DAM SAFETY ACT
"The legislation created the National Dam Safety Authority, which has the following key responsibilities:
- Setting and upholding dam safety standards
- Mitigating the risk of dam-related disasters
- Resolving inter-State dam concerns
- Overseeing surveillance, inspection, operation, and maintenance of dams
- Maintaining and organizing dam-related records
- Establishing Hydrology units and reviewing Design Floods
- Monitoring the safety aspects of inter-State dams through Sub-Committees."
- The National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) is a regulatory body established by the government of India to oversee and regulate the safety of dams in the country. Its primary purpose is to ensure the safety and stability of dams, with a focus on preventing dam failures and the potential disasters they can cause.
- The NDSA plays a crucial role in setting and maintaining dam safety standards, preventing dam-related disasters, addressing inter-State concerns related to dams, and overseeing various aspects of dam safety, including surveillance, inspection, operation, and maintenance.
- It also has responsibilities related to the upkeep and archival of dam-related records, the establishment of Hydrology units, and the review of Design Floods.
- The NDSA is instrumental in monitoring the safety aspects of inter-State dams through its Sub-Committees.
- Its establishment is part of India's efforts to enhance dam safety and protect lives, property, and the environment.
-
Regulation and Supervision: States are frequently tasked with the creation and enforcement of laws and regulations pertaining to dam safety. This encompasses the establishment and upkeep of criteria for dam construction, operation, and maintenance.
-
Permitting and Licensing: States might mandate permits and licenses for dam construction and operation. These authorizations are designed to ensure that dams adhere to safety standards and environmental requirements.
-
Examination and Upkeep: Typically, states oversee regular assessments of dams to evaluate their condition and confirm that they are being appropriately preserved. Dam proprietors are frequently obligated to provide regular inspection reports.
-
Emergency Response Plans: States may insist that dam owners develop and submit emergency action plans (EAPs). These plans detail the procedures to be followed in the event of potential dam failures or other emergencies. EAPs are crucial for safeguarding communities downstream.
-
Monitoring and Surveillance: States can require the installation of monitoring equipment to continuously assess the performance of dams. Data collected from these instruments aids in the early identification of potential issues and facilitates prompt intervention.
- The DSA does not promote risk-based decision-making and fails to incentivise transparency
- The frequency and scale of such disasters reveal a pattern of neglect: “It keeps happening regularly, people face disastrous consequences and we call these ‘natural disasters’. But there’s nothing natural about them.”
- A robust DSA should allow different stakeholders to access information easily, but India’s framework falls short.
“Dam safety is a public purpose function. Everything about dam safety, functions of all the institutions and committees and authorities, their reports, decisions minutes and agendas, everything should be promptly available to the public,” - Transparency is further obstructed when national and State bodies comprise government employees and engineers who worked on these projects, compromising objective decision making and lacking “people with a proven track record of taking independent decisions.”
Dam safety is undertaken through a combination of regulatory measures, engineering practices, inspections, maintenance, and emergency preparedness. Here is an overview of how dam safety is typically managed:
-
Regulation and Legislation: Dam safety often begins with the establishment of laws and regulations at the national, state, or local level. These regulations set forth the standards and requirements for dam construction, operation, and maintenance. They may also address issues related to licensing, permitting, and emergency preparedness.
-
Design and Construction: The safety of a dam begins with its design and construction. Engineers and geologists play a critical role in ensuring that dams are designed to withstand expected loads and environmental conditions. Proper materials, construction techniques, and quality control are essential.
-
Inspections and Monitoring: Routine inspections are conducted to assess the condition of dams. These inspections may be performed by dam owners, regulatory agencies, or independent experts. Monitoring equipment, such as sensors and gauges, is often installed to continuously collect data on dam performance.
-
Maintenance and Repairs: Maintenance is crucial to dam safety. Regular upkeep includes tasks such as vegetation control, spillway clearing, and embankment repairs. If issues are identified during inspections, they must be addressed promptly to prevent potential failures.
-
Emergency Action Plans (EAPs): Dam owners are typically required to develop and maintain Emergency Action Plans (EAPs). These plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a dam failure or other emergencies. They are essential for protecting downstream communities.
-
Risk Assessments: Periodic risk assessments are conducted to evaluate the potential risks associated with a dam. These assessments consider factors such as downstream population, the condition of the dam, and the consequences of failure.
-
Community Awareness: Educating and informing communities downstream from dams about potential risks and emergency procedures is essential. Public awareness campaigns can help ensure that people are prepared in case of a dam-related emergency.
