CCHF
1. Context
- Europe is currently experiencing a heatwave and widespread wildfires, leading to concerns about the spread of viruses typically found in warmer climates.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has sounded the alert about the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF), a tick-borne infection with a high fatality rate.
2. Key Points
- CCHF is endemic to regions such as Africa, the Balkan countries, the Middle East, and parts of Asia.
- While the first European fatality from CCHF was reported in Spain in 2016, scientists are now warning of its northward and westward spread in Europe, according to Horizon, a publication focused on European Union-funded research.
- Cases have been reported in Spain, Russia, Turkey, and the UK.
- In India, Gujarat has reported the majority of CCHF cases. Last month, one person in Gujarat succumbed to the disease.
3. About CCHF
- CCHF is a viral haemorrhagic fever primarily transmitted by ticks.
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues during and immediately after the slaughter of animals.
- CCHF outbreaks pose a threat to public health due to their potential for epidemics, high case-fatality ratio (10-40%), and difficulty in prevention and treatment, as stated by the WHO.
4. Transmission and Hosts
- The virus primarily resides in ticks, with animals like cattle, goats, sheep, and hares serving as amplifying hosts.
- Transmission to humans occurs through contact with infected ticks or animal blood.
- Additionally, CCHF can be transmitted from one infected human to another through contact with infectious blood or body fluids.
- Migratory birds can also host ticks, contributing to the long-distance spread of the virus.
 Image Source: CDC
Image Source: CDC5. Symptoms and Treatment
- Symptoms of CCHF include fever, muscle aches, dizziness, neck and back pain, headache, sore eyes, and sensitivity to light.
- Early stages may present with nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, and sore throat, followed by mood swings and confusion.
- As the infection progresses, agitation may give way to sleepiness, depression, and lassitude.
- Currently, there is no vaccine for CCHF in humans or animals, and treatment primarily focuses on managing symptoms.
- The antiviral drug ribavirin has shown apparent benefits in treating CCHF infection, according to the WHO.
6. Climate Change and Disease Spread
- Climate change is a contributing factor to the expansion of diseases into new geographies.
- Warmer temperatures create more favourable conditions for pathogens previously restricted to different regions.
- Regarding CCHF ticks are moving up through Europe due to climate change, facilitated by longer and drier summers.
7. Impact of Climate Change on Disease Spread
- Climate change affects disease spread through various mechanisms.
- Warmer temperatures expand the habitat of ticks and other insects, providing them with extended reproduction periods.
- Changes in water habitats also influence disease transmission, and shifts in animal populations bring them into contact with new areas and people.
8. Conclusion
- CCHF is a serious disease that can be fatal. However, several things can be done to prevent the spread of the disease.
- By being aware of the risks and taking precautions, we can help to protect ourselves from CCHF.
|
For Prelims: World Health Organization, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever, heatwave, wildfires, Climate change,
For Mains:
1. Discuss the significance of international cooperation and coordination in addressing the spread of diseases like CCHF in a changing climate scenario. What strategies can be adopted to mitigate the risks and enhance preparedness for such diseases? (250 words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Comprehension Direction: In the following passage some words have been deleted. Fill in the blanks with the help of the alternatives given. Select the most appropriate option for each blank. (SSC CHSL 2020)
Forest fire always (1) ______ by one of two reasons-naturally caused or human-caused. Natural fire is generally (2) ______ by lightning, with a very small percentage (3) ______ by spontaneous combustion of dry fuel such as sawdust and leaves. (4) ______, human-caused fire can happen (5) ______ any number of reasons.
Select the most appropriate option for blank No. 1.
A. takes up B. happens C. causes D. creates
Answer: B
|
RCEP
1. Context
2. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
- The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a significant free trade agreement (FTA) that was signed on November 15, 2020.
- It is a comprehensive trade pact involving 15 countries from the Asia-Pacific region, including 10 member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and five of ASEAN's trading partners: China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand.
