MEITEI TRIBE
1. Context
2. About Manipur's ethnic composition
- Geography has a lot to do with Manipur's problems. Four highways, two of them lifelines for the State, are the valley's access points to the world beyond.
- The valley, which comprises about 10 per cent of Manipur's landmass, is dominated by the nontribal Meitei who account for more than 64 per cent of the population of the State and yields 40 of the State's 60 MLAs.
- The hills comprising 90 per cent of the geographical area are inhabited by more than 35 per cent recognised tribes but send only 20 MLAs to the Assembly.
- While a majority of the Meities are Hindus followed by Muslims, the 33 recognised tribes, broadly classified into "Any Naga Tribes" and Any Kuki Tribes" are largely Christians.
3. Meitei's arguments
- Hearing a petition by eight people representing the Meeti (Meitei) Tribe Union, the Manipur High Court directed the State government to submit, within four weeks, a 10-year-old recommendation to the Union Tribal Affairs Ministry for the inclusion of the Meitei community in the ST list.
- The court referred to the Ministry's letter in May 2013 to the Manipur government seeking specific recommendations along with the latest socioeconomic survey and ethnographic report.
- The letter followed a representation submitted by the Scheduled Tribe Demand Committee of Manipur (STDCM), which began demanding ST status for the Meiteis in 2012.
- The petitioners told the High Court that the Meiteis were recognised as a tribe before the merger of the State with the Union of India in 1949.
- They argued that the ST status is needed to "preserve" the community and "save the ancestral land, tradition, culture and language" of the Meities.
- The STDCM also said the Meiteis needed constitutional safeguards against outsiders, stating that the community has been kept away from the hills while the tribal people can buy land in the "shrinking" Imphal Valley.
4. Reasons for the tribal groups against ST status for Meiteis
- The tribal groups say the Meiteis have a demographic and political advantage besides being more advanced than them academically and in other aspects.
- They feel the ST status to the Meiteis would lead to loss of job opportunities and allow them to acquire land in the hills and push the tribals out.
- Groups such as the All Tribal Students Union of Manipur point out that the language of the Meitei people is included in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution and many of them have access to benefits associated with the SC, OBC or EWS status.
- To the hill tribal people of Manipur, the demand for ST status is a ploy to attenuate the fervent political demands of the Kukis and Nagas as well as a tacit strategy of the dominant valley dwellers to make inroads into the hill areas of the State.
5. Factors that led to the unrest
- Pro-government groups in Manipur claim some tribal groups with vested interests are trying to scuttle Chief Minister Nongthombam Biren Singh's crusade against drugs.
- The anti-drug drive began with destroying poppy fields and the theory that "illegal settlers" from Myanmar ethnically related to the KukiZomi people of Manipur are behind clearing forests and government lands to grow opium and cannabis.
- The first violent protest was against the eviction of the residents of a Kuki village.
- This made the State government withdraw from the suspension of operations with two Kuki extremist groups accused of inciting the protesters.
- The large-scale arson and violence claiming the life of at least one person on May 3 and 4, 2023, following a "Tribal solidarity rally" against the reported move to include the Meiteis in the ST list.
|
For Prelims: Meitie tribe, opium, cannabis, Naga Tribes, Kuki Tribes, Imphal Valley,
For Mains 1. Who are Meitei's People? Discuss the Reasons why the tribal groups are against ST status for Meiteis. (250 Words)
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1. Non-scheduled population concentrated in central valley of Manipur is called (BPSC CDPO 2018)
1. Meitei
2. Mishmi
3. Kuki
4. Apatanis
5. None of the above/More than one of the above
Answer: 1
2. Consider the following pairs: (UPSC 2018)
Tradition State
1. Chapchar Kut festival Mizoram
2. Khongjom Parba ballad Manipur
3. Thang-Ta dance Sikkim
Which of the pairs given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only B. 1 and 2 C. 3 only D. 2 and 3
Answer: B
3. Which of the following statements related to tribes in India are correct? (UPSC CAPF 2017)
1. Tharu tribes are found in Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand
2. Irula, Chenchu and Sumali tribes are found in Kerala
3. Garasia tribes are found in Goa
4. Gaddi tribes are nomadic herders of Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 4 only B. 2 and 3 only C. 1, 2 and 4 only D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: C