Provisions require States to classify dams based on hazard risk, conduct regular inspections, create emergency action plans, institute emergency flood warning systems, and undertake safety reviews and period risk assessment studies.
VISA SHOPPING
1. Context
2. About Visa Shopping
Visa shopping, a growing trend in several Indian states, especially Punjab, is when individuals acquire visas for countries they may not visit during the visa's validity period. This practice is primarily to gain easier entry into their preferred countries, notably in Europe, even if they already hold a visa for a different European nation.
3. Reasons for Visa Shopping
People engage in visa shopping for various reasons:
- Some individuals purchase visas for countries they have no immediate plans to visit, aiming to boost their chances of obtaining visas for their preferred countries in the future. This is because visa applications can be time-consuming and have the risk of rejection, and visas often remain valid for several years.
- The Schengen Visa, a prominent example, allows travellers to explore multiple European countries without obtaining separate visas. This visa simplifies travel within the Schengen Area, comprising more than 24 European nations, as travellers can move freely without border controls.
4. The Schengen Visa
The Schengen Visa, widely used in visa shopping, offers a valuable advantage for travellers:
- By obtaining a Schengen Visa from a country with a more straightforward application process, travellers can explore multiple Schengen region countries without the need for individual visas.
- Punjab travel agencies have cited instances where travellers obtained a Schengen Visa from one country when their direct visa application for another Schengen nation was rejected.
- For instance, a rejected Spanish visa application led to entry through a different Schengen country. Similarly, a student initially denied a German visa, secured a Luxembourg visa to travel to Germany.
- Some individuals also engage in visa shopping to enter countries with favourable employment prospects, such as Portugal. Local agents assist in obtaining work visas and facilitating settlement in these countries.
5. Legal Implications of Visa Shopping
- Visa shopping is not inherently illegal, provided travellers adhere to the visa application procedures and acquire valid permission to stay in the country of entry.
- Legal concerns arise when individuals apply for a visa for one country but intend to stay in another or use it solely as an entry point.
- The Embassy of Estonia in New Delhi issued a statement cautioning against visa shopping. It emphasized that, according to Schengen Visa rules, travellers should apply for a visa from the country where they plan to spend the most time.
- The embassy warned that embassies conduct thorough checks of travel plans, and severe consequences, including visa refusal and potential offloading from flights or return home, may follow if travellers engage in visa shopping repeatedly.
- Repetitive visa shopping may arouse suspicion among immigration officials.
- Some countries may object at the airport if a person's visa is for one European nation but intends to enter another.
6. Conclusion
Visa shopping is a practice that offers flexibility in travel, but travellers must carefully adhere to visa rules and intentions to avoid legal complications and possible entry issues.
|
For Prelims: Visa Shopping, Schengen Visa
For Mains:
|
BAT GENOMES
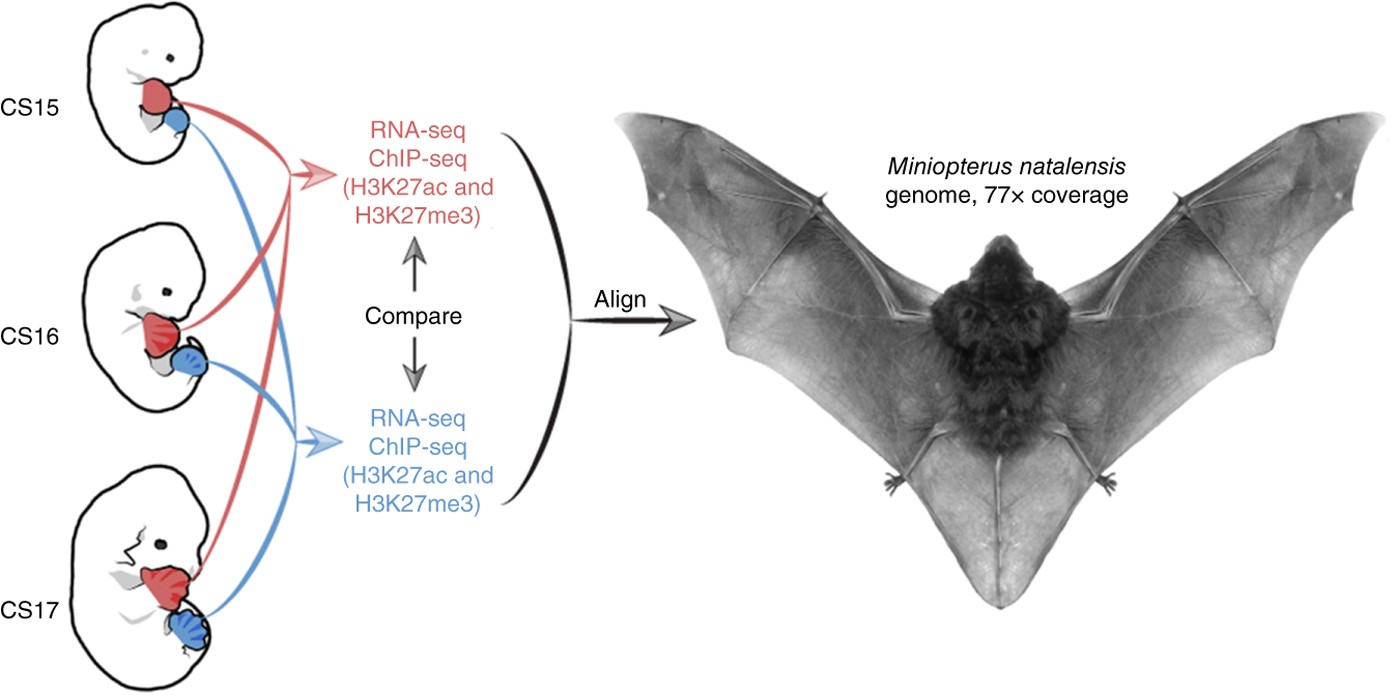
- Bats typically have large and complex genomes. The genome size varies among different bat species, but many have genomes that are relatively large compared to other mammals.
