c. Large downstream discharge causing floods
d. Rapid event casting for few seconds
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
A. (a) and (b) are correct
B. (c) and (d) are correct
C. (a), (b) and (c) are correct
D. (b), (c) and (d) are correct
Answer: C
4. With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2016)
1. The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017
2. The Agreement aims to limit greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2°C or even 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
3. Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $ 1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 3 only B. 2 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
5. A new type of El Nino called El Nino Modoki appeared in the news. In this context, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2010)
1. Normal El Nino forms in the Central Pacific ocean whereas El Nino Modoki forms in the Eastern Pacific ocean.
2. Normal El Nino results in diminished hurricanes in the Atlantic ocean but El Nino Modoki results in a greater number of hurricanes with greater frequency.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
6. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (UPSC 2011)
1. La Nina is characterized by unusually cold ocean temperature in the equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
2. El Nino has an adverse effect on the south-west monsoon of India, but La Nina has no effect on the monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
7. Consider the following statements: (MPSC 2017)
a. La Nina is a little girl.
b. During the time of La Nina cold water in the ocean rises to the surface.
c. La Nina strengthens the Indian monsoon.
d. During the time of El Nino, trade winds weaken, and warm water moves east in the ocean. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. Only a and b B. a, b and c C. Only b and c D. All of the above
Answer: D
8. With reference to Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT), which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2020)
1. OMT is measured up to a depth of 26°C isotherm which is 129 meters in the south-western Indian Ocean during January-March.
2. OMT collected during January-March can be used in assessing whether the amount of rainfall in monsoon will be less or more than a certain long-term mean.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
9. With reference to 'Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)' sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2017)
1. IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
2. An IOD phenomenon can influence an EI Nino's impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
10. "EL Nino" refers to a temperature anomaly in the ________ ocean. (NTPC 2017)
A. Indian B. Pacific C. Southern D. Atlantic
Answer: B
11. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change recently published the draft Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, in 2020. Which of the following statements is correct about EIA? (Punjab Civil Service 2020)
1. It predicts the effect of a proposed industrial/infrastructural project on the environment.
2. It prevents the proposed activity/project from being approved without proper oversight or taking adverse consequences into account.
3. It compares various alternatives for a project and seeks to identify the one which represents the best combination of economic and environmental costs and benefits.
4. As per the new notification, Coal and non-Coal mineral prospecting and solar photovoltaic projects do not need prior environmental clearance.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. Only 1 and 2
B. Only 2, 3 and 4
C. Only 1, 2 and 3
D. Only 1, 2 and 4
Answer: D
12. In the context of India’s preparation for Climate -Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2021)
1. The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research program.
2. The project of CCAFS is carried out under the Consultative Group on International Agricultural (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
3. The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centers.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
13. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2017)
1. In India, the Himalayas are spread over five States only.
2. Western Ghats are spread over five States only.
3. Pulicat Lake is spread over two States only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only B. 3 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1 and 3 only
Answer: B
14. Which of the following statements in respect of landslides are correct? (NDA 2022) 1. These occur only on gentle slopes during rain.
2. They generally occur in clay-rich soil.
3. Earthquakes trigger landslides.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 1 and 3 D. 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B 15. With reference to River Teesta, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2017)
1. The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
2. River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
3. River Teesta flows into the Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only B. 2 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B 16. Teesta River is the tributary of _______. (Kerala PSC Secretariat Assistant 2018) A. Ganga B. Yamuna C. Brahmaputra D. Narmada Answer: C Mains 1.Describe the various causes and the effects of landslides. Mention the important components of the National Landslide Risk Management Strategy. (2021, GS3)
|
Source: indianexpress
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION (ISS)
1. Context
2. About the International Space Station
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a habitable artificial satellite in low Earth orbit that serves as a microgravity research laboratory. It is the largest artificial object in space and the largest international space project in history, involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).
- The ISS was constructed in space over 13 years, with the first module, Zarya, launched on November 20, 1998. The last module, Poisk, was launched on December 10, 2016. The ISS has been continuously crewed since November 2000 and has hosted crews from 21 different countries.
- The ISS is used to conduct scientific research in a variety of fields, including astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and materials science. It has also been used to develop new technologies, such as water recycling systems and solar panels.
- The ISS has six sleeping quarters, two bathrooms, a gym, and a 360-degree view bay window. It measures 109 meters (357 feet) end-to-end, and its solar array wingspan is also 109 meters. The ISS orbits Earth 16 times in one day, every 90 minutes to be precise, at a speed of 8 kilometres (5 miles) per second.
3. Astronaut Activities on the ISS
- Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) primarily engage in scientific experiments, focusing on research that cannot be conducted on Earth. These experiments cover various fields and contribute to scientific breakthroughs.
