ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
1. Context
Urban sewage in India is known to be a hotspot and reservoir for antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which the team was able to confirm. But equally importantly, the findings validated the scientific test, or assay, the team developed for the purpose, which the team said was affordable without sacrificing efficiency, and thus a solution suitable for use in low- and middle-income countries.
2. What is Anti Microbial Resistance?
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicine making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread severe illness, and death.

3. Emergence and spread of AMR
- AMR occurs naturally over time, usually through genetic changes.
- Antimicrobial-resistant organisms are found in people, animals, food, plants, and the environment (in water, soil, and air).
- They can spread from person to person or between people and animals, including from food of animal origin.
- The main drivers of antimicrobial resistance include the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials, lack of access to clean water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) for both humans and animals, and poor infection and disease prevention and control in healthcare facilities and farms. Poor access to quality, affordable medicines, vaccines, and diagnostics, lack of awareness and knowledge, and lack of enforcement of legislation.
4. Factors causing AMR in India
- The high disease burden
- The rising income
- The easy and cheap availability of these medicines to the public.
- The uncontrolled sales of antibiotics
- Poor Public health infrastructure
- Lack of awareness regarding the misuse of antibiotics.
6. Government Initiatives that help to curb Antimicrobial Resistance In India
- Through the Swacch Bharat Program, the government has taken active steps to improve hygiene and sanitation and reduce the environmental spread of pathogens.
- Vaccination is an equally important public health measure, and through Mission Indradhaniush, India has set itself an ambitious goal of increasing routine immunization coverage to 90% within just a few years.
6.1 Red Line Campaign
7. WHO's Global plan on Anti-Microbial Resistance?
- To improve awareness and understanding of antimicrobial resistance through effective communication, education, and training.
- To Strengthen the knowledge and evidence base through surveillance and research.
- To reduce the incidence of infection through effective sanitation, hygiene, and infection prevention measures.
- To Optimize the use of antimicrobial medicines in human and animal health.
- To develop the economic case for sustainable investment that takes account of the needs of all countries and to increase investment in new medicines, diagnostic tools, vaccines, and other interventions.
8. Global efforts
|
For Prelims: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), UN Environment Programme, the World Health Organization (WHO), World Organisation for Animal Health, Mission Indradhaniush, Red Line Campaign.
For Mains: 1.Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is considered one of the most significant challenges the world faces today. Discuss.
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? ( UPSC CSE 2019)
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 Answer: (b) |
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION (UGC)
The primary functions of the UGC include:
- Allocating funds to universities and colleges.
- Formulating and implementing academic standards for higher education institutions.
- Monitoring and maintaining the quality of teaching, research, and examinations in universities.
- Providing guidance and coordination among universities and colleges in the country.
- Supporting and promoting innovations and improvements in the education system
University Grants Commission (UGC) Appointment, Tenure, and Eligibility
| Position | Appointment Method | Tenure | Minimum Eligibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairperson | Appointed by the President of India | 5 years, extendable for another 5 years (subject to review) | Distinguished academician with: * Minimum 10 years of experience as Professor in a University system or 10 years in equivalent position at a reputed research/academic administrative organization. * Eminence in higher education. * No connection with the concerned university or its colleges. |
| Member | Appointed by the President of India | 5 years, extendable for another 5 years (subject to review) | Renowned scholar/expert with: * Proven track record in teaching/research/administration in relevant field. * Minimum 10 years of experience as Professor/equivalent in a University/College/Institute of national importance. * Demonstrated commitment to higher education development. |
| Vice-Chancellor (University) | Appointed by Executive Council of the University | 5 years, extendable for another 5 years | Distinguished academician with: * Minimum 10 years of experience as Professor in a University system or 10 years in equivalent position at a reputed research/academic administrative organization. * Eminence in the sphere of higher education. * No connection with the concerned university or its colleges. |
| Dean (Faculty) or Director (School/Institute) | Appointed by Executive Council of the University/Governing Council of the Institute | 5 years, extendable for another 5 years | Eminent scholar with: * Minimum 10 years of experience as Professor in relevant field. * Exceptional research record and contributions to the discipline. * Strong administrative and leadership skills. |
| Professor | Through Selection Committee constituted by the University | Up to 5 years (initially), extendable based on performance review | Ph.D. in relevant subject with: * Proven track record of research publications in peer-reviewed journals. * Significant contribution to the discipline. * Experience in research supervision. |
| Associate Professor | Through Selection Committee constituted by the University | Up to 5 years (initially), extendable based on performance review | Ph.D. in relevant subject with: * Good academic record and publications. * Minimum 8 years of teaching/research experience in relevant field. |
| Assistant Professor | Through Selection Committee constituted by the University | Up to 5 years (initially), extendable based on performance review | Master's degree with at least 55% marks and Ph.D. in relevant/allied/cognate discipline OR Master's degree with NET/SLET/SET qualification. |
The University Grants Commission (UGC) operates under statutory provisions outlined primarily in the University Grants Commission Act, 1956. Here are some of the key statutory provisions governing the UGC:
-
University Grants Commission Act, 1956: This is the primary legislation that established the UGC. It defines the roles, functions, powers, and responsibilities of the Commission. It also outlines the composition of the UGC, appointment procedures, and its authority to allocate funds to universities and colleges.