4. With reference to Manipuri Sankirtana, consider the following statements: (UPSC 2017)
1. It is a song and dance performance.
2. Cymbals are the only musical instruments used in the performance.
3. It is performed to narrate the life and deeds of Lord Krishna.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1, 2 and 3 B. 1 and 3 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 1 only
Answer: B
5. Comprehension
Nagaland, one of India's smallest states, is located in the north-east. It is bounded by Myanmar on the east, Arunachal Pradesh on the north, Assam on the west and Manipur on the south. Nagaland is mostly mountainous except the part bordering the Assam valley. Mount Saramati is the highest peak and forms a natural barrier between Nagaland and Myanmar. The Nagas, inhabitants of Nagaland, form more than twenty tribes. Konyak is the largest of the Naga tribes. Traditionally, the Nagas wear colourful tribal outfits with bamboo shields and decorated spears. They are simple at heart, are known for their festive spirit and burst into dance and music on such occasions as festivals, marriages and harvest. Folk songs and ballads popular among the Nagas uphold such values as bravery, love, generosity, etc. Dances are mostly woven around war themes and are performed with amazing mock war emotions. Bamboo dance is a well-known dance of the Nagas. Colourfully dressed young girls performing the bamboo dance at an incredible speed and with great accuracy present a fascinating sight. The Nagas celebrate their festivals with great enthusiasm. Almost every Naga tribe has its own festival. Sankarni is the major festival of the Zemis tribe. This religious festival coincides with Shivratri. Sekrenyi is a festival celebrated by the Angamis tribe to ensure the health and well-being of the community. Moatsu is the most important festival celebrated by the Aos tribe after the sowing is over. Feasting and merry-making invariably accompany festivals. Wood-carving is a famous Naga craft. The Konyaks, the best wood-carvers among all the Naga tribes, are skilled in carving human and animal figures. Weaving is a traditional Naga art in which each tribe has its own special designs and colours. Shawls, shoulder bags, and intricately woven mats and baskets make magnificent souvenirs for the tourists.
The largest Naga tribe is (Odisha Police SI 2022)
A. Konyak.
B. Zemis.
C. Aos
D. Angami
Answer: A
6. Which of the following tribes belongs to Nagaland? (NTPC 2021)
A. Bonda
B. Limboo
C. Rengma
D. Pnar
Answer: C
|
LANDSLIDES
1. Context
Types of landslides include:
- Falls: Sudden drops of rock or soil from a steep slope or cliff.
- Slides: Movement of material along a defined plane, such as a rockslide or landslide.
- Flows: Fluid-like movement of loose material, such as mudflows or debris flows.
- Creeps: Slow, gradual downslope movement of soil or rock
- The recent cases of land subsidence in Joshimath, Uttarakhand, captured the spotlight.
- On June 29, 2022, at least 79 people were killed in a landslide in the Noney district of Manipur.
- The risk analysis in the report was based on the density of human and livestock populations, which indicates the impacts on people due to these landslides.
- The disaster in Kedaranath in 2013 and the landslides caused by the devastating Sikkim earthquake in 2011 are also included in this atlas.
|
Between 1988 and 2022, the maximum number of landslides 12, 385 recorded in Mizoram.
Uttarakhand followed it at 11, 219, Tripura at 8, 070, Arunachal Pradesh at 7, 689, and Jammu and Kashmir at 7,280. Kerala saw 6,039, Manipur 5,494 and Maharashtra recorded 5, 112 incidents of landslides.
|
- Globally, landslides rank third in terms of deaths among natural disasters.
- However, deforestation due to unplanned urbanisation and human greed increases the risk of such incidents.
- In 2006, about 4 million people were affected by landslides, including a large number of Indians.
- India is among the four major countries where the risk of landslides is the highest; it added. If we look at the figures, about 0.42 million square kilometres in the country are prone to landslides, which is 12.6 per cent of the total land area of the country.
- However, the figure does not include snow-covered areas. Around 0.18 million sq km of landslide-prone areas in the country are in North East Himalayas, including Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas.
- Of the rest, 0.14 million sq km falls in North West Himalaya (Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir); 90, 000 sq km in the Western Ghats and Konkan hills (Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Goa and Maharashtra) and 10, 000 sq km in Eastern Ghats of Aruku in Andhra Pradesh.
4. Reasons for landslides
- Sudden heavy rains due to climate change are also increasing landslides. Around 73 per cent of landslides in the Himalayan region are attributed to heavy rains and reduced water-absorbing capacity of the soil.
- Global climate change is causing heavy rainfall that erodes steep slopes with loose soil found in a 2020 study by the Indian Institute of Technology in Delhi.
- Therefore, the increasing number of landslides can no longer be termed as just natural disasters, as human actions have also played a major role in it.
