ARCTIC COUNCIL
1. Context
2. What is happening in the Arctic?
The Arctic is warming at twice the global average rate, due to climate change. This is causing several changes in the region, including:
- Sea ice is melting rapidly, opening up new shipping routes and making it easier to access oil and gas resources.
- Permafrost is thawing, releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and destabilizing infrastructure.
- Sea levels are rising, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Plant and animal life is being disrupted, as species are forced to migrate to new areas in search of cooler temperatures.
3. How India can help in protecting Arctic?
India has been inducted into the Arctic Council as an observer state, giving it a greater say in managing the Arctic region's activities and resources. This is a significant diplomatic achievement for India, which has been working to get observer status for several years. India's membership also reflects its growing scientific expertise in polar research, and it has committed to contributing its expertise to the Arctic Council's work. India can play a role in protecting the Arctic in several ways, including:
- India has a strong scientific research program in the Arctic and can share its findings with the Arctic Council to help inform decision-making.
- India can promote sustainable development practices in the Arctic, such as by investing in renewable energy and energy efficiency.
- India can help to raise awareness of the importance of the Arctic and the challenges it faces.
- India can work with other countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the Arctic.
4. What is the Arctic Council?
The Arctic Council is an intergovernmental forum that promotes cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic states, Arctic indigenous communities and other interested parties on common Arctic issues, to advance sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic. The eight member states of the Arctic Council are Canada, Denmark (Greenland and Faroe Islands), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States.

5. What do the Arctic Council do?
The Arctic Council works on a wide range of issues related to the Arctic, including:
- Climate change and environmental protection
- Sustainable development
- Economic and social issues
- Education and research
- Culture and languages
6. Conclusion
India's induction into the Arctic Council is a positive development for both India and the Arctic region. It will help to promote cooperation between Arctic and non-Arctic states and ensure that the region is managed sustainably.
|
For Prelims: Arctic Council, India, Climate Change, G20 Summit, Sustainable development
For Mains:
1. Critically examine the challenges and opportunities for India in the Arctic region. (250 words)
2. Assess the role of the Arctic Council in promoting sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic. (250 words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Consider the following countries: (UPSC 2014)
1. Denmark
2. Japan
3. Russian Federation
4. United Kingdom
5. United States of America
Which of the above are the members of the 'Arctic Council'?
A. 1, 2 and 3 B. 2, 3 and 4 C. 1, 4 and 5 D. 1, 3 and 5
Answer: D
2. Which one of the following is associated with the issue of control and phasing out of the use of ozone-depleting substance? (UPSC CSE 2015)
A.Bretton woods conference
B. Montreal Protocol
C. Kyoto Protocol
D. Nagoya Protocol
Answer: B
3. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (UPSC 2020)
A. Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
B. Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
C. Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
D. Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Answer: A
4. With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2016)
1. The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017
2. The Agreement aims to limit greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2°C or even 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
3. Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $ 1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 3 only B. 2 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
5. A new type of El Nino called El Nino Modoki appeared in the news. In this context, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2010)
1. Normal El Nino forms in the Central Pacific ocean whereas El Nino Modoki forms in the Eastern Pacific ocean.
2. Normal El Nino results in diminished hurricanes in the Atlantic ocean but El Nino Modoki results in a greater number of hurricanes with greater frequency.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
6. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (UPSC 2011)
1. La Nina is characterized by unusually cold ocean temperature in the equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
2. El Nino has an adverse effect on the south-west monsoon of India, but La Nina has no effect on the monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
7. Consider the following statements: (MPSC 2017)
a. La Nina is a little girl.
b. During the time of La Nina cold water in the ocean rises to the surface.
c. La Nina strengthens the Indian monsoon.
d. During the time of El Nino, trade winds weaken, and warm water moves east in the ocean. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. Only a and b B. a, b and c C. Only b and c D. All of the above
Answer: D
8. With reference to Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT), which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2020)
1. OMT is measured up to a depth of 26°C isotherm which is 129 meters in the south-western Indian Ocean during January-March.