-
UGC (Institutions Deemed to be Universities) Regulations, 2016: These regulations provide guidelines for institutions seeking the status of "Deemed to be University." They specify the criteria, application process, and conditions for granting this status.
-
UGC (Minimum Standards of Instruction for the Grant of the First Degree through Non-formal/Distance Education) Regulations, 2017: These regulations specify the minimum standards for offering programs through distance education mode, ensuring quality education delivery.
-
UGC (Open and Distance Learning) Regulations, 2017: These regulations govern the standards and norms for open and distance learning programs offered by universities and institutions in India.
-
UGC (Establishment and Maintenance of Standards in Private Universities) Regulations, 2003: These regulations outline the norms and standards for the establishment and functioning of private universities, ensuring quality education.
-
UGC (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal of Sexual Harassment of Women Employees and Students in Higher Educational Institutions) Regulations, 2015: These regulations mandate higher educational institutions to establish mechanisms for preventing and addressing sexual harassment.
-
UGC (Promotion of Equity in Higher Educational Institutions) Regulations, 2012: These regulations aim to promote equity in higher education, focusing on providing opportunities to disadvantaged sections of society.
- UGC allocates funds to universities and colleges for their development, improvement, and maintenance
- Provides financial assistance to encourage and support research activities in various academic disciplines
- UGC establishes and maintains academic standards in higher education to ensure quality across universities and colleges
- Develops frameworks and guidelines for curriculum development in different academic programs
- UGC recognizes universities in India and provides approval for the establishment of new universities
- Monitors the quality of education, teaching, research, and examinations in universities to ensure adherence to set standards
- UGC promotes and supports research activities by providing grants, fellowships, and scholarships to students and faculty members
- Facilitates coordination and cooperation among universities and other higher educational institutions
- Advises the Central and State governments on matters related to higher education policies, regulations, and development
- Provides guidance, assistance, and recommendations to universities for enhancing their academic and research standards
- Conducts assessments and accredits higher education institutions to ensure and improve quality
- Undertakes periodic reviews and assessments to maintain and enhance the quality of education
- Implements programs and initiatives to promote access to higher education for underprivileged and marginalized sections of society
- Develops and revises regulations and guidelines governing various aspects of higher education, such as distance education, deemed universities, private universities, etc
- Collects, analyzes, and maintains data related to higher education for policy formulation and decision-making purposes
- Central Universities: Established by an Act of Parliament and are under the purview of the central government.
- State Universities: Established by state governments within their respective states.
- Deemed Universities: Granted the status of "Deemed to be University" by the University Grants Commission (UGC)
- Many colleges are affiliated with universities and offer undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The degrees awarded by these colleges are conferred by the affiliated university
- Some colleges have been granted autonomy by the University Grants Commission or the respective university. These colleges have the authority to design their curriculum and conduct examinations, and they award degrees on their own
- Certain institutes, like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), National Institutes of Technology (NITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), and others designated as Institutes of National Importance, have the authority to award degrees
- Institutions like Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU) and others recognized by the Distance Education Bureau (DEB) offer distance education programs and award degrees
The University Grants Commission (UGC) in India has a rich historical background that traces back to the pre-independence era and has evolved significantly over time:
Pre-Independence Era:
- 1920s-1940s: Before India gained independence, the idea of a body to oversee and promote higher education emerged. The need for such an institution was discussed during the 1920s and 1930s.
Post-Independence Formation:
- 1947: After India gained independence in 1947, discussions intensified regarding the establishment of a commission to oversee higher education and allocate funds to universities and colleges.
- 1950: The UGC was initially set up as an ad-hoc committee to oversee the allocation of grants to universities and colleges.
- 1956: The University Grants Commission Act was passed on December 28, 1956, establishing the UGC as a statutory body. This formalized its role in overseeing and promoting higher education.
Evolution and Functions:
- Early Years: Initially, the UGC focused on disbursing grants and fostering the development of universities and colleges.
- Expanding Role: Over time, the UGC's role expanded to encompass setting academic standards, promoting research, and advising the government on higher education policies.
- Regulatory Functions: It started playing a more regulatory role by formulating guidelines and regulations for various aspects of higher education.