- Uttakarkhand, Kerala, Jammu and Kashmir, Mizoram, Tripura, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh reported the highest number of landslides during 1998 – 2022
- Mizoram topped the list, recording 12,385 landslide events in the past 25 years, of which 8,926 were recorded in 2017 alone
- Likewise, 2,071 events of the total 2,132 landslides reported in Nagaland during this period occurred during the 2017 monsoon season
- Manipur, too, showed a similar trend, wherein 4,559 out of 5,494 landslide events were experienced during the rainy season of 2017, Of the total 690, Tamil Nadu suffered 603 landslide events in 2018 alone
- Among all these states, an alarming situation is emerging from Uttarakhand and Kerala

- While Uttarakhand’s fragility was recently exposed during the land subsidence events reported from Joshimath since January, this Himalayan state has experienced the second highest number (11,219) of landslides since 1998, all events since occurring post 2000
- The year-wise number of landslide events in the state is: 2003 (32), 2010 (307), 2012 (473), 2013 (6,610), 2017 (1), 2021 (329) and 2022 (1)
- The number of districts with the maximum landslide exposure are in Arunachal Pradesh (16), Kerala (14), Uttarakhand and Jammu and Kashmir (13 each), Himachal Pradesh, Assam and Maharashtra (11 each), Mizoram (8) and Nagaland (7)
- Kerala has been consistently reporting massive landslides since it suffered the century’s worst floods in 2018
- The year-wise landslide events here are 2018 (5,191), 2019 (756), 2020 (9) and 2021 (29).
- From the events and images obtained, the NRSC ranked Rudraprayag in Uttarakhand at the top of 147 vulnerable districts
- It has the highest landslide density in the country, along with having the highest exposure to total population and number of houses
For Prelims & Mains
| For Prelims: Landslides, climate change, ISRO, Disaster management, National Remote Sensing Centre, Landslide Atlas of India |
Previous year questions
|
1. Which of the following statements in respect of landslides are correct? (NDA 2022) 1. These occur only on gentle slopes during rain.
2. They generally occur in clay-rich soil.
3. Earthquakes trigger landslides.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 1 and 3 D. 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (B) For Mains: 1. Describe the various causes and the effects of landslides. Mention the important components of the National Landslide Risk Management Strategy. (250 words) (2021)
|
Source: The Down to Earth
LOW EARTH ORBIT (LEO)
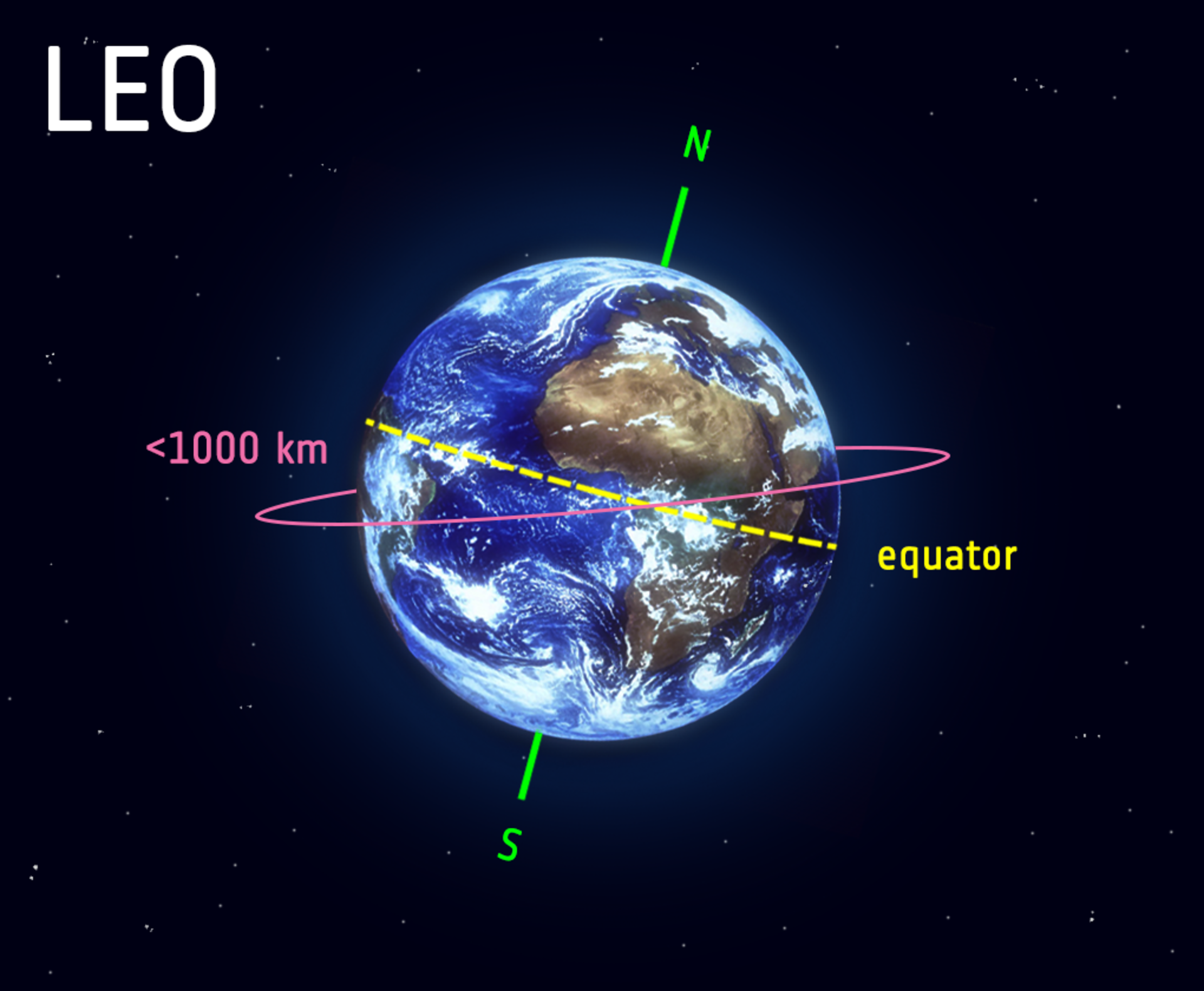
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with an altitude of 2,000 kilometers (1,200 miles) or less. It is the most common type of orbit for artificial satellites, and it is used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Earth observation: LEO satellites can provide high-resolution images of the Earth's surface, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as monitoring environmental change, tracking weather patterns, and providing military intelligence.
- Communication: LEO satellites can be used to relay communications signals between different parts of the Earth. This is especially useful in remote areas that are not served by terrestrial communications infrastructure.
- Navigation: LEO satellites are used by the Global Positioning System (GPS) to provide accurate positioning information to users on the ground.
- Scientific research: LEO satellites can be used to conduct a variety of scientific experiments, such as studying the Earth's atmosphere, the Sun, and the stars.
