SUPERCONDUCTIVITY
1. Context
Two South Korean researchers posted two related papers on the internet, not yet peer-reviewed, claiming that a lead-based compound they had developed had shown superconducting properties at room temperature, under normal pressure conditions
2. SuperConductivity
- Superconductivity refers to a state in which a material offers zero, or near-zero, resistance to electric current.
- A current is nothing but the movement of charged particles, electrons in most cases, in a particular direction.
- When the electrons move, they collide, and interact, with other atoms in the material
- Elimination of this resistance can result in super-efficient electrical appliances, removal of transmission losses in power cables, and massive gains in energy
- Superconducting materials show very interesting behaviour under magnetic field which allows the functioning of systems like the MRI scan machine and the superfast Maglev trains that float above the tracks.
- Superconductors have very critical uses in a wide variety of other scenarios as well
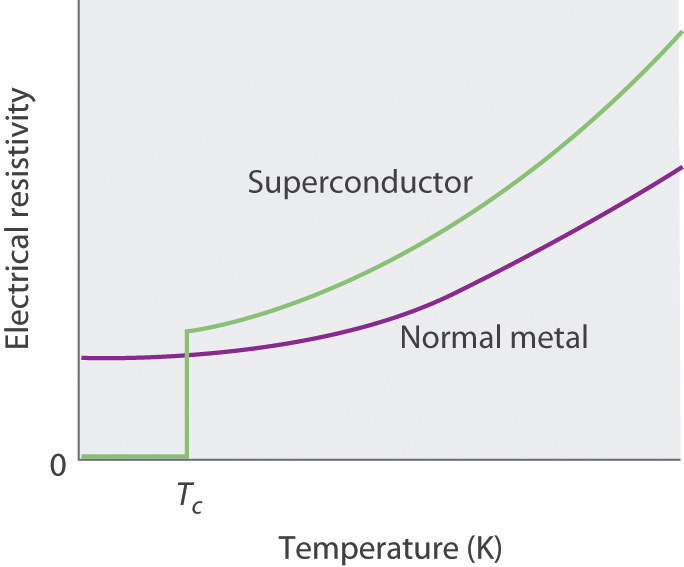
3. Temperature vs Superconductivity
- As of now, superconductivity can be achieved only at very low temperatures, more than 250 degree Celsius below zero, very close to absolute zero which is – 273 degree Celsius.
- The first material to have been discovered to show super conductive properties was Mercury, which becomes a superconductor at close to 270 degree Celsius below zero
- Most of the other materials commonly used as superconductors – Lead, Aluminum, Tin, Niobium, and several others – also become superconducting at comparable temperatures, called critical temperature
- In some cases, materials can exhibit superconductivity at slightly higher temperatures as well, but under increased pressure conditions
- It is all about creating the right kind of conditions for the electrons in the material to move without resistance, and a variety of tweaks are experimented with depending upon the internal atomic structure of the material.
- Even the materials that are classified as ‘high-temperature’ superconductors, as of now, show superconductive properties only well below -150 degrees Celsius
- There have been claims for superconductivity at much higher temperatures, in some cases, above zero degree Celsius as well, but these are either contested or require extreme pressure conditions
4. Advantages of Superconducters
Superconductors are materials that conduct electricity with zero resistance. This means that no energy is lost when electricity flows through a superconductor, which has a number of potential advantages.
4.1.Efficiency: Superconductors can be used to create more efficient electrical devices. For example, superconducting wires can be used to transmit electricity over long distances with little loss of power. This could lead to lower energy bills for consumers and businesses
4.2.Speed: Superconductors can also be used to create faster electronic devices. This is because superconductors can carry more current than traditional conductors, which allows them to operate at higher frequencies. This could lead to faster computers, telecommunications devices, and other electronic equipment
4.3.Sensitivity: Superconductors can also be used to create more sensitive devices. This is because superconductors can detect very small changes in magnetic fields. This could lead to new medical imaging devices, navigation systems, and other sensitive equipment
4.4.Magnetic fields: Superconductors can be used to create powerful magnetic fields. This is because superconducting magnets can carry more current than traditional magnets, which allows them to generate stronger fields. This could lead to new applications in medical imaging, particle accelerators, and other fields.
5. Way forward
he potential advantages of superconductors are significant, but there are also some challenges that need to be addressed before they can be widely used. One challenge is the need to cool superconductors to very low temperatures. This can be expensive and complex. Another challenge is that superconductors are often brittle and difficult to work with
|
For Prelims: Conductors, Insulators, Conductivity, Electrons
For Mains: 1.Discuss the significance of superconductors in modern technology and their potential applications in various sectors like energy, transportation, and medicine. What challenges need to be overcome to realize their full potential?
2.Explain the principles of superconductivity and the factors that influence the critical temperature of superconducting materials. Discuss the different types of superconductors and their unique properties
|
Source: indianexpress