Milestones and Amendments:
- 1960s-1970s: The UGC underwent amendments to accommodate changes in the higher education landscape and to enhance its effectiveness.
- Subsequent Decades: The UGC continued to evolve, adapting to the changing needs of higher education, introducing reforms, and addressing emerging challenges.
FREE TRADE AGREEMENT
1. Context
2. About the Free Trade Agreement
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more countries to reduce or eliminate barriers to trade, such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies.
- FTAs can also include provisions on other issues, such as investment, intellectual property, and labour standards.
- The goal of an FTA is to promote trade and economic growth between the signatory countries.
- By reducing or eliminating trade barriers, FTAs can make it easier for businesses to export their goods and services to other countries, which can lead to increased production, employment, and innovation.
3. Types of Free Trade Agreement
- Bilateral Free Trade Agreement (BFTA) involves two countries, aiming to promote trade and eliminate tariffs on goods and services between them. It establishes a direct trade relationship, allowing for a more focused and tailored agreement between the two nations.
- Multilateral Free Trade Agreement (MFTA) Involving three or more countries, an MFTA seeks to create a comprehensive trade bloc, promoting economic integration on a larger scale. It requires coordination among multiple parties, addressing diverse economic interests and fostering a broader regional economic landscape.
- Regional Free Trade Agreement (RFTA) involves countries within a specific geographic region, aiming to enhance economic cooperation and integration within that particular area. It focuses on addressing regional economic challenges and fostering collaboration among neighbouring nations.
- Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) involves a reciprocal reduction of tariffs and trade barriers between participating countries, granting preferential treatment to each other's goods and services. It allows countries to enjoy trading advantages with specific partners while maintaining autonomy in their trade policies with non-participating nations.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) is a broad and advanced form of FTA that goes beyond traditional trade barriers, encompassing various economic aspects such as investment, intellectual property, and services. It aims for a more comprehensive economic partnership, encouraging deeper integration and collaboration between participating countries.
- Customs Union While not strictly an FTA, a Customs Union involves the elimination of tariffs among member countries and the establishment of a common external tariff against non-member nations. It goes beyond standard FTAs by harmonizing external trade policies, creating a unified approach to trade with the rest of the world.
- Free Trade Area (FTA) with Trade in Goods (TIG) and Trade in Services (TIS): Some FTAs specifically emphasize either trade in goods or trade in services, tailoring the agreement to the specific economic strengths and priorities of the participating countries. This approach allows nations to focus on areas where they have a comparative advantage, fostering specialization and efficiency.
4. India's Free Trade Agreements
India is a member of several free trade agreements (FTAs) and is currently negotiating others. India's FTAs have helped to reduce trade barriers and promote trade and economic growth. They have also helped to attract foreign investment and create jobs.
- The South Asian Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA) was signed in 1995 by the seven countries of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). SAFTA aims to reduce or eliminate tariffs on trade between the member countries.
- The India-Bangladesh FTA was signed in 2010 and came into force in 2011. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-Sri Lanka FTA was signed in 1999 and came into force in 2000. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement was signed in 2002 and came into force in 2010. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) was signed in 2010 and came into force in 2011. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement(CEPA) was signed in 2022 and came into effect in 2023. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-UAE Comprehensive Partnership Agreement (CEPA) was signed in 2022 and came into effect in 2022. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) was signed in 2022 and came into effect in 2022. It is a comprehensive FTA that covers goods, services, and investments.
- The India-Malaysia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) was signed in 2010 and aims to enhance economic ties by addressing trade in goods and services, as well as investment and other areas of economic cooperation.
- The India-Thailand Free Trade Agreement was signed in 2003 and focuses on reducing tariffs and promoting trade in goods and services between India and Thailand.
- The India-Singapore Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) has been operational since 2005, this agreement covers trade in goods and services, as well as investment and intellectual property.
- The India-Nepal Trade Treaty While not a comprehensive FTA, India and Nepal have a trade treaty that facilitates the exchange of goods between the two countries.
- The India-Chile Preferential Trade Agreement was signed in 2006 and aims to enhance economic cooperation and reduce tariffs on certain products traded between India and Chile.
5. India - UK Free Trade Agreement
5.1. Background
- Both countries have agreed to avoid sensitive issues in the negotiations.
- The interim (early harvest agreement) aims to achieve up to 65 per cent coverage for goods and up to 40 per cent coverage for services.
- By the time the final agreement is inked, the coverage for goods is expected to go up to "90 plus a percentage" of goods.
- India is also negotiating a similar early harvest agreement with Australia, which is supposed to set the stage for a long-pending Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement that both countries have been pursuing for nearly a decade.
- While the commencement of negotiations does mark a step forward in the otherwise rigid stance adopted and when it comes to trade liberalisation, experts point to impediments and the potential for legal challenges going ahead.