2. OMT collected during January-March can be used in assessing whether the amount of rainfall in monsoon will be less or more than a certain long-term mean.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
9. With reference to 'Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)' sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2017)
1. IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
2. An IOD phenomenon can influence an EI Nino's impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
10. "EL Nino" refers to a temperature anomaly in the ________ ocean. (NTPC 2017)
A. Indian B. Pacific C. Southern D. Atlantic
Answer: B
11. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change recently published the draft Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, in 2020. Which of the following statements is correct about EIA? (Punjab Civil Service 2020)
1. It predicts the effect of a proposed industrial/infrastructural project on the environment.
2. It prevents the proposed activity/project from being approved without proper oversight or taking adverse consequences into account.
3. It compares various alternatives for a project and seeks to identify the one which represents the best combination of economic and environmental costs and benefits.
4. As per the new notification, Coal and non-Coal mineral prospecting and solar photovoltaic projects do not need prior environmental clearance.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. Only 1 and 2
B. Only 2, 3 and 4
C. Only 1, 2 and 3
D. Only 1, 2 and 4
Answer: D
12. In the context of India’s preparation for Climate -Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2021)
1. The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research program.
2. The project of CCAFS is carried out under the Consultative Group on International Agricultural (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
3. The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centers.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
13. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2012)
1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.
2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
14. With reference to the "G20 Common Framework", consider the following statements: (UPSC 2022)
1. It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with the Paris Club.
2. It is an initiative to support Low Income Countries with unsustainable debt.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
15. Consider the following statements
1. The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the 'Club of Rome
2. Sustainable Development goals has to be achieved by the year 2030
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct
A. 1 Only B. 2 Only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 Nor 2
Answer: B
|
APAAR ID
1. Context
Several state governments have recently requested schools to seek parental consent for the creation of a new student identity card known as the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR). This initiative is part of the 'One Nation, One Student ID' program, which stems from the National Education Policy of 2020.
2. About APAAR
- APAAR, or the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry, is designed to serve as a unique ID system for all students in India, starting from a young age.
- The initiative aims to provide each student with a lifelong APAAR ID, facilitating the tracking of academic progress from pre-primary education to higher education.
- APAAR will also function as a gateway to Digilocker, a digital platform where students can securely store essential documents and achievements digitally, such as exam results and report cards.
- This digitalization streamlines access and utilization for purposes like pursuing higher education or seeking employment.
3. The Motivation Behind APAAR Implementation
- The introduction of APAAR is driven by the goal of simplifying the education process and reducing the necessity for students to carry physical documents.
- It seeks to create a positive change, allowing state governments to monitor literacy rates, dropout rates, and other vital metrics for educational improvements.
- APAAR also has the objective of curbing fraud and the issuance of duplicate educational certificates by providing a single, trusted reference for educational institutions.
- Only authorized sources that issue certificates will be permitted to deposit credits into the system, ensuring the authenticity of the documents.
4. The Functionality of APAAR ID
- Every individual will be assigned a unique APAAR ID, linked to the Academic Bank Credit (ABC), a digital repository containing information about the credits earned by students throughout their educational journey.
- With the APAAR ID, students can store all their certificates and credits, whether from formal or informal learning.
- When a student changes schools, her data in the ABC is seamlessly transferred to the new institution simply by sharing the APAAR ID.
- To obtain their single ID, students need to provide basic information such as name, age, date of birth, gender, and a photograph.
- This information is verified using their Aadhar number, with the Aadhar number used solely for verification purposes.
- Students will sign a consent form, choosing whether to share their Aadhar number and demographic information with the Ministry of Education for APAAR ID creation. For minors, parental consent is required.
5. Concerns and Privacy Issues
- Some parents and students have expressed concerns about sharing their Aadhar details, fearing potential data leaks to external parties.
- The government reassures that the shared information will remain confidential and will only be accessible to entities engaged in educational activities, such as the Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) database, scholarships, maintenance of academic records, educational institutions, and recruitment agencies.
- Students retain the ability to stop sharing their information with these designated parties at any time, and data processing will cease upon withdrawal of consent.