- The purpose of the deal is to create an “integrated market” spanning all 16 countries. This means that it would be easier for the products and services of each of these countries to be available across the entire region.
.png)
3. Key features of the RCEP:
- Economic Scope: RCEP is the largest free trade agreement in the world in terms of economic significance. It covers a vast region, comprising approximately 30% of the global population and accounting for about 30% of the world's GDP. This agreement aims to promote economic integration and facilitate trade and investment among member countries.
- Tariff Reductions and Market Access: RCEP seeks to eliminate or reduce tariffs and other trade barriers among its member nations. This reduction in trade barriers is expected to create more opportunities for businesses to access larger markets and promote economic growth.
- Rules of Origin: RCEP establishes rules of origin to determine the country of origin of goods. This is crucial to prevent non-member countries from benefiting from the preferential trade provisions and ensures that only products manufactured within the RCEP member countries can avail of the agreed-upon trade benefits.
- Trade in Services: The agreement also addresses trade in services, promoting greater access and liberalization in sectors such as telecommunications, finance, professional services, and e-commerce, among others.
- Intellectual Property Rights: RCEP includes provisions related to the protection of intellectual property rights, which is important for fostering innovation and creativity within member countries.
- Investment: The agreement aims to improve investment opportunities and create a more predictable and secure investment environment among member countries. This includes provisions related to investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS) mechanisms.
- Economic Cooperation: RCEP promotes economic cooperation in various areas, such as customs procedures, trade facilitation, technical barriers to trade, and economic and technical assistance for less-developed member countries.
4. Outstanding issues in RCEP
- Tariff Reductions: Agreeing on tariff reduction schedules is another significant challenge. Each member country may have different priorities and sensitivities regarding the products they want to protect or liberalize. Negotiating tariff reductions requires balancing the interests of all parties involved to achieve a mutually beneficial outcome.
- Services and Investment: The liberalization of trade in services and investment is a contentious issue in many trade agreements. RCEP member countries have different levels of development and varying domestic regulations. Negotiating how much to open up services and investment sectors to foreign participation while safeguarding national interests can be challenging.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Balancing intellectual property rights protection with access to affordable medicines and technologies is a delicate matter. RCEP countries need to find a middle ground that promotes innovation while ensuring access to essential medicines and technologies for their populations.
- Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) Mechanism: The inclusion of ISDS in trade agreements has been a contentious issue globally. RCEP member countries need to agree on the scope and limitations of ISDS to protect investor rights while safeguarding the government's right to regulate in the public interest.
- Data Protection and E-commerce: With the increasing importance of digital trade and e-commerce, addressing data protection, privacy, and cross-border data flows is a crucial issue for RCEP members. Negotiating agreements on these issues requires balancing economic interests with the need to protect individual privacy and national security.
5. Concerns of India Including Civil Society, and Political Opposition regarding RCEP:
- Impact on Domestic Industries: India's domestic industries have expressed concerns that the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) could lead to increased competition for goods and services imported from other member countries. There are fears that cheaper imports could negatively affect certain sectors, potentially leading to job losses and economic challenges for domestic industries.
- Trade Deficit: India has had a persistent trade deficit with several RCEP member countries, especially China. Critics worry that the agreement may exacerbate the trade imbalance, leading to an influx of cheaper Chinese goods that could further widen the deficit and harm domestic manufacturing.
- Agriculture Sector: India's agricultural sector has raised concerns over the potential impact of RCEP on farmers. They fear that cheaper agricultural imports from other member countries could harm domestic farmers by reducing the prices and competitiveness of Indian agricultural products.
- Impact on Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) form a significant part of India's economy. Some worry that increased competition from larger corporations in other RCEP member countries might pose challenges for Indian SMEs, limiting their growth prospects.
- Safeguarding Agriculture and Dairy: India's dairy and agricultural sectors have been vocal about protecting their interests in any trade agreement. They fear that certain provisions in RCEP could adversely affect the livelihoods of farmers and the dairy industry.
