SPACE WEATHER
With an exponential rise in satellite-based services used for navigation and communications, obtaining forecasts and data on the health of Space weather is of supreme importance.
But what factors drive Space weather? National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is set to launch the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) to study one of the important drivers of Space weather – the Earth’s weather
2. What is Space weather?
Similar to how Earth experiences weather patterns, the space encompassing Earth and other planets remains constantly affected by the Sun and its activities, such as solar flares and emissions, as well as the various materials present in the surrounding space. When Earth encounters severe or turbulent weather conditions, space weather can also undergo extreme events. These events directly affect crucial Earth-based installations like satellite communication systems, radio communication, and the orbits or stations of space-based aircraft, thereby disrupting the smooth functioning of navigation systems, Global Positioning Systems (GPS), and power grids.
In addition to the influence of solar emissions, space weather is also impacted by conditions originating from terrestrial weather.
3. What is a Gravity wave?
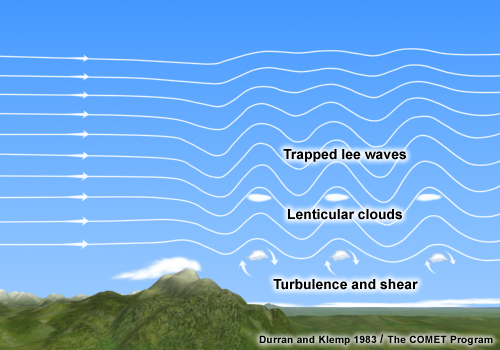
- Gravity waves are not to be confused with gravitational waves, which are ripples in space-time predicted by Einstein's theory of general relativity and are caused by the acceleration of massive objects.
- Gravity waves, on the other hand, refer to waves generated in the Earth's atmosphere or any other fluid medium (like oceans) due to the force of gravity attempting to restore equilibrium after it's been disrupted.
- These waves are caused by disturbances such as air moving over mountains, turbulent atmospheric conditions, or even the passage of weather systems.
- They propagate vertically through the atmosphere and can transfer energy and momentum from one location to another.
- Gravity waves are often associated with changes in temperature, wind, and pressure in the atmosphere. While they play a role in redistributing energy in the atmosphere and influencing weather patterns, they are distinct from gravitational waves in physics
- In the atmosphere, there are a wide variety of waves, travelling both horizontally and vertically. Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGW) are one such kind of vertical wave.
- They are mostly generated when there is an extreme weather event or a sudden disturbance leading to a vertical displacement of stable air
- Natural phenomena like thunderstorms, hurricanes, tornadoes, regional orography and others have the potential to send out a variety of periodic waves, including AGWs, in the lower levels of the atmosphere
- A stable atmosphere plays an important role in the generation of gravity waves, that is, when the atmosphere is stable, the temperature difference between the rising air and the atmosphere produces a force that pushes this air to its original position. The air will continuously rise and sink, thus creating a wave-like pattern
- AGW is a wave that moves through a stable layer of the atmosphere, wherein the upward-moving region is the most favourable for the formation of cloud patterns or streaks. AGWs continue all the way to Space, where they contribute to the Space weather
4. What is the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE)?

- AWE represents a pioneering NASA initiative designed to explore the connections between terrestrial and space weather phenomena.
- Developed as part of NASA's Heliophysics Explorers Program and funded at $42 million, this mission seeks to investigate how waves in the lower layers of the atmosphere influence the upper atmosphere and, consequently, space weather.
- The AWE mission will be launched and affixed to the exterior of the International Space Station (ISS) in Earth's orbit. Its observational position will allow it to observe Earth and capture the colorful luminous bands, known as airglow.
- "AWE has the potential to introduce a novel realm of research, delving into the inquiry of whether space weather is influenced by forces originating from Earth's atmosphere and from bottom-up mechanisms," explained Dibyendu Nandi, a solar physicist and the head of the Center of Excellence in Space Sciences India at IISER, Kolkata.
Onboard AWE is an Advanced Mesospheric Temperature Mapper (ATMT), an instrument that will scan or map the mesopause (a region between the mesosphere and thermosphere). Using the four identical telescopes comprising an imaging radiometer, scientists hope to obtain the brightness of light at specific wavelengths.
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (UPSC CSE 2019) (a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected. Answer: (b) 2. India’s first Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) laboratory will be set up in which State? (BPSC 2016) A.Uttar Pradesh B.Maharashtra C.Andhra Pradesh D.Bihar E.None of the above/More than one of the above Answer (B) |




