CRIMEAN CONGO HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER (CCHF)
1. Context
According to the WHO, “Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral haemorrhagic fever usually transmitted by ticks
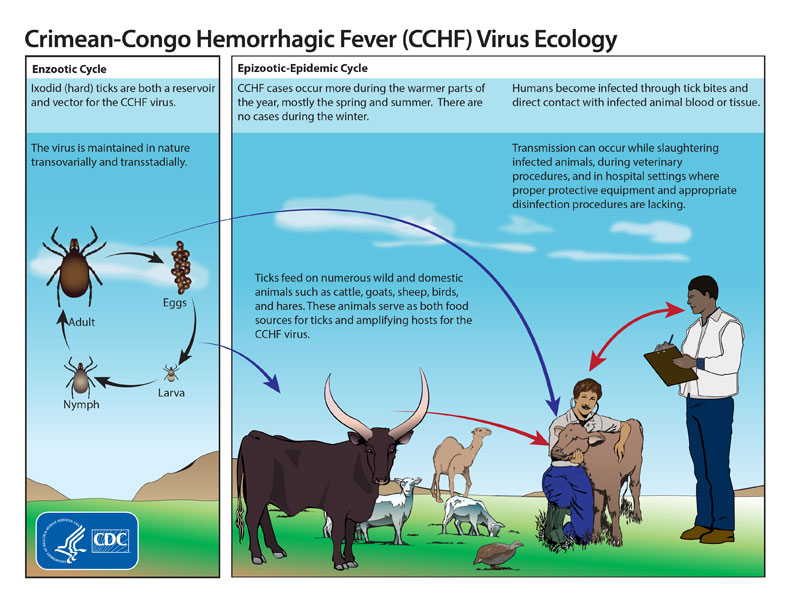
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), animals such as cattle, goats, sheep and hares “serve as amplifying hosts for the virus.
2. About Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF)
- Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a severe viral disease that affects both animals and humans.
- It is caused by the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), which belongs to the Nairovirus genus in the Bunyaviridae family.
- The disease is primarily transmitted to humans through ticks, but it can also spread through contact with infected animal blood or tissues during slaughter or while caring for sick animals.
- Transmission to humans can occur through tick bites or through contact with infected animals, particularly livestock such as cattle, sheep, and goats.
- The virus is also capable of human-to-human transmission through contact with blood or other bodily fluids of infected individuals, making it a potential source of nosocomial outbreaks in healthcare settings
3. Transmission
- According to the WHO, “Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral haemorrhagic fever usually transmitted by ticks
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues (animal tissue where the virus has entered the bloodstream) during and immediately post-slaughter of animals.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), animals such as cattle, goats, sheep and hares “serve as amplifying hosts for the virus
- Transmission to humans occurs through contact with infected ticks or animal blood. CCHF can be transmitted from one infected human to another by contact with infectious blood or body fluids”, such as sweat and saliva
- The ticks can also be hosted by migratory birds, thus carrying the virus over long distances
4. History
- While the disease was first detected among soldiers in the Crimean Peninsula (near the Black Sea) in 1944, in 1969, it was found that an ailment identified in the Congo Basin was caused by the same pathogen. Thus, the disease was named the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever
- CCHF is found in various countries in Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and some regions of Europe.
- The disease is considered a zoonosis, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans, and outbreaks often coincide with the tick season.
- Preventive measures include avoiding tick bites, wearing protective clothing in areas where ticks are prevalent, and taking precautions when handling or caring for animals
Source: indianexpress