6. Why did India withdraw from the RCEP?
- The free trade agreement with the member countries might force them to dump cheap and low-quality products from countries like China, Thailand, South Korea, and Japan, etc., This will result in the occupation of the Indian market by foreign products while the Indian products will be out of the market.
- It will increase the number of imports and exports simultaneously, resulting in a decrement in the forex reserves in India.
- India's concern about its country of origin has not been seriously entertained by the RCEP.
|
For Prelims: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS) mechanism, and Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs).
For Mains: 1. Discuss the significance of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) as a major free trade agreement in the Asia-Pacific region. Analyze its potential impact on trade, investment, and economic cooperation among member countries. (250 words).
|
Previous year Questions1. The term 'Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership; often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (UPSC 2016)
A. G20
B. ASEAN
C. SCO
D.SAARC
Answer: B
2. Consider the following statements about Regional Comprehensive Economic Programme (RCEP). (WBCS 2019)
1. It is an economic cooperation for China-led free trade.
2. It is a counter-cooperation for the America-led trans-Pacific partnership.
3. In the countries involved in this cooperation Indian Professionals will have a job market.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 2 and 3
D. All of the above
Answer: D
3. Recently launched Regional Comprehensive economic partnership, RCEP is the largest regional trading block at present. Which of the following countries is NOT a member of this free trade agreement? (Haryana Civil Services, 2021)
A. Australia
B. New Zealand
C. Brunei
D. Bangladesh
Answer: D
|
MOON MISSIONS
1. Context
2. Background
- In the past one-and-a-half-decade, there has been a renewed interest in exploring the Moon.
- After the last Apollo mission in the early 1970s, there was a complete lull regarding sending spacecraft there as everything that could be done on the Moon with the technology of that time had been done.
- Although this began to change in the 1990s, the real impetus came after Chandrayaan-1, in 2008, discovered the presence of water on the lunar surface.
3. Types of Moon Missions
4. The Chandrayaan-3 Mission
- The Chandrayaan-3 mission is a lander mission, and it will carry a rover to explore the Moon's surface.
- The lander will also deploy several instruments to study the Moon's composition and atmosphere.
- The Chandrayaan-3 mission is a significant step forward in India's lunar exploration program.
- It will help scientists to learn more about the Moon and its potential resources.
- The mission will also pave the way for future human missions to the Moon.
5. Conclusion
- The current wave of lunar exploration, represented by missions like Chandrayaan-3, Luna 25, and Artemis II, demonstrates the ongoing global interest in unlocking the Moon's secrets and potential.
- These missions, alongside past endeavours, continue to expand our understanding of the Moon's composition, resources, and possibilities for future scientific and commercial endeavours.
|
For Prelims: Chandrayaan-3, Luna 25, Artemis II, Satish Dhawan Space Center, lunar mission, NASA, ISRO, Apollo mission,
For Mains:
1. Examine the challenges involved in achieving a successful soft landing on the Moon's surface. Discuss the significance of Chandrayaan-3 as India's second attempt in making a soft landing and its implications for future lunar exploration. (250 words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Which of the following is the name of the NASA programme to land first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024? (SSC MTS 2021)
A. Orion B. Apollo C. Artemis D. Nike
Answer: C
2. Satish Dhawan Space Centre is located at (MP Police Constable 2017)
A. Thiruvananthapuram B. Sriharikota C. Narendrapuri D. Mahendragiri
Answer: B
3. Sriharikota, where Satish Dhawan Space Centre is located, is situated next to which lake? (Haryana Civil Services 2021)
A. Chilika B. Pulicat C. Vembanad D. Kolar
Answer: B
4. “The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to (UPSC 2020)
A. Voyager-2 B. New Horizons C. LISA Pathfinder D. Evolved LISA
Answer: D
5. ISRO is related to: (SSC JE EE 2020)
A. space research B. agricultural research C. seed research D. marine research
Answer: A
|
ASPARTAME
1. Context
2. About Aspartame
- Chemically, aspartame is a methyl ester of the dipeptide of two natural amino acids, L-aspartic acid, and L-phenylalanine.