- Bats are one of the most genetically diverse groups of mammals. This diversity allows them to adapt to a wide range of ecological niches, from fruit-feeding bats to insect-eating bats
- Bats have undergone specific genetic adaptations to support their unique ability to fly. This includes changes in genes related to wing development, muscle structure, and energy metabolism
- Bats are known for their use of echolocation, a system of using sound waves to navigate and locate prey. Genes associated with echolocation have been of particular interest in bat genomics
- Comparative genomics studies have been conducted to compare bat genomes with those of other mammals. These studies have provided insights into the genetic basis of various traits, such as flight, echolocation, and longevity
- Bats have also been the focus of genomic research related to disease transmission. They are reservoir hosts for several viruses, including coronaviruses, and understanding their genomes can help in disease prevention and management.
- Immunity-related genes have been one of the more well-studied gene classes in bats. The fraction of these genes is also unique in bats: some 2.7-3.5% of the bat genome versus roughly 7% of the human genome.
- Emerging evidence also suggests that a set of immune-related genes have been undergoing positive selection in bats, adapting them to control the spread of viruses while mitigating the antiviral inflammatory response
- One of the first Bat1K genome consortium papers described six high-quality bat species genomes in the journal Nature.
- It suggested that echolocation, loss of pro-inflammatory genes, and expansion of antiviral genes are ancestral traits of bats. This suggests that bats have molecular mechanisms that allow them to host a range of deadly viruses but evade clinical disease.
- Long-read sequencing technologies are those that can ‘read’ thousands to tens of thousands of bases of a genome at a time
- It has become possible today for scientists to quickly assemble the nearly complete whole genomes of organisms. Another benefit to them is that they no longer had to use more complex, time-consuming, and expensive molecular technologies in the pursuit of building complete genomes
- The researchers reported that subsets of genes involved in mounting an immune response – which encode proteins called interferons (IFN) – had contracted significantly. This in turn changed the relative proportions of two subsets, interferon-alpha (IFN-α) and interferon-omega (IFN-ω), relative to each other.
- The researchers attributed bats’
immune properties to these changes. By shedding the genes for IFN-α, bats can dampen the pro-inflammatoryresponse against a number of viruses, thus protecting themselves from clinical disease.
violating the balances of nature
BEDOUIN ARABS
1. Context
Since the October 7 Hamas assault that brought Israel and Gaza into a period of heightened violence, at least four Bedouin soldiers have been among the casualties on the Israeli side.
2. About Bedouins
The Bedouins are nomadic Muslim Arab people primarily residing in the Negev desert of southern Israel. Historically, they were pastoralists with no strong national affiliations, roaming the region between Saudi Arabia and the Sinai with their livestock.
3. Historical Integration into the Israel Defence Forces (IDF)
- Before the establishment of Israel, Bedouin groups were employed by early Jewish settlers to protect their communities in Palestine.
- During the Arab-Israeli war of 1948-49, many Bedouins provided valuable intelligence to Jewish militias and the newly formed IDF. Some even fought alongside Jewish forces against the Arab armies.