- Regular spacewalks are undertaken by ISS astronauts to install new components, such as robotic arms, and to perform maintenance tasks. This includes inspecting and repairing damage caused by space debris.
- Due to the effects of microgravity on the human body, astronauts adhere to a strict health regimen. This includes workouts on specially designed machines like treadmills for a minimum of two hours a day.
- As researchers focus on prolonged human habitation in space, ISS astronauts contribute to our understanding of the effects of microgravity. Daily exercise routines are not only for astronaut health but also aid scientific investigations into the potential long-term impacts on the human body.
4. Scientific Discoveries Benefiting Earth
- Astronauts conduct experiments on themselves, monitoring general health, nutrition, and the effects of solar radiation. Scientific breakthroughs from these studies have contributed to our understanding of diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, cancer, asthma, and heart disease.
- Discoveries on the ISS have directly benefited drug development on Earth. The unique conditions of microgravity allow researchers to study cell behaviour more closely resembling that inside the human body.
- Experiments on the ISS have led to advancements in water purification systems, crucial for sustaining life in space. These innovations have practical applications on Earth, improving water purification technologies.
- Research on the ISS has provided methods to mitigate muscle and bone atrophy caused by extended periods in microgravity. These findings have implications for developing countermeasures to address similar health challenges on Earth.
- Scientific experiments on the ISS have contributed to innovations in food production. These advancements are essential for developing sustainable and efficient food production systems for long-term space missions and have practical applications on Earth.
5. Future of the ISS
- Plans for the future of the ISS faced uncertainty with Russia's invasion of Ukraine, leading to disruptions in international collaborations. Russia's decision to leave the ISS and pursue its own space station further added complexity to the situation.
- New and established spacefaring nations, including Japan, China, India, and the United Arab Emirates, express interest in independent space exploration, marking a shift in the landscape of international collaboration.
- While the US and Europe have expressed commitment to the ISS until 2030, discussions about a post-ISS era are underway. NASA's Artemis program focuses on lunar exploration, while the European Space Agency (ESA) plans the development of a new space station named Starlab.
- The phrase "watch this space" takes on new significance as the ISS navigates geopolitical challenges and evolving ambitions in space exploration. Plans for lunar missions and new space stations signal a transformative era in human space exploration.
6. Conclusion
|
For Prelims: International Space Station, NASA, Roscosmos, JAXA, CSA, European Space Agency, ISRO, Zarya, Posik, artificial satellite, low Earth orbit, space debris
For Mains:
1. Discuss the role of the International Space Station (ISS) in advancing scientific research in microgravity and its contributions to technological innovations. Highlight specific experiments conducted on the ISS that have benefited various fields of science. (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. What is the purpose of the US Space Agency’s Themis Mission, which was recently in the news? (UPSC 2008)
A. To study the possibility of life on Mars
B. To study the satellites of Saturn
C. To study the colorful display of high-latitude skies
D. To build a space laboratory to study the stellar explosions
2. In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (UPSC 2010)
A. A mini-satellite launched by ISRO for promoting distance education in India
B. The name was given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
C. A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
D. A space telescope developed by India
3. Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched? (UPSC 2014)
Spacecraft Purpose
1. Cassini-Huygens: Orbiting Venus and transmitting data to theEarth
2. Messenger: Mapping and investigating the Mercury
3. Voyager 1 and 2: Exploring the outer solar system
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
4. Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (UPSC 2019) (a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
5. India’s first Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) laboratory will be set up in which State? (BPSC 2016) A.Uttar Pradesh B.Maharashtra C.Andhra Pradesh D.Bihar E.None of the above/More than one of the above 6. With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements: (UPSC 2018)
1. IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
2. IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq.km beyond its borders.
3. India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)1 only b)1 and 2 only c)2 and 3 only d)None
7. Which of the following is the name of the NASA programme to land first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024? (SSC MTS 2021)
A. Orion
B. Apollo
C. Artemis
D. Nike
8. Consider the following statements: The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO (UPSC 2016)
1. is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
2. made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after the USA
3. made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 and 3 only C. 1 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
9. A low earth orbit satellite can provide large signal strength at an earth station because: (ESE Electronics 2011)
A. Path loss is low
B. These orbits are immune to noise
C. Large solar power can be generated at these orbits
D. Lower microwave frequencies in s-band can be used
10. Comprehension
Direction: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
Astroscale is a space sustainability company headquartered in Tokyo that is committed to creating solutions for removing potentially dangerous space junk. As space tourism missions to the ISS (International Space Station) become more prevalent, even more attention will have to be paid to orbital highways to ensure their maintenance and cleanliness. It’s more than a courtesy, it’s a matter of space safety. Even without private space tours, the prevalence of space junk and the risk of collisions have skyrocketed with the emergence of SpaceX, OneWeb, and other companies that send thousands of rockets into LEO. It is quickly becoming a safety issue—SpaceX’s huge Starlink project has made Earth’s orbit much more dangerous which is why Astroscale aerospace engineer Jonathan Rasmussen is calling for more accountability from prominent satellite companies around the life and death of satellites and intentional de-orbiting. De-orbiting refers to the discarding of defunct junk in space. “In order to mitigate space debris,” he says. “There should be some form of binding international policy where satellite operators and builders send out their satellites with a predetermined plan for the end of life, where they purposely de-orbit it with their last ounce of fuel versus letting the satellites just float around up there.” The company’s End-of-Life Services demonstration (ELSA-d) mission, launching in less than two months, seeks to exhibit the company’s ability to capably and safely find, dock with, and remove orbital debris. The ELSA-d space debris removal mission revolves around two pieces of machinery: a service vehicle (approximately 175 kg) and a smaller client vehicle (approximately 17 kg). The service vehicle is the deorbiter, which physically seeks out, latches onto, and retrieves target debris objects.
What is space debris? (IBPS Clerk Mains 2021)
A. It is a functional artificial material that is orbiting Earth.
B. It is an artificial material that is orbiting Earth but is no longer functional.
C. It is a natural material orbiting around the Earth. Astrocycle is sending debris to space.
D. It is referred to the collision of the satellites that happens in space.
Answers: 1-C, 2-C, 3-B, 4-B, 5-B, 6-A, 7-C, 8-C, 9-A, 10-B
Mains
1. What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (UPSC 2019)
2. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (UPSC 2016)
3. International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above their territory. What do you understand by ‘airspace’? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggest ways to contain the threat. (UPSC 2014)
|
UNIFORM CIVIL CODE (UCC)
- Underlining that the Uniform Civil Code is “neither necessary nor desirable at this stage”, the 21st Law Commission of India, in 2018, argued for reform of family laws of every religion through amendments and codification of certain aspects so as to make them gender-just
- In its ‘Consultation Paper on Family Law Reforms’, the Law Commission took a stand in favour of “equality ‘within communities’ between men and women” (personal law reform), “rather than ‘equality between’ communities” (UCC)
- According to the 22nd Law Commission Cultural diversity cannot be compromised to the extent that our urge for uniformity itself becomes a reason for threat to the territorial integrity of the nation
- women must be guaranteed their freedom of faith without any compromise on their right to equality
- A UCC would provide for one law for the entire country, applicable to all religious communities, in their personal matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, adoption etc
- Currently, Indian personal law is fairly complex, with each religion adhering to its own specific laws
- Separate laws govern Hindus including Sikhs, Jains and Buddhist, Muslims, Christians, and followers of other religions
- Moreover, there is diversity even within communities. All Hindus of the country are not governed by one law, nor are all Muslims or all Christians
- For instance, in the Northeast, there are more than 200 tribes with their own varied customary laws
- The Constitution itself protects local customs in Nagaland. Similar protections are enjoyed by Meghalaya and Mizoram. Even reformed Hindu law, in spite of codification, protects customary practices
- The exception to this rule is the state of Goa, where all religions have a common law regarding marriages, divorces, and adoption
- Article 44 of the Constitution lays down that the state shall endeavour to secure a UCC for citizens throughout the territory of India
- Article 44 is among the Directive Principles of State Policy. Directive Principles are not enforceable by court, but are supposed to inform and guide governance
- However, in some senses, Article 44 is unique in this manner. While Article 44 uses the words “state shall endeavour”, other Articles in the ‘Directive Principles’ chapter use words such as “in particular strive”; “shall in particular direct its policy”; “shall be obligation of the state
- The phrase “by suitable legislation” is absent in Article 44. All this implies that the duty of the state is greater in other directive principles than in Article 44
|
For Prelims: Unifrom Civil Code (UCC), DPSP, Fundamental rights, Law Commission
For Mains: 1. What is the Uniform Civil Code? What are the challenges in implementing a Uniform Civil Code in a diverse country like India?
|
|
Previous Year Questions
Q1. Consider the following provisions under the Directive Principles of State Policy as enshrined in the Constitution of India: (2012)
Which of the above are the Gandhian Principles that are reflected in the Directive Principles of State Policy? (a) 1, 2 and 4 only Answer (b) 2. A legislation that confers on the executive or administrative authority an unguided and uncontrolled discretionary power in the matter of the application of law violates which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India? Answer (a) Mains 1.Discuss the possible factors that inhibit India from enacting for its citizens a uniform civil code as provided for in the Directive Principles of State Policy. (2015) |