- It was discovered by James M Schlatter, a chemist at the American pharmaceutical company G D Searle & Co. (which is now a subsidiary of Pfizer) in 1965, apparently by accident, when, while researching an anti-ulcer drug, he happened to lick his finger and detected a sweet taste.
- Aspartame is an artificial sweetener used as a sugar substitute in a wide range of food and beverage products.
- It is one of the most popular low-calorie sweeteners in the world. As a synthetic compound, aspartame is created through the combination of two amino acids: aspartic acid and phenylalanine.
.png)
3. Some key points about aspartame:
- Sweetness and Caloric Content: Aspartame is approximately 200 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar). Due to its intense sweetness, only a small amount of aspartame is needed to achieve the desired level of sweetness in food and drinks. Unlike sugar, it contains negligible calories, making it a favored choice for those looking to reduce their caloric intake or manage weight.
- FDA Approval and Safety: Aspartame was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use as a food additive in 1981. However, it has been the subject of numerous controversies and health concerns over the years. Extensive scientific research and reviews have been conducted to evaluate its safety, and regulatory bodies around the world, including the FDA and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), have consistently reaffirmed its safety for consumption at acceptable daily intake levels.
- Phenylketonuria (PKU) and Phenylalanine: One critical consideration with aspartame is its phenylalanine content. Phenylalanine is one of the amino acids used to make aspartame. People with a rare genetic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU) cannot metabolize phenylalanine properly, leading to its accumulation in the body. PKU patients need to strictly monitor their phenylalanine intake and typically avoid aspartame-containing products.
- Heat Stability: Aspartame is relatively heat-sensitive, meaning it may break down and lose its sweetness when exposed to high temperatures during cooking or baking. Consequently, it is often not recommended for use in recipes that require prolonged heating.
- Wide Application: Aspartame can be found in various food and drink products, including diet sodas, sugar-free chewing gum, low-calorie desserts, protein powders, and many other processed foods labeled as "diet" or "sugar-free."
4. Is Aspartame Dangerous?
- Aspartame is a widely studied artificial sweetener used in food for over 40 years.
- More than 100 studies found no evidence of harm from aspartame, except for phenylketonurics (PKU) which lack the enzyme to break down phenylalanine in aspartame.
- Aspartame is considered safe for all groups except PKU patients.
- The USFDA and EFSA, along with other national regulators, have certified its safety.
- Aspartame is permitted in around 100 countries, including India.
- IARC rulings on aspartame have caused confusion and raised concerns among consumers, leading to lawsuits and recipe changes.
5. About U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) responsible for protecting public health and ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of food, drugs, medical devices, vaccines, cosmetics, and other products.
- It was established in 1906 with the signing of the Pure Food and Drugs Act, the FDA has become one of the world's most influential regulatory bodies for the oversight of various consumer products and medical advancements.
|
For Prelims: World Health Organisation (WHO), International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Aspartame, European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), and Phenylketonuria (PKU).
|
|
Previous year Question
1. Aspartame is an artificial sweetener sold in the market. It consists of amino acids and provides calories like other amino acids. Yet, it is used as a low-calorie sweetening agent in food items. What is the basis of this use? (UPSC 2011)
A. Aspartame is as sweet as table sugar, but unlike table sugar, it is not readily oxidized in the human body due to a lack of requisite enzymes.
B. When aspartame is used in food processing, the sweet taste remains, but it becomes resistant to oxidation.
C. Aspartame is as sweet as sugar, but after ingestion into the body, it is converted into metabolites that yield no calories.
D. Aspartame is several times sweeter than table sugar, hence food items made with small quantities of aspartame yield fewer calories on oxidation.
Answer: D
|
INDIA-UAE
-
Economic Relations: The UAE is India's third-largest trading partner and one of the major investors in India. Bilateral trade between the two countries has been growing steadily, with a focus on sectors like energy, information technology, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and agriculture. The UAE is also a significant source of remittances for India due to the large Indian diaspora residing in the UAE.