- However, data already processed will remain unaffected even if consent is later withdrawn.
6. Conclusion
The introduction of APAAR, the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry, marks a significant step in streamlining education, reducing document-related hassles for students, and enhancing data security. It is designed to benefit both students and educational institutions by offering a unified and accessible digital platform for academic records. Concerns about data privacy are addressed with strict controls and consent mechanisms.
|
For Prelims: APAAR, National Educational Policy 2020, Digilocker, Aadhar, Unified District Information System for Education Plus, Academic Bank Credit,
For Mains:
1. Critically analyze the concerns raised about the privacy of student data in the context of the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry. Suggest measures to mitigate these concerns. (250 words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2018)
1. As per the Right to Education (RTE) Act, to be eligible for appointment as a teacher in a State, a person would be required to possess the minimum qualification laid down by the State Council of Teacher Education concerned.
2. As per the RTE Act, for teaching primary classes, a candidate is required to pass a Teacher Eligibility Test conducted in accordance with the National Council of Teacher Education guidelines.
3. In India, more than 90% of teacher education institutions are directly under the State Governments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 3 only
Answer: B
2. The objective(s) of Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyaan is/are: (UKSSSC Forest Guard 2021)
A. To provide quality based education to all children from 14 to 18 years
B. Universal standstill till the year 2020
C. To provide residential school for the students of remote areas
D. All of the above
Answer: D
3. Consider the following: (UPSC 2011)
1. Right to education.
2. Right to equal access to public service.
3. Right to food.
Which of the above is/are Human Right/Human Rights under the "Universal Declaration of Human Rights"?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3 Answer
Answer: D
4. Regarding 'DigiLocker', sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC 2016)
1. It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
2. It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
5. Consider the following: (UPSC 2022)
1. Aarogya Setu
2. CoWIN
3. DigiLocker
4. DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
A. 1 and 2 only B. 2, 3 and 4 only C. 1, 3 and 4 only D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: D
6. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2020)
1. Aadhaar metadata cannot be stored for more than three months.
2. State cannot enter into any contract with private corporations for sharing of Aadhaar data.
3. Aadhaar is mandatory for obtaining insurance products.
4. Aadhaar is mandatory for getting benefits funded out of the Consolidated Fund of India. Which of the statements given above is / are correct?
A. 1 and 4 only B. 2 and 4 only C. 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3 only
Answer: B
7. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2018)
1. Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
2. Once issued, the Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 2 only C. Both 1 and 2 D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
8. The Academic Bank of Credit (ABC) scheme, which was launched in ________________ 2021, aims at facilitating the academic mobility of students, giving them the freedom to study across the higher educational institutions in India with the help of a ‘credit scheme’ mechanism. (SSC CHSL 2022)
A. July B. March C. April D. June
Answer: A
9. Given below are two statements (UGC NET 2022)
Statement I: With Academic Bank of Credit facility in place, a student will be able to customize and design own degree, provided 50% of credit are from the higher education institutions awarding the degree.
Statement II: Credits once used or redeemed by a student cannot be used for any other formal purpose or course wavers.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
A. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
B. Both Statement I and Statement Il are incorrect
C. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
D. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Answer: A
Mains
1. The quality of higher education in India requires major improvements to make it internationally competitive. Do you think that the entry of foreign educational institutions would help improve the quality of technical and higher education in the country? Discuss. (UPSC 2015) 2. The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 remains inadequate in promoting incentive-based systems for children's education without generating awareness about the importance of schooling. Analyse. (UPSC 2022) |
FIVE EYES ALLIANCE
The Five Eyes is an intelligence alliance consisting of five English-speaking countries that collaborate on signals intelligence (SIGINT) and share classified intelligence with one another. The member countries of the Five Eyes alliance are:
-
United States: The United States, through its National Security Agency (NSA), plays a central role in the alliance and is responsible for significant SIGINT operations.
-
United Kingdom: The United Kingdom conducts SIGINT operations primarily through its Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ).
-
Canada: Canada's primary SIGINT agency is the Communications Security Establishment (CSE).