5.2. GATT (General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs)
- The exception to the rule is full-scale FTAs, subject to some conditions.
- One rider, incorporated in Article XXIV.8 (b) of GATT, stipulates that a deal should aim to eliminate customs duties and other trade barriers on "Substantially all the trade" between the WTO member countries that are signatories to an FTA.
- For this Agreement, a free-trade area shall be understood to mean a group of two or more customs territories in which the duties and other restrictive regulations of commerce are eliminated on substantially all the trade between the constituent territories in products originating in such territories.
- It is often beneficial to negotiate the entire deal together, as an early harvest deal may reduce the incentive for one side to work towards a full FTA.
- These agreements are not just about goods and services but also issues like investment.
- If you are trying to weigh the costs and benefits, it is always better to have the larger picture in front of you.
- In the case of the early harvest agreement inked with Thailand, automobile industry associations had complained that relaxations extended to Bangkok in the early harvest had reduced the incentive for Thailand to work towards a full FTA.
- Early harvest agreements may serve the function of keeping trading partners interested as they promise some benefits without long delays, as India becomes known for long-drawn negotiations for FTAs.
- Government emphasis on interim agreements may be tactical so that a deal may be achieved with minimum commitments and would allow for contentious issues to be resolved later.
|
For Prelims: Free Trade Agreement, India-U.K, Bilateral Free Trade Agreement, G-20 Summit, Agenda 2030, Covid-19 Pandemic, SAARC, General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement, Multilateral Free Trade Agreement, Regional Free Trade Agreement, Preferential Trade Agreement, Customs Union,
For Mains:
1. Evaluate the potential impact of the India-UK FTA on the Indian economy, considering both positive and negative aspects (250 Words)
2. Critically evaluate the significance of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) in promoting trade and economic growth, considering their potential benefits and drawbacks. (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Consider the following countries:
1. Australia
2. Canada
3. China
4. India
5. Japan
6. USA
Which of the above are among the free-trade partners' of ASEAN? (UPSC 2018)
A. 1, 2, 4 and 5 B. 3, 4, 5 and 6 C. 1, 3, 4 and 5 D. 2, 3, 4 and 6
Answer: C
2. Increase in absolute and per capita real GNP do not connote a higher level of economic development, if (UPSC 2018) (a) Industrial output fails to keep pace with agricultural output. Answer: C 3. The SEZ Act, 2005 which came into effect in February 2006 has certain objectives. In this context, consider the following: (2010)
Which of the above are the objectives of this Act? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: A 4. A “closed economy” is an economy in which (UPSC 2011) (a) the money supply is fully controlled Answer: D 5. With reference to the “G20 Common Framework”, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2022)
1. It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with the Paris Club. 2. It is an initiative to support Low Income Countries with unsustainable debt. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: C
|
INTERNATIONAL SOLAR ALLIANCE (ISA)
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an initiative led by India and France, launched during the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris in 2015.
- It aims to promote the use of solar energy globally, especially in solar-rich countries lying fully or partially between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. However, membership is now open to all UN member countries
- India, as a founding member, uses ISA as a platform to advance its renewable energy targets, including the ambitious goal of achieving 500 GW of renewable capacity by 2030.
- The ISA complements India's domestic initiatives, like the National Solar Mission
- In 2021, the United States joined the ISA, signaling global support for solar energy adoption.
- The One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG) initiative, also led by India, aligns with ISA’s objectives by advocating for a transnational solar grid that connects renewable energy sources globally.
-
The ISA was intended to act as a catalyst, helping countries tackle challenges like financial, technological, and regulatory barriers to adopt solar energy effectively.
-
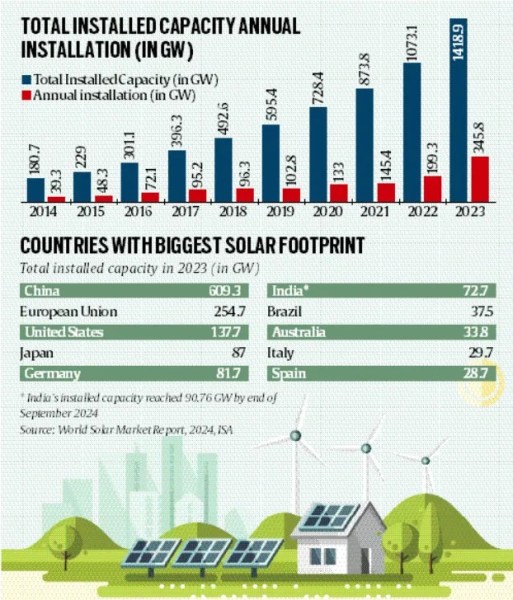
Despite significant advancements in solar energy deployment, ISA has had limited success in facilitating a large number of projects. Over the past five years, global solar power capacity has grown by over 20% annually, with a more than 30% increase reported last year, as indicated by ISA’s World Solar Market Report 2024.
