CREDIT SUISSE CRISIS (CDS)
Context:
What are CDS?
CDS is an insurance instrument. If an investor who has lent money to a firm (say Credit Suisse) is unsure about the firm’s ability to repay, the investor can buy a CDS on Credit Suisse’s bond. A CDS promises that if Credit Suisse fails to pay back, the insurer would pay the amount.
In return, the insurance firm selling the CDS gets a certain interest. This interest is called the spread of CDS. When these spreads rise, they signal the rising probability that a particular bond will fail. For Credit Suisse bonds, CDS spreads have spiked to 14-year highs.
Concerns around Credit Susie
| Example:In 2020, then CEO Tidjane Thiam had to quit after it became clear that he had been spying on Credit Suisse’s wealth management executive Iqbal Khan. |
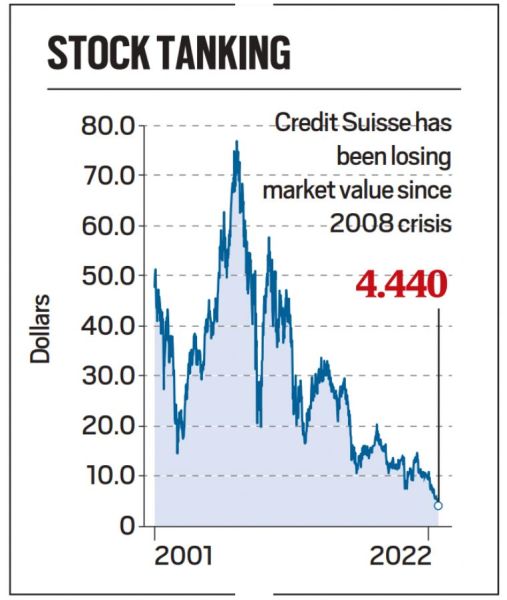
How did it impact Credit Suisse?
- The secular decline in Credit Suisse’s share price is one good way to understand how investors have progressively shrugged away from the iconic bank.
- Further, Credit Suisse bonds have increasingly become cheaper because fewer people want to lend money to it and this has resulted in the yields rising quite sharply.
- Higher yields essentially imply that the bank would have to pay higher returns for every dollar or euro it borrows from the market.
- This becomes a problem, especially in the current scenario facing the developed economies, when growth prospects are tanking and central banks are raising interest rates to contain inflation
|
For Prelims: 1.Which of the following is correct about Credit Susie crisis? A. Angel investor B.Capital Investor C. Credit rating Agency D.Insurance instrument Answer (D) |