- In the 1950s, Israel recognized a significant number of Bedouins as its citizens and initiated the construction of settlements for them in the Negev.
- Many Bedouins continued to serve in the IDF, often in scouting or tracking units.
- In 1970, a Bedouin scouting unit was established in the IDF's Southern Command, and similar units emerged in other regions.
- In 1986, a desert-scouting unit was stationed near the Gaza Strip.
- The IDF, in 2003, established specialized search and rescue units mainly composed of Bedouin members to serve in border areas.
- Furthermore, Israel inaugurated a memorial in 1993 to honour Bedouin warriors, featuring the names of 154 Bedouin soldiers who sacrificed their lives for the country.
- The "Garden of the Broken Heart" is dedicated to Bedouin soldiers whose burial locations are unknown.
4. Voluntary Service
- It's essential to note that army training is not compulsory for the Bedouin population in Israel; it is mandatory only for the Jewish population.
- However, many Bedouin youths voluntarily choose to enlist in the IDF, with some coming from families with a tradition of serving in the defence forces.
- In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the number of Bedouin volunteers.
5. Integration in Israeli Society
- Bedouin soldiers, particularly those serving in desert reconnaissance units, often hail from the northern regions of Israel.
- In communities like Shibli, Bedouins have coexisted with Jewish and Arab communities since the 1950s.
- Some Bedouin soldiers who underwent army conscription reported gaining an appreciation for aspects of Jewish culture, despite initial language barriers.
- The Bedouin population in Israel currently numbers around 210,000 individuals, residing in various regions of the state, with a significant presence in the Negev desert.
6. Initiatives for Integration
- Israel has taken steps to promote the integration of Bedouin communities into society.
- In 2020, Ishmael Khaldi became Israel's first Bedouin ambassador. Additionally, the first Bedouin high-tech company in Israel, Sadel Technologies, was co-founded by Ibrahim Sana, a Bedouin entrepreneur, and his partners.
- In November 2022, the Israeli government launched Operation Negev Shield, aiming to facilitate Bedouin community integration through educational programs, especially focusing on steering young men away from criminal activities.
- IDF officers also regularly visit schools in various Bedouin communities to educate children about various aspects of Israeli society.
|
For Prelims: Israel Defence Forces, Bedouin, Operation Negev Shield, Garden of the Broken Heart, Gaza Strip, Arab-Israeli war,
For Mains:
1. Discuss the historical role of Bedouin soldiers within the Israel Defence Forces (IDF). How did their integration into the IDF evolve over the years, and what contributions have they made during times of conflict? (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Recently Iran has clinched a deal with six world powers to curb nuclear activities. Which one among the following is not a party to it? (UPSC CAPF 2014)
A. USA B. France C. Russia D. Japan
Answer: D
2. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (UPSC 2015)
(a) Syria (b) Jordan (c) Lebanon (d) Israel Answer: B 3. Match List - I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists: (UPPSC BEO 2020) List - I (Tribes) List - II (Area)
A. Khirghiz 1. Japan
B. Bushman 2. Arab
C. Ainu 3. Central Asia
D. Bedouin 4. Kalahari
1. A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
2. A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
3. A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
4. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
Answer: 3
4. The term "two-state solution" is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (UPSC CSE 2018)
A. China B. Israel C. Iraq D. Yemen
Answer: B
5. The area known as ‘Golan Heights’ sometimes appears in the news in the context of the events related to (UPSC 2015) (a) Central Asia (b) Middle East (c) South-East Asia (d) Central Africa Answer: B 6. Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries? (2017)
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 3 and 4 only Answer: C 7. Yom Kippur War was fought between which sides/ countries? (2008) (a) Turkey and Greece Answer: C Mains1. ‘Too little cash, too much politics, leaves UNESCO fighting for life.’ Discuss the statement in the light of US’ withdrawal and its accusation of the cultural body as being ‘anti-Israel bias’. (UPSC 2019)
2 . “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (UPSC 2018)
|
SIKKIM FLOODS AFFECTING HYDEL PROJECTS
1. Context
Recently, a sudden surge in the Teesta River caused catastrophic floods in Sikkim, resulting in loss of life, destruction of infrastructure, and widespread displacement.
2. The Trigger of the Sikkim Floods
The floods in the Teesta River, affecting both Sikkim and West Bengal, were primarily triggered by Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), a phenomenon involving the sudden release of water from glacial lakes fed by glacier melt. Satellite imagery suggests that a significant ice chunk may have fallen into a lake, leading to the toppling of a moraine dam and subsequent flash floods downstream in the Teesta.