-
Ajay Mathur, director general of ISA, noted that most of these new installations are concentrated in a few countries, with China leading the way. Of the 345 GW of solar capacity added in 2023, China alone contributed over 216 GW, representing more than 62% of the total.
-
More than 80% of global solar energy investments go to developed countries, China, and major emerging markets like India.
-
Many countries lack experience with large-scale energy projects, especially in solar, which is a relatively new technology. Local developers are often absent, meaning international companies are needed for investment. However, these investors typically look for policy stability and well-defined regulatory frameworks.
-
ISA has partnered with governments and local organizations to help establish regulatory frameworks, prepare power purchase agreements, and train local professionals
| India’s dedication to renewable energy and climate action was fundamental to the establishment of the ISA. With a goal of reaching 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy by 2030, India’s renewable energy targets align with the ISA’s mission to promote solar energy worldwide. This target is part of India’s broader Panchamrit Initiative, which focuses on reducing carbon emissions and advancing sustainable development. Additionally, India is instrumental in shaping ISA’s programs and promoting global cooperation. Its extensive experience in scaling solar energy projects and developing supportive policies serves as a model for other member nations, particularly those aiming to expand energy access. By sharing best practices and technical knowledge, India seeks to support other countries in advancing their solar energy initiatives. |
- Solar energy plays a pivotal role in the global shift to renewable energy, which is essential for addressing climate change. It is the fastest-growing renewable source, though it does face the challenge of intermittency.
-
In many parts of the world, solar is now the most cost-effective energy source when sunlight is available. Projections for solar energy capacity show it could expand by 3 to 15 times by 2050, depending on the pathway chosen to reach global net-zero emissions.
-
China leads in solar PV installations, accounting for about 43% of the world's total. The top ten markets together hold over 95% of installed capacity, while less than 2% of new solar installations are in Africa—a region where nearly 80% of the 745 million people without electricity reside.
-
The ISA was founded with a broader strategic vision for India, aiming to enhance its influence, especially among the Global South, with a particular focus on African nations
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) seeks to mobilize $1 trillion in solar investments by 2030 through its 'Towards 1000' strategy, which aims to lower both technology and financing costs.
- This ambitious plan targets energy access for 1 billion people and the installation of 1,000 GW of solar capacity. Achieving these objectives would reduce global carbon emissions by approximately 1,000 million tonnes of CO₂ per year.
- ISA’s programs focus on three core areas—Analytics & Advocacy, Capacity Building, and Programmatic Support—to establish a supportive environment for solar investments and share best practices among member nations.
- ISA also drives solar adoption across sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, transportation, and power generation. By promoting policies and facilitating the exchange of successful strategies, ISA enables member countries to encourage solar energy deployment.
- The alliance has introduced innovative business models, supported governments in developing solar-friendly policies via its Ease of Doing Solar analytics, and pooled demand to reduce costs of solar technologies.
- Additionally, ISA enhances financing access by lowering investment risks, making the solar sector more attractive to private investors and paving the way toward a sustainable energy future.
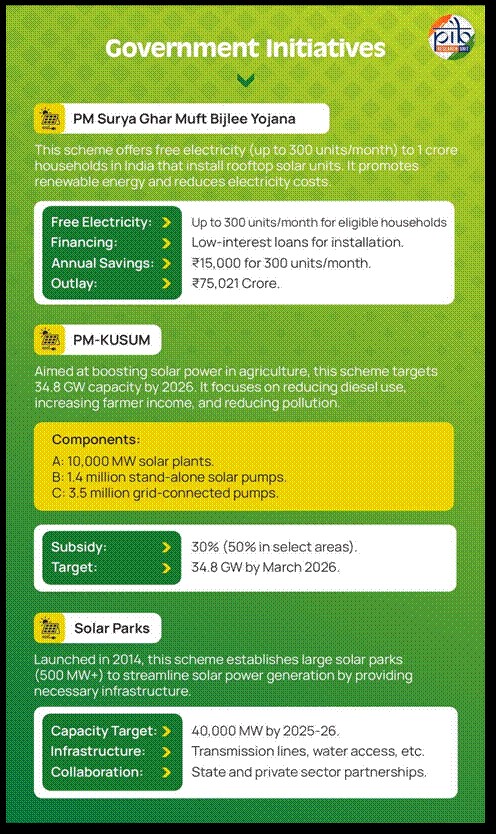
- India's solar sector is growing rapidly, placing the country fifth globally in terms of solar power capacity. As of September 2024, India’s installed solar capacity has reached around 90.76 GW, a 30-fold increase over the last nine years. According to the National Institute of Solar Energy, the country’s solar potential is estimated at 748 GW.