-
Australia: The Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) is Australia's primary SIGINT agency.
-
New Zealand: New Zealand's primary SIGINT agency is the Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB)
CAPITAL AND REVENUE EXPENDITURE
- Purchasing or upgrading machinery and equipment to improve production processes or expand manufacturing capacity.
- Acquiring or developing real property such as land, buildings, or facilities for commercial, residential, or investment purposes
- Building or maintaining infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, airports, and utilities to support economic development.
- Investing in computer systems, software, and hardware to improve business operations and technological capabilities.
- Allocating funds for research and development projects to create new products, technologies, or processes
- Acquiring other businesses or merging with them to expand market presence or diversify operations
- Upgrading or renovating existing assets or making significant repairs to extend their useful life
- Purchasing stocks or bonds of other companies or government entities as an investment
- With an intent to tap into a higher multiplier effect of capital expenditure by frontloading the spending by states, the amount has been approved for 16 states including Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Mizoram, Odisha, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and West Bengal
- The approval has been given under the scheme titled ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24’.
- The scheme, which was announced in the Budget for 2023-24 in continuation of a similar push for capex from the last three years, special assistance is being provided to the state governments in the form of 50-year interest-free loan up to an overall sum of Rs 1.3 lakh crore during the financial year 2023-24
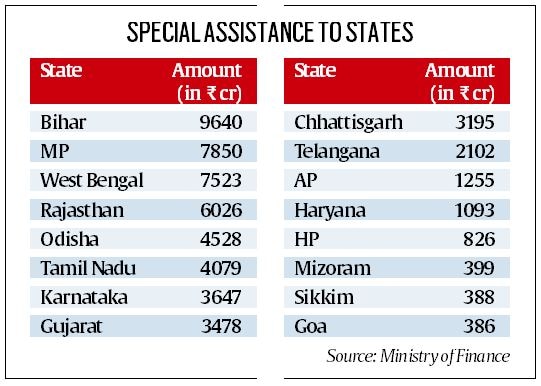
- The scheme has eight parts, Part-I being the largest with grant-like special capex facility. In this part, the amount has been allocated amongst states in proportion to their share of central taxes and duties as per the award of the 15th Finance Commission, while other parts of the scheme are either linked to reforms or are for sector-specific projects
- Capital expenditure, often abbreviated as CapEx, refers to the funds that a company or organization spends on acquiring, upgrading, or maintaining physical assets, infrastructure, or other long-term assets that are necessary for its ongoing operations or to support future growth.
- Capital expenditures are typically associated with investments in assets that have a useful life extending beyond the current accounting period. These assets are considered vital to the business and are expected to generate benefits and income over an extended period
- Capital expenditures are recorded on a company's balance sheet as assets, and their costs are typically depreciated over time.
- Depreciation is the accounting method used to allocate the cost of the asset over its estimated useful life, which helps match the expense with the revenue generated by the asset
- Revenue expenditure, often referred to as "OpEx" (Operational Expenditure), represents the day-to-day or ongoing expenses that a company incurs in the normal course of its business operations.
- These expenditures are not meant to acquire long-term assets or provide future benefits; instead, they are necessary to sustain the company's current operations and generate immediate revenue.
- Revenue expenditures are typically fully expensed on the income statement in the period in which they are incurred.
- Revenue expenditures are distinct from capital expenditures (CapEx), which involve investing in long-term assets that are expected to provide benefits over multiple accounting periods.
- While capital expenditures are capitalized and depreciated over time, revenue expenditures are fully expensed immediately.
- Properly distinguishing between these two types of expenditures is important for accurate financial reporting and tax considerations.