-
Investment: The UAE has made substantial investments in India across sectors such as infrastructure, real estate, hospitality, logistics, and renewable energy. The Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) and the Dubai-based DP World are prominent examples of UAE investments in India.
-
Energy Cooperation: The UAE is a crucial source of energy for India. The Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) supplies crude oil to Indian refineries, and both countries have explored opportunities for collaboration in the energy sector, including renewable energy projects.
-
Defense and Security: India and the UAE have enhanced cooperation in defense and security matters. They conduct joint military exercises, exchange intelligence, and cooperate in countering terrorism and maritime security. The UAE has also supported India's efforts to combat terrorism and extradite wanted individuals.
-
Strategic Partnership: In 2015, India and the UAE elevated their bilateral relationship to a "Comprehensive Strategic Partnership." This designation reflects the deepening ties and shared interests between the two countries.
-
Cultural Exchanges and People-to-People Contacts: There is a significant Indian community in the UAE, comprising professionals, skilled workers, and businesspeople. Both countries have encouraged cultural exchanges, tourism, and educational cooperation to strengthen people-to-people contacts and promote mutual understanding.
-
Diplomatic Engagements: High-level visits between India and the UAE have been frequent, reflecting the importance both countries attach to the relationship. The leaders of both countries have engaged in regular dialogues to enhance bilateral cooperation and address common challenges.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) holds significant importance to India for several reasons:
-
Economic Relations: The UAE is one of India's major trading partners and a significant source of investment. Bilateral trade between the two countries has been growing steadily, with the UAE being India's third-largest trading partner. The UAE's investments in India span various sectors, including infrastructure, real estate, hospitality, logistics, and renewable energy. This economic partnership contributes to India's economic growth and development.
-
Energy Security: The UAE is an important source of energy for India. It supplies crude oil to Indian refineries, helping to meet India's energy needs. Ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply is crucial for India's growing economy, and the UAE plays a significant role in fulfilling India's energy requirements.
-
Indian Diaspora: The UAE is home to a large Indian diaspora, comprising professionals, skilled workers, and businesspeople. The Indian community in the UAE plays a vital role in strengthening people-to-people ties and contributing to the UAE's economy through their work and remittances. The UAE's favorable policies towards the Indian community and its contributions have fostered a sense of goodwill and mutual understanding between the two countries.
-
Defense and Security Cooperation: India and the UAE have been strengthening their defense and security cooperation in recent years. They conduct joint military exercises, share intelligence, and collaborate in countering terrorism and ensuring maritime security. The UAE's support to India's counter-terrorism efforts and extradition of wanted individuals have been crucial in addressing shared security concerns.
-
Strategic Location: The UAE's geographic location at the crossroads of Asia, Europe, and Africa makes it an important hub for trade, connectivity, and investment. Its modern infrastructure, world-class ports, and air connectivity make it an attractive destination for Indian businesses looking to expand their reach globally. The UAE's strategic location serves as a gateway for India's trade with the Middle East, North Africa, and beyond.
-
Cultural Exchanges and Tourism: The UAE and India have fostered cultural exchanges and tourism, facilitating people-to-people contacts and enhancing mutual understanding. Millions of Indians visit the UAE for business, tourism, and religious purposes, strengthening the cultural and social ties between the two countries.
-
Diplomatic Engagements: India and the UAE maintain regular high-level engagements, with frequent visits by leaders and officials from both sides. These interactions help in deepening bilateral relations, addressing common challenges, and exploring new avenues of cooperation..
