CPTPP
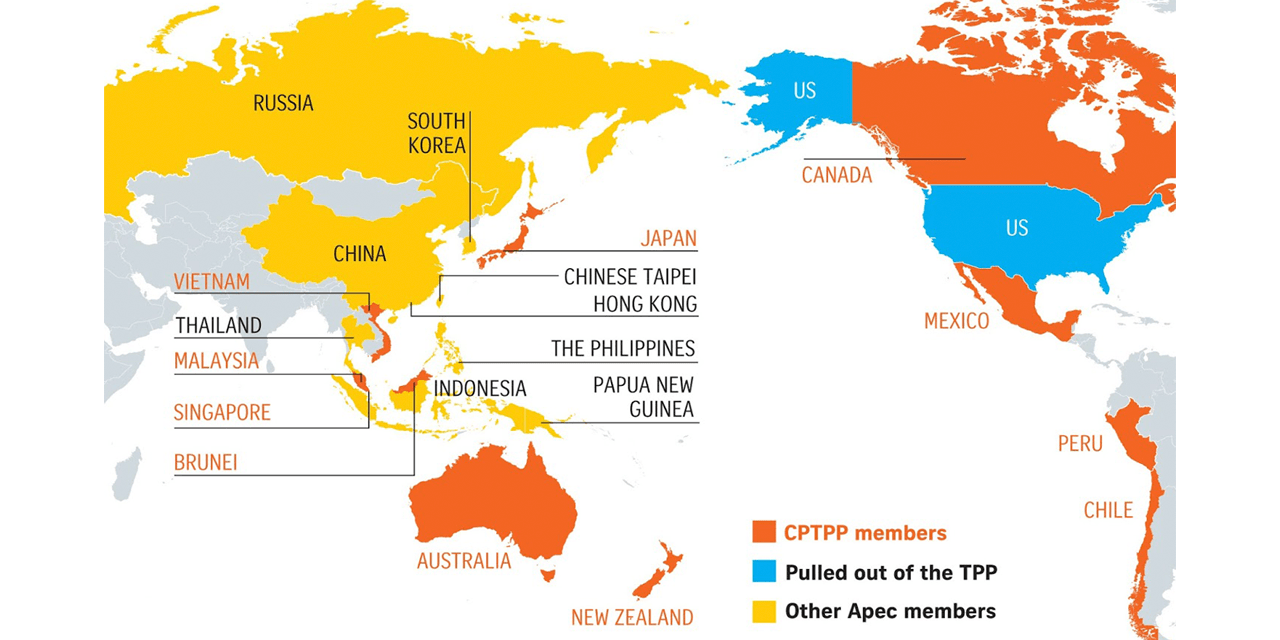
- The UK government says CPTTP will cut tariffs for UK exports to Asia Pacific countries and with UK membership, the trading bloc will have a combined GDP of 12 trillion pounds and account for 15% of global trade
- Britain is keen to deepen trade ties in the Pacific after Brexit in 2020
- London has been pushing a “Global Britain” strategy since it gave up EU membership after nearly 50 years, leaving the bloc’s single market and customs union
- Instead, former British Prime Minister Boris Johnson negotiated a trade deal called the EU–UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement
- Since Brexit, the UK has sought other trade deals with countries and trading blocs around the world that the government says have faster-growing economies than the EU
- But London will likely struggle to achieve free trade deals with large powers like China in the near term and even its closest ally, the United States has said further trade liberalization with Britain is currently off the table
- Critics say CPTTP and other deals will struggle to compensate for the economic damage sustained by leaving the now-27-member EU — the world’s largest trading bloc and collective economy
- The UK’s long-term productivity is forecast to be reduced by 4% as a result of Brexit, according to the government’s spending watchdog, the Office for Budget Responsibility.
- The UK already has trade deals with 10 of the 11 other CPTPP members and the eventual economic boost is likely to increase GDP by just 0.08% annually.
- In 2022, Britain exported 340 billion pounds of goods and services to the EU, 42% of total UK exports
|
For Prelims: Free Trade Agreement, North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
For Mains: 1.Explain the concept of preferential trade agreements (PTAs). Compare and contrast PTAs with free trade agreements (FTAs) and customs unions. Assess the advantages and limitations of PTAs.
2.Discuss the role of intellectual property rights (IPRs) in international trade agreements. Examine the challenges and opportunities associated with the protection and enforcement of IPRs in the context of global trade. |