- India’s Panchamrit targets include: (i) achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy capacity by 2030, (ii) sourcing 50% of its energy from renewables by 2030, (iii) reducing projected carbon emissions by one billion tonnes by 2030, (iv) cutting carbon intensity by 45% by 2030, and (v) reaching Net Zero by 2070.
- India has made significant progress, with its non-fossil fuel capacity increasing by 396% over the past 8.5 years, and 46.3% of its total energy capacity now comes from non-fossil sources, underscoring its dedication to sustainable energy as highlighted in international climate forums.
- Government policies, including the 100% FDI allowance in renewable energy projects, have enhanced the sector's appeal to investors. Additionally, technological advancements and a strong regulatory framework are creating an enabling environment for the continued expansion of solar energy projects
The International Solar Alliance (ISA) represents a pivotal shift towards a sustainable energy future, with India at the forefront of this initiative. The ISA’s mission extends beyond improving energy access and security to making substantial global carbon emissions reductions. The upcoming assembly offers an essential platform for nations to collaborate and emphasize the urgent need to accelerate solar energy adoption.
As more countries align with ISA’s mission, solar energy is positioned to play a central role in the global energy landscape. The ISA’s efforts, coupled with India’s strong commitment to solar advancement, pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable world for future generations. Through international cooperation and innovative approaches, the ISA is well-positioned to contribute meaningfully to global climate objectives and universal energy access
|
For Prelims: General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity & climate change For Mains: GS-III: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment. |
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Consider the following statements: (2016)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only Answer (a)
|
DIGITAL PERSONAL DATA PROTECTION RULES

- The Government of India issued the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025 on 14 November 2025, completing the implementation of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- With both the Act and Rules now in place, India has a comprehensive, citizen-oriented framework that balances personal data rights with legitimate data processing requirements.
- Before finalising the Rules, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology sought inputs from the public. Consultations were organised across several major cities—Delhi, Mumbai, Guwahati, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Bengaluru and Chennai—drawing participation from startups, MSMEs, industry associations, civil society organisations, and government bodies.
- Citizens also contributed actively. Altogether, 6,915 suggestions and comments were submitted, significantly influencing the final version of the Rules.
- The notification of these Rules establishes a practical, innovation-supportive data protection regime for the country. It promotes clarity, encourages adherence to the law, and enhances public confidence in India’s expanding digital landscape.
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act was passed by Parliament on 11 August 2023, establishing a comprehensive legal structure for safeguarding digital personal information in India.
- It outlines the responsibilities of organisations when they gather or process such data. The Act is built on the SARAL philosophy—Simple, Accessible, Rational and Actionable—using straightforward language and clear examples so that individuals and businesses can easily understand the requirements.
- The Act is anchored in seven foundational principles: consent and transparency, limitation of purpose, minimal collection of data, accuracy, restricted data retention, strong security measures and accountability. These principles shape each step of data handling and ensure that personal information is processed only for legitimate and defined purposes.
- A key highlight of the law is the establishment of the Data Protection Board of India, an autonomous authority responsible for monitoring compliance, investigating violations and ensuring that necessary corrective actions are taken.
- The Board is central to protecting user rights and fostering confidence in the data protection framework
Key Terms under the DPDP Act, 2023
|
The Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025 operationalise the DPDP Act, 2023, creating a practical and transparent system for safeguarding personal data in India’s rapidly growing digital landscape. These Rules place strong emphasis on citizen rights and responsible data handling by organisations. Their objective is to prevent misuse of personal information, minimise digital risks, and foster an environment that supports safe innovation—thereby strengthening trust in India’s digital economy.
To achieve these goals, the Rules lay down several key provisions:
- A phased compliance period of 18 months has been introduced so organisations have adequate time to upgrade systems and adopt sound data-protection practices.
- All Data Fiduciaries must issue a separate, easy-to-read consent notice clearly stating the specific purpose for which personal data is collected and processed.
- Consent Managers—entities that help people manage their permissions—must operate as companies incorporated in India.
- The Rules also define a clear and prompt procedure for reporting data breaches. In the event of a breach, the Data Fiduciary must immediately notify every affected person in simple language, outlining what occurred, potential consequences and the corrective measures taken. The communication must also include relevant contact details for assistance.
- Each Data Fiduciary is required to provide accessible contact information for queries related to personal data—whether that is a designated officer or a Data Protection Officer. Significant Data Fiduciaries have additional responsibilities: they must conduct external audits, undertake impact assessments and implement stricter controls when using emerging or sensitive technologies.
- They may also be required to comply with government directions regarding restricted data categories, including localisation requirements when necessary.