- Shorter orbital periods: Satellites in LEO have shorter orbital periods than satellites in higher orbits. This means that they can transmit data to Earth more quickly.
- Lower communication latency: The lower orbital period of LEO satellites also means that there is lower communication latency, which is the time it takes for a signal to travel from the satellite to Earth.
- Closer to Earth: LEO satellites are closer to Earth than satellites in higher orbits. This means that they can be serviced more easily, and they are less likely to be affected by space debris.
DS-SAR stands for Dual-Speed Synthetic Aperture Radar. It is a Singaporean SAR Earth Observation satellite that was launched into orbit on July 30, 2023.
The satellite was developed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Defence Science and Technology Agency (DSTA) of Singapore.
DS-SAR is a dual-frequency SAR satellite, meaning that it can operate at two different radar frequencies: C-band and L-band.
This allows the satellite to produce images with different characteristics, depending on the frequency used. For example, C-band images are typically better at resolving fine details, while L-band images are better at penetrating clouds and other obscurants.
6.Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is an expendable launch vehicle developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
It is a three-stage, solid-and-liquid-fueled rocket that is capable of launching satellites into Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Sun-synchronous orbits, and Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO)
The PSLV has been used to launch a wide variety of satellites, including Earth observation satellites, communication satellites, and scientific satellites.
It has also been used to launch commercial satellites for customers around the world
7.Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
The GSLV is an expendable launch vehicle developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
It is a three-stage, liquid-fueled rocket that is capable of launching satellites into geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO)
The GSLV was first launched in 2001, and has since been used to launch a variety of satellites, including communication satellites, weather satellites, and scientific satellites
|
For Prelims: Low Earth Orbit (LEO), PSLV, GSLV
For Mains: 1.Discuss the significance of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in India's space program. Highlight its features and capabilities that have made it a reliable and preferred launch vehicle for both domestic and international satellite missions
2.GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) is a crucial component of India's space endeavors. Elaborate on its design, stages, and payload capacity. Compare and contrast GSLV with PSLV in terms of their applications and advantages
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1.A low earth orbit satellite can provide large signal strength at an earth station because: (ESE Electronics 2011)
A. Path loss is low
B. These orbits are immune to noise
C. Large solar power can be generated at these orbits
D. Lower microwave frequencies in s-band can be used
Answer-A
|
FIRE SAFETY REGULATIONS IN INDIA
The Union of India’s stance on fire safety emphasizes the Model Building Bye-Laws, 2016, particularly Chapter 11 on “Fire Protection and Fire Safety Requirements,” which serves as a framework for State governments responsible for fire safety enforcement. Adherence to fire safety norms and standards outlined in Part 4 of the National Building Code (NBC) is required, with States tasked with incorporating these mandatory provisions.