- Revenue expenditures are considered necessary to maintain the company's ongoing operations and are essential for generating revenue in the short term.
| Subject | Capital Expenditure | Revenue Expenditure (OpEX) |
| Purpose | CapEx involves spending on assets that provide long-term benefits and are expected to generate revenue or provide value over an extended period. These expenditures are typically investments in the business's growth and expansion, such as acquiring new assets, upgrading existing ones, or building infrastructure | OpEx includes day-to-day operating expenses that are necessary to maintain the company's current operations and generate immediate revenue. These expenses are typically recurring and are incurred to sustain the normal business activities. |
| Treatment on Financial Statements | CapEx is recorded as an asset on the balance sheet and is typically depreciated over the asset's estimated useful life. This spreads the cost of the asset over multiple accounting periods. The depreciation expense is then recognized on the income statement. | OpEx is fully expensed in the period in which it is incurred. It is recorded as an expense on the income statement, reducing the company's net income for that period |
| Tax Implications | Depending on tax regulations and the jurisdiction, capital expenditures may be eligible for tax benefits, such as depreciation deductions or investment tax credits. These tax benefits can help reduce the company's taxable income and, therefore, its tax liability | Revenue expenditures are typically fully deductible in the year they are incurred for tax purposes, which can help reduce the company's taxable income in that specific tax year |
| Long-Term vs. Short-Term Impact | CapEx has a long-term impact on a company's financial position. It represents investments in assets that are expected to provide value and benefits over an extended period, contributing to the company's growth and profitability | OpEx has a short-term impact and is necessary to maintain the company's day-to-day operations. While important for generating immediate revenue, these expenses do not typically result in long-term assets or lasting benefits. |
|
For Prelims: Capital Expenditure, Revenue Expenditure, Revenue receipts
For Mains: Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24
|
J FORM
1. Context
Recently, The Punjab Mandi Board has introduced a digital version of the 'J form,' which will be sent to farmers via WhatsApp during the Rabi procurement season, marking Punjab as the first state in India to provide digitized 'form J' in real time. This innovation aims to enhance transparency and empower farmers, benefiting around 9 lakh registered wheat farmers looking to sell their produce at Minimum Support Price (MSP) this season.
2. About the 'J Form' and Its Digitization
- The 'J form' is essentially a sale receipt for a farmer's agricultural produce in grain markets or mandis.
- Previously, these forms were manually issued by commission agents known as arthiyas, who play a vital role in the sale of crops in Punjab.
- This form also serves as income proof for farmers when they sell their crops. Before digitization, many arhtiyas held onto these forms, denying farmers their right to a record of their income from crop sales.
- The digitized 'J form' now provides farmers with a clear record of their sales and income, eliminating the need to chase arhtiyas for copies.
- These digital forms are promptly delivered to a farmer's WhatsApp number once a sale is confirmed in the system by arthiyas and government procurement agencies.
3. The Digital J Form's Benefits for Farmers
The digital 'J form' offers a multitude of advantages for farmers, such as:
- It can be used to secure loans from financial institutions and claim IT waivers and subsidies.
- Farmers can use the form for insurance purposes.
- For farmers with children studying abroad, the form serves as income proof for educational institutes, like the Canadian embassy.
- It ensures that farmers do not hide their income, addressing issues where some farmers might misuse the funds for non-essential purposes like purchasing liquor.
4. Ensuring Authenticity and Preventing Theft
- To enhance authenticity, the digital J forms will be equipped with a QR code, watermark, and a unique number.
- This ensures not only a farmer-friendly service but also safeguards the interests of their families and the government.
- The digital 'J form' discourages the theft of grains by some arhtiyas and discourages landowners from falsely claiming farming income to evade income tax payments.
5. The Transition to Digital
- The Punjab Mandi Board initiated the move to digitize the 'J form' in response to farmers' complaints about lack of access to authentic forms.
- The process took two years to complete. Initially, farmers' accounts were linked to their Aadhaar card numbers in the Anaj Kharif portal, designed for direct payment transfer to farmers.
- Subsequently, land records for both landowners and cultivators were recorded. In the previous paddy procurement season, J forms were made available through the Digilocker system.
- For this wheat procurement season, the forms have been integrated with farmers' WhatsApp numbers.
6. Government Gains from Digital 'J Forms'
- The government stands to benefit significantly from this digital initiative. It will have a comprehensive record of the land under cultivation for both wheat and paddy crops, aiding in assessing the average per-acre yield.