- The Rules strengthen the rights granted under the Act. Individuals can request access to their personal information, corrections or updates, and deletion in permitted situations.
- They may also authorize another person to exercise these rights on their behalf. Data Fiduciaries must respond to such requests within 90 days.
- Additionally, the Rules provide for a fully digital Data Protection Board of India with four members. Citizens will be able to submit complaints online and track them through a dedicated website and mobile app, making grievance resolution faster and more efficient.
- Appeals against the Board’s orders will be handled by the Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT)
The DPDP framework puts citizens at the heart of India’s data protection regime. Its core purpose is to ensure that individuals have clear authority over their personal information and can trust that it is handled responsibly. The rules are drafted in simple, user-friendly language so people can easily understand their rights, while also ensuring that organisations remain accountable for how they manage personal data.
Key Rights and Safeguards Provided to Citizens:
- Right to Give or Withhold Consent
Individuals have the freedom to agree or refuse the use of their personal data. Consent must be informed, specific, and easy to comprehend, and it can be withdrawn at any point. - Right to Know How Data is Used
People are entitled to know what information has been collected about them, the purpose of its collection, and the ways it is being processed. Organisations must share this information in a clear and straightforward format. - Right to Access Personal Data
Any individual may request a copy of the personal data that a Data Fiduciary holds about them. - Right to Correct Personal Data
Citizens can ask for corrections if their personal information is wrong, inaccurate, or incomplete. - Right to Update Personal Data
Individuals may request updates when their details change—such as a new phone number or address. - Right to Delete Personal Data
People have the option to seek erasure of their personal data under specific circumstances. The Data Fiduciary must review and act on such requests within the stipulated timeframe. - Right to Appoint a Representative
Every person may nominate someone else to exercise their data rights on their behalf—useful during illness or other situations where they cannot act themselves. - Mandatory Response Within 90 Days
Data Fiduciaries must respond to requests for access, correction, updating, or deletion within a maximum of ninety days, promoting timely redressal and accountability. - Protection in Case of Data Breaches
If a data breach occurs, affected individuals must be informed promptly. The notification must explain the incident and outline the steps they can take to reduce any potential harm. - Clear Contact Point for Help
Organisations must provide easily accessible contact details—either of a designated official or a Data Protection Officer—for queries or complaints related to personal data. - Extra Safeguards for Children
Processing children’s personal data requires verifiable consent from a parent or guardian, except when the data is used for essential services like medical care, education or immediate safety.
- As the DPDP Act and its Rules strengthen citizens’ privacy protections, they also clarify how these enhanced rights coexist with the Right to Information (RTI) Act, which ensures public access to information.
- The amendments made through the DPDP Act modify Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act in a manner that upholds both privacy and transparency without undermining either.
- This change is consistent with the Supreme Court’s recognition of privacy as a fundamental right in the Puttaswamy judgment.
- It aligns the RTI law with judicial reasoning that has, for years, applied reasonable limits to protect personal information.
- By formally incorporating this approach into the statute, the amendment removes ambiguity and avoids any clash between the RTI Act’s transparency mandate and the privacy protections embedded in the DPDP framework.
- Importantly, the updated provision does not prohibit the release of personal data. Instead, it requires authorities to make a careful, case-specific assessment before sharing such information, keeping the individual’s privacy interests in mind.
- Meanwhile, Section 8(2) of the RTI Act remains unchanged. It empowers public authorities to disclose information whenever the public interest is compelling enough to outweigh potential harm to protected interests.
- This ensures that the core purpose of the RTI Act—promoting openness, accountability and informed citizen participation—continues to shape how information requests are handled
|
For Prelims: Personality rights, Delhi High Court, Madras High Court, Right to property, trademark, right to privacy, Article 21, Copyright Act, 1957
For Mains:
1. Explain how can the legal framework for protecting personality rights in India be strengthened to better address the challenges of the digital age. (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. What is the position of the Right to Property in India? (UPSC 2021)
A. Legal right available to citizens only
B. Legal right available to any person
C. Fundamental Right available, to citizens only
D. Neither Fundamental Right nor legal right
Answer: B
2. In order to comply with TRIPS Agreement, India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection) Act, 1999. The difference/differences between a "Trade Mark" and a Geographical Indication is/are (UPSC 2010)
1. A Trade Mark is an individual or a company's right whereas a Geographical Indication is a community's right.
2. A Trade Mark can be licensed whereas a Geographical Indication cannot be licensed.
3. A Trade Mark is assigned to the manufactured goods whereas the Geographical Indication is assigned to the agricultural goods/products and handicrafts only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 1 and 2 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