Classification of Assembly Buildings
- According to the bylaws, the Rajkot game zone would be categorised under assembly buildings.
- This classification includes venues without permanent seating where 300 or more people gather.
- The definition of assembly buildings is broad, encompassing any building or part of a building where “not less than 50 gather for amusement, recreation, social, religious, patriotic, civil, travel and similar purposes.”
- Examples include theatres, motion picture houses, assembly halls, museums, skating rinks, gymnasiums, restaurants, places of worship, dance halls, club rooms, passenger stations, terminals of public transportation services, recreation piers, and stadia.
Regulations for Other Building Types
- Hospitals, custodial, penal, or mental health institutions are classified as institutional buildings. Separate categories exist for educational, business, industrial, and specialized-use buildings.
Pandemic-Era Fire Safety Guidelines
- Amidst a series of fires during the pandemic, the Health Ministry issued guidelines on September 28, 2020, mandating third-party accreditation for fire safety and the implementation of a fire response plan. Chapter 11 of the Bye-Laws specifies fire safety and infrastructure requirements for buildings 49 feet in height or more and those with low occupancies across various categories for the issuance of a No Objection Certificate (NOC).
Gujarat's Specific Fire Safety Regulations
- Under Gujarat’s Comprehensive Development Control Regulations 2017, obtaining the Chief Fire Officer’s opinion is mandatory even for temporary structures.
- These regulations require all structures to comply with fire prevention and safety provisions as specified by the Fire Authority, in the Fire Prevention and Life Safety Measures Act, 2013.
Compliance Issues at Rajkot Game Zone
- The Rajkot game zone was reportedly constructed as a non-standard structure to bypass regulatory requirements.
- The ongoing inquiry will determine whether it meets the qualifications for use as an assembly building offering leisure and entertainment services.
2. Judicial Perspective on Fire Safety Neglect
Uphaar Cinema Tragedy
- The Uphaar cinema tragedy of 1997 in Delhi remains one of the most high-profile deadly fire accidents in India.
- The fire resulted in the deaths of 59 people trapped in the balcony due to illegally installed seats and a blocked exit.
- This incident led to the conviction of the venue owners, Sushil Ansal and Gopal Ansal, along with others for negligence and evidence tampering.
- The legal battle was lengthy, with victims' families forming an association to seek justice.
- The owners were prosecuted under charges of causing death by negligence (IPC 304A), hurt or grievous hurt by rash or negligent act (337, 338), and culpable homicide (304).
- Additionally, theatre staff and public agency employees, such as those from the electricity authority, were held accountable.
- The fire was triggered by an unsanctioned transformer installed without safeguards, for which the owners bore direct responsibility due to structural deviations.
- The court held property owners, employees, and electricity agency staff liable for the fire's devastating toll.
- Despite their convictions, the Ansal brothers' reduced sentences sparked criticism from the Association of Victims of Uphaar Tragedy, particularly on the fire's anniversary, June 13.
High Court's Suo Motu Action
- Following the Rajkot gaming centre fire, the Gujarat High Court took suo motu cognizance, scrutinizing the enforcement of fire and building laws and identifying unauthorized leisure and entertainment venues.
- The court was informed by the Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation about the Gujarat Regularisation of Unauthorised Development Act, 2022, which has been in force since January 2, 2023. This law was cited by an unauthorized game zone seeking regularization.
Previous Incidents and Ongoing Concerns
- Gujarat has experienced several tragic fires in recent years, prompting calls for stricter fire safety regulations.
- Notably, the 2019 fire in Surat’s Takshashila Arcade tuition centre claimed the lives of over 20 students.
- In the wake of the Rajkot fire, the Gujarat High Court acknowledged a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) and criticized the State government for not complying with its earlier orders, stating that “insult [had been] added to injury.”
- The judiciary's stance on these incidents underscores the critical need for stringent adherence to fire safety regulations and proactive measures to prevent such tragedies in the future.
3. Enforcing Fire Safety Laws