- This data can enable the government to aim for precision, eventually extending the use of 'J forms' to cover other crops not procured by the government.
- Additionally, it can help monitor the sale of crops from other states in Punjab mandis, as the government will have detailed information on total land and production.
7. Preventing Cross-State Crop Sale
- The digital 'J form' system can effectively curb the sale of crops from other states in Punjab's mandis.
- By providing accurate data on cultivated land and yield, the government can identify and investigate unusual procurements or fraudulent transactions.
- The state has also introduced a vehicle tracking system to monitor the influx of grains into Punjab's mandis from other states, reinforcing control over cross-border crop sales.
8. Conclusion
The digitisation of form J is a farmer-friendly move that will help farmers keep a record of their income, get access to finance and other benefits, and stop the theft of grains and evasion of Income Tax payments. The government will also benefit from the system by having a proper record of land under cultivation and the total yield of wheat and paddy crops.
|
For Prelims: J-Forms, Punjab Mandi Board, Minimum Support Price, Rabi Crops, Wheat, Paddy, Digilocker,
For Mains:
1. Critically examine the role of technology in transforming the agricultural sector in India. (250 words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2020)
1. In the case of all cereals, pulses, and oil seeds, the procurement at Minimum Support Price (MSP) is unlimited in any State/UT of India.
2. In the case of cereals and pulses, the MSP is fixed in any State/UT at a level to which the market price will never rise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
2. Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past? (UPSC CSE, 2020)
(1) Minimum Support Price (2) Government’s trading (3) Government’s stockpiling (4) Consumer subsidies Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 4 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 Answer: D
3. In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? (UPSC GS1, 2020)
(1) Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops (2) Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (3) Social Capital development (4) Free electricity supply to farmers (5) Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system (6) Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments. In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 5 only (b) 1, 3, 4 and 5 only (c) 2, 3 and 6 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 Answer: C
4. The Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane is approved by the (UPSC CSE, 2015)
(a) Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (b) Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (c) Directorate of Marketing and Inspection, Ministry of Agriculture (d) Agricultural Produce Market Committee Answer: A
5. Consider the following crops: (UPSC 2013)
1. Cotton
2. Groundnut
3. Rice
4. Wheat
Which of these are Kharif crops?
A. 1 and 4
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 2, 3 and 4
Answer: C
6. "System of Rice Intensification" of cultivation, in which alternate wetting and drying of rice fields is practised, results in: (UPSC 2022)
1. Reduced seed requirement
2. Reduced methane production
3. Reduced electricity consumption
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only B. 2 and 3 only C. 1 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
|
IMPACT OF SOCIAL MEDIA
1.Context:
Dozens of US states have sued Instagram and Facebook’s parent company Meta, accusing the tech giant of contributing to the youth mental health crisis through the addictive nature of its social media platforms.
 PC: Searchenginejournal
PC: Searchenginejournal
2.Case study:
- One cannot deny that Social media has become a daily habit, especially among youth.
- Individuals across different age groups use social media platforms for communication & networking.
- There is a growing dependency on social media.
- Constant use of social media leads to many problems like-
- Changes in behavioural pattern
- Exposure to risky content
- Cyber-bullying
- Inferiority complex, resulting in grave mental health challenges & illness.
3.Issue:
Impact of social media on youth. It is imperative to address the current challenges to regulating social media use, especially among the young generation.
There can be many problems which can be highlighted, but let us focus on three of them-
- According to UNICEF, 1 in 7 Indians aged 15-24 years feel depressed.
- Depression is linked to lack of self-esteem, poor concentration & other maladaptive symptoms and can lead to difficulties in communication, failure to work or study productively, amplified risk of substance use & abuse, as well as suicidal thoughts.
- One of the key risk factors for this depression is social media.
- As social beings, humans inherently need social acceptance & social media often becomes a tool for validation.
- The number of likes one’s posts or images garners becomes a quantitative measure for many, about their looks, and intelligence and even extends to their worth as a person.
- Individuals strive to maintain an “internet persona” which paints a rosy picture of one’s life, using filters to hide parts considered” not enough good”.