CPTPP
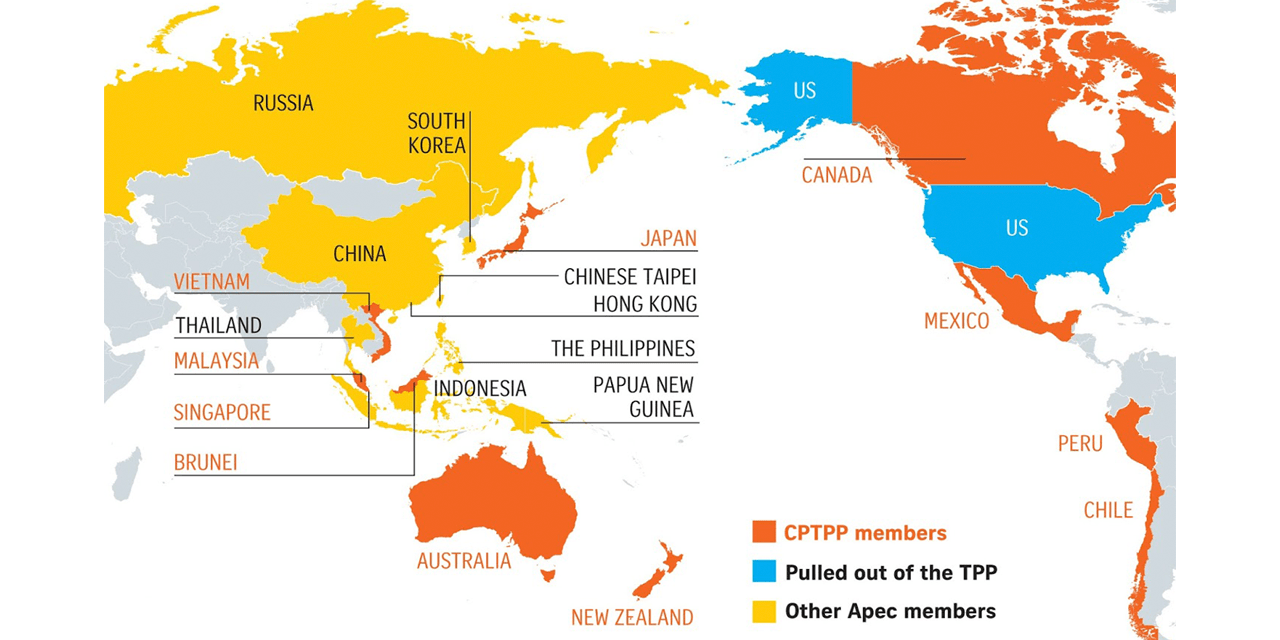
- The UK government says CPTTP will cut tariffs for UK exports to Asia Pacific countries and with UK membership, the trading bloc will have a combined GDP of 12 trillion pounds and account for 15% of global trade
- Britain is keen to deepen trade ties in the Pacific after Brexit in 2020
- London has been pushing a “Global Britain” strategy since it gave up EU membership after nearly 50 years, leaving the bloc’s single market and customs union
- Instead, former British Prime Minister Boris Johnson negotiated a trade deal called the EU–UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement
- Since Brexit, the UK has sought other trade deals with countries and trading blocs around the world that the government says have faster-growing economies than the EU
- But London will likely struggle to achieve free trade deals with large powers like China in the near term and even its closest ally, the United States has said further trade liberalization with Britain is currently off the table
- Critics say CPTTP and other deals will struggle to compensate for the economic damage sustained by leaving the now-27-member EU — the world’s largest trading bloc and collective economy
- The UK’s long-term productivity is forecast to be reduced by 4% as a result of Brexit, according to the government’s spending watchdog, the Office for Budget Responsibility.
- The UK already has trade deals with 10 of the 11 other CPTPP members and the eventual economic boost is likely to increase GDP by just 0.08% annually.
- In 2022, Britain exported 340 billion pounds of goods and services to the EU, 42% of total UK exports
|
For Prelims: Free Trade Agreement, North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
For Mains: 1.Explain the concept of preferential trade agreements (PTAs). Compare and contrast PTAs with free trade agreements (FTAs) and customs unions. Assess the advantages and limitations of PTAs.
2.Discuss the role of intellectual property rights (IPRs) in international trade agreements. Examine the challenges and opportunities associated with the protection and enforcement of IPRs in the context of global trade. |