3. Which of the following statements regarding Article 21 of the Constitution of India is/ is correct? (CDS GK 2017)
1. Article 21 is violated when under-trial prisoners are detained under judicial custody for an indefinite period.
2. Right to life is one of the basic human rights and not even the state has the authority to violate that right.
3. Under Article 21, the right of a woman to make reproductive choices is not a dimension of personal liberty.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1, 2 and 3 B. 1 and 2 only C. 1 and 3 only D. 2 only
Answer: B
4. Article 21 of Indian Constitution secures: (OPSC OAS 2018)
A. Right to life only
B. Right to personal liberty only
C. Right to liberty and privacy
D. Right to life, personal liberty and right to privacy
Answer: D
5. ‘Right to Privacy’ is protected under which Article of the Constitution of India? (UPSC 2021) (a) Article 15 Answer: C 6. Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? (2018) (a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution. (b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV. (c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part III. (d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution. Answer: C |
CENTRAL CONSUMER PROTECTION AUTHORITY(CCPA)
- This Act provides for the establishment of the CCPA to promote, protect, and enforce consumer rights. The CCPA has the authority to investigate, recall unsafe goods, order discontinuation of unfair trade practices, and impose penalties for misleading advertisements affecting consumers
- The Act enumerates the rights of consumers, including the right to be informed, right to choose, right to be heard, right to seek redressal, and the right to consumer education
- It prohibits unfair trade practices such as false advertising, misleading information, deceptive packaging, and selling goods/services that pose a danger to consumers' lives and safety
- The Act introduces the concept of product liability, holding manufacturers, sellers, and service providers accountable for any harm caused by defective products or deficient services
- The Act establishes Consumer Disputes Redressal Commissions at the district, state, and national levels to expedite the resolution of consumer disputes. These commissions provide simple, speedy, and cost-effective dispute resolution mechanisms
- It includes provisions specifically addressing consumer rights and liabilities related to e-commerce transactions and direct selling, ensuring adequate protection for consumers engaged in online purchases and transactions
- The Act emphasizes the importance of consumer awareness and education through outreach programs, campaigns, and educational initiatives to empower consumers with knowledge about their rights and responsibilities
- The penalties for misleading advertisements, unfair trade practices, and violations of consumer rights have been increased, along with provisions for compensating consumers for any loss or injury suffered due to a defective product or deficient service
Here's a breakdown of the SCPC's key functions:
Composition:
- Each SCPC is headed by the Minister-in-charge of Consumer Affairs in the state government.
- It includes other official and non-official members representing various interests, such as:
- Members of the state Legislative Assembly
- Representatives from consumer organizations
- Representatives from farmers, manufacturers, traders, and industrialists
- Experts in consumer affairs and law
Responsibilities:
- The SCPC organizes awareness campaigns to educate consumers about their rights and responsibilities. It also disseminates information about consumer laws and redressal mechanisms.
- The SCPC receives and investigates consumer complaints against unfair trade practices, defective goods and services, and misleading advertisements. It can recommend action against businesses violating consumer rights.
- The SCPC advises the state government on matters related to consumer protection. This includes proposing new laws, policies, and initiatives to strengthen consumer rights within the state.
- The SCPC monitors the market for unfair trade practices and emerging consumer issues. It may conduct research and studies to identify and address emerging consumer concerns.
- The SCPC coordinates with the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) and other consumer protection agencies to ensure effective enforcement of consumer rights across the country
The Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) is a quasi-judicial regulatory body established under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, in India. It plays a pivotal role in promoting, protecting, and enforcing consumer rights at the national level.
Functions:
The CCPA is empowered with a wide range of functions to safeguard consumer interests, including:
- It can investigate unfair trade practices, misleading advertisements, and violations of consumer rights. Additionally, it has the authority to prosecute entities found guilty of such offenses.
- The CCPA can order the recall of unsafe or defective products from the market. It can also direct businesses to issue refunds or replacements for defective products or services.
- The CCPA can impose significant penalties on businesses found indulging in unfair trade practices, misleading advertisements, or violating consumer rights.
- It can file class-action suits on behalf of groups of consumers affected by the same unfair practice.
- The CCPA can issue guidelines and standards for product safety and service quality.
- It can undertake initiatives to raise awareness about consumer rights and educate consumers about redressal mechanisms.
- The CCPA collaborates with State Consumer Protection Councils (SCPCs) to ensure effective consumer protection across the country.
Structure:
The CCPA is headed by a Chief Commissioner and three other Commissioners, all appointed by the Central Government. It also has a team of supporting staff that assists in carrying out its various functions.
|
For Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
For Mains: General Studies II: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Which of the following statements about the 'Consumer Protection Act 2019' is not true? (UGC NET 2020)
A.It has widened the definition of consumer
B.It provides for E-filing of complaints
C.It establishes Central Consumer Protection Authority
D.It ignores mediation as an alternate disputes resolution mechanism
Answer (D)
|