3. Risks Associated with Glacial Lakes
- South Lhonak Lake has been closely monitored for GLOFs, recent satellite images indicate that the risk persists.
- Although it was initially believed that the lake had partially drained, the presence of water beneath the ice suggests that the risk is not fully mitigated.
- The catastrophic floods resulted in the collapse of the 1,200 MW Teesta Stage III hydropower project at Chungthang village in north Sikkim.
- The Sikkim government, environmentalists, and scientists raised concerns about the project's approval process and the discrepancy between the proposed concrete gravity dam and the actual rock-filled dam.
- This incident, along with the effects of the floods, has halted the operation of all hydel power projects on the Teesta River in Sikkim.
- The National Hydel Power Corporation (NHPC) reported losses of ₹233.56 crore, and electricity generation from hydel power projects in Sikkim ceased.
- Additionally, the Dikchu Hydroelectric Project (96 MW) was impacted by the entry of flood debris.
4. The Extent of Damage and Future Considerations
- The Sikkim government has not yet quantified the monetary extent of the damage, but it is expected to be substantial.
- The floods have raised concerns among activists and scientists, prompting calls for a reconsideration of proposed hydel power projects.
- Union Minister for Power and Renewable Energy R. K Singh, however, emphasized that the floods will not deter India's reliance on hydropower.
- India has a significant number of operational and proposed hydroelectricity projects (HEPs) across the Himalayan belt.
- In Sikkim alone, several projects are under development. In response to the recent tragedy, calls for a review of proposed projects and inquiries into the construction of existing projects have gained momentum.
- The government's decision to direct the State's Vigilance Police to conduct a comprehensive inquiry into any criminal irregularities in the construction of the Teesta III dam project and transfer the case to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) signals an effort to address accountability in the aftermath of the floods.
- Gyatso Lepcha, general secretary of the Affected Citizens of Teesta (ACT), an organisation campaigning against HEPs on the Teesta said in the aftermath of the tragedy, the government should scrap the proposed Teesta IV project and review the upcoming Teesta VI project.
- The Sikkim government directed the State’s Vigilance Police to conduct a comprehensive inquiry into any criminal irregularities in the construction of the Teesta III dam project, submit a report and transfer the case to the CBI.
|
For Prelims: Teesta River, Glacial Lake Outburst Floods, Sikkim, Central Bureau of Investigation, Himalayan belt, National Hydel Power Corporation,
For Mains:
1. Examine the risks associated with glacial lakes and their potential for causing Glacial Lake Outburst Floods. How does the monitoring and mitigation of these risks impact regions and what are the challenges in ensuring safety? (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
Prelims
1. On the planet earth, most of the freshwater exists as ice caps and glaciers. Out of the remaining freshwater, the largest proportion (UPSC CSE 2013) (a) is found in the atmosphere as moisture and clouds (b) is found in freshwater lakes and rivers (c) exists as groundwater (d) exists as soil moisture Answer: C 2. Consider the following pairs: (UPSC CSE 2019) Glacier River 1. Bandarpunch Yamuna 2. Bara Shigri Chenab 3. Milam Mandakini 4. Siachen Nubra 5. Zemu Manas Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched? A. 1, 2 and 4 B. 1, 3 and 4 C. 2 and 5 D. 3 and 5 Answer: A 3. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (UPSC CSE 2020) A. East of Aksai Chin
B. East of Leh
C. North of Gilgit
D. North of Nubra Valley
Answer: D 4. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2017) 1. The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
2. River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
3. River Teesta flows into the Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only B. 2 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B 5. Teesta river is the tributary of _______. (Kerala PSC 2018) A. Ganga B. Yamuna C. Brahmaputra D. Narmada Answer: C 6. Consider the following features related to a glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF): (UGC NET Paper-2 Geography 2019) a. Involves sudden release of meltwater
b. Failure of moraine and ice dam
c. Large downstream discharge causing floods
d. Rapid event casting for few seconds
Select the correct answer from the options given below: A. (a) and (b) are correct
B. (c) and (d) are correct
C. (a), (b) and (c) are correct
D. (b), (c) and (d) are correct
Answer: C 7. "Central Bureau of Intelligence and Investigation" is listed in the __________ list given in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India. (SSC CGL 2017) A. Union B. State C. Global D. Concurrent Answer: A Mains 1. Dam failures are always catastrophic, especially on the downstream side, resulting in a colossal loss of life and property. Analyze the various causes of dam failures. Give two examples of large dam failures. (UPSC 2023) |