- Body Dysmorphia- It is common among young people & increased over the past few years.
- Use of algorithms on these platforms forces people to only watch similar content.
Excessive social media use takes time away from doing other things that may benefit our mental health like connecting with others in person, spending time in nature and taking care of ourselves.
4.Solutions
- Action must be taken on mental health seriously & monitor the incidence of psychiatric disorders like depression, and anxiety and identify the factors of risk & resilience.
- Need to focus on socialization in familiar places & professional spaces along with physical exercises and meditation. Getting closer to nature and natural things is necessary.
- Need of creating awareness & dialogue that would help in de-stigmatizing the issue, to allow autonomy for the individual to share feelings in a safe space.
- To address the structural challenges, there is a need to reimagine the workspace & educational framework. Social media dependence in such spaces can be reduced to an extent that it doesn’t become addictive.
- Support systems like family & peers, need to be equipped with understanding the factors related to the issue & initiate supportive steps.
- Family and teachers are seen as role models. Restricting them from social media will inspire youth.
- Pragmatic government policies based on empirical evidence, strong political will, social inclusion, mental health literacy, vibrant media and a responsive corporate sector coupled with innovative technologies & crowdsourcing could mitigate this apathy.
5.Mental Health Issue
- Mental illness is an amalgamation of biological, social, psychological, hereditary and environmental stressors.
- The WHO defines mental health as a state of well-being, where an individual realizes their capabilities, can cope with the normal stress of life, work productively and can contribute to their community.
- According to recent research, there is an estimated increase of about 35% in the prevalence of anxiety & depression in India during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- As per the National Mental Survey, 2016, the prevalence of mental disorders in the age group 13-17 years was 7.3%. The most common prevalent problems were Depressive Episodes & Recurrent Depressive Disorder(2.6%), Agoraphobia(2.3%), Intellectual Disability(1.7%), Autism Spectrum Disorder(1.6%), phobic anxiety disorder(1.3%) and Psychotic disorder(1.3%).
- As per WHO, for 1lakh population India has 0.3 psychiatrists, 0.12 nurses & 0.007 psychologists & 0.007 health workers. These reflect an alarming shortage of Human Resources & a dire need to scale up investments to address the issue.
- Though Mental Health Act 2017 granted patients the legal right to live with dignity without discrimination, coercion, or harassment, the endeavour in this segment is too scattered & lacks focus & coordination.
- It should be noted that this act envisages the establishment of the Central Mental Health Authority & State Mental Health Authority.
- The Union Budget 2022-23, took the consideration the issue of mental health & announced the National Tele-Mental Health Program in India.
- An efficient & robust community-integrated model will have the ability to build a response system of cadres of community volunteers & leaders to create ‘safe spaces. They would build upon locally established peer support networks like Self-help Groups(SHGs), activity-based groups and civil society organizations to provide care.
- It is important that any community-based mental health program provides access to institutional social care benefits by building strategic partnerships with local governments, panchayats, educational institutions & other stakeholders to enable referrals & access to existing social benefit schemes.
- Prioritizing availability of essential psychotropic drugs at all levels of healthcare.
- The theme of World Mental Health Day 2022, 10th October is ‘Make mental health & well-being for all a global priority.
- In 1982, the Indian government launched the National Mental Health Program(NMHP) to improve the status of mental health in India. It has three components treatment of the mentally ill, rehabilitation, prevention & promotion of positive mental health.
- WHO’s Comprehensive Mental Action Plan 2013-2020 was adopted by the 66th World Health Assembly. The Mental Health Atlas was launched by WHO in 2017.
- The Sustainable Development Goals target 3.4 & 3.5 talks about reducing mental illness.
- The Supreme Court held healthcare to be a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution.
| Along the lines of community participation, awareness campaigns can reduce the issue of mental health. |
|
Previous Year Questions 1.Child cuddling is now being replaced by mobile phones. Discuss its impact on the socialization of children. (UPSC CSE GS1, 2023) |
Source: indianexpress




