SPECTRO POLARIMETRY OF HABITABLE PLANET EARTH (SHAPE)
- Chandrayaan-3 had been proposed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) as a follow-up mission to the Chandrayaan-2 lunar mission. Chandrayaan-2, launched in July 2019, aimed to study the Moon's south polar region and included an orbiter, a lander (Vikram), and a rover (Pragyan)
- The Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft comprises two parts
- The Lander Module, which also houses the rover component, is designed to travel to the Moon and is expected to land on the lunar surface
- The leftover part, the Propulsion Module, whose job was to transport the Lander to the Moon orbit, will continue to go around the Moon for a few months, possibly even years, in an outer orbit
- The Lander Module is scheduled to make two orbit-reduction manoeuvres over the coming days, first attaining a circular 100 km x 100 km orbit, then coming down further into a 100 km x 30 km orbit
- It is from here that the Lander will begin its final descent to make a touchdown on the Moon
- The Propulsion Module of Chandrayaan-3 has been doing the job of the Orbiter component in Chandrayaan-2.
- It is equipped with one instrument called SHAPE (Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth) whose job is to make spectroscopic study of the Earth’s atmosphere from that distance, and try to pick up signals that will help scientists understand the markers of life on planets outside our solar system

- The SHAPE mission is a collaborative effort between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (IKI)
- The Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) is an experimental payload onboard the Chandrayaan-3 mission. It is designed to study the spectro-polarimetric signatures of Earth in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range (1.0 – 1.7 μm)
- Polarimetry is a technique that measures the polarization of light. Polarization refers to the direction of the electric field of light waves. Light that is not polarized has its electric field randomly oriented in all directions. Polarized light has its electric field oriented in a specific direction.
- Spectro-polarimetry is a combination of spectroscopy and polarimetry. Spectroscopy is the study of the spectrum of light, which is the distribution of light energy over different wavelengths
The SHAPE instrument will use spectro-polarimetry to study the following aspects of Earth's atmosphere:
- The distribution of water vapor and other gases
- The presence of clouds and aerosols
- The structure of the atmosphere
- The changes in the atmosphere caused by human activity
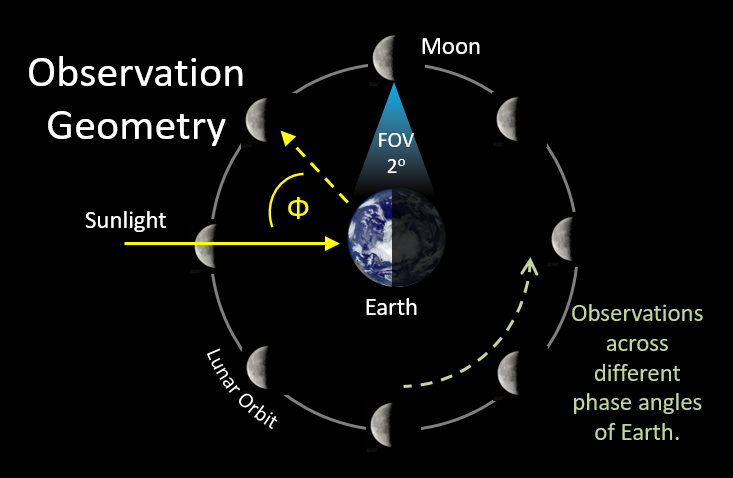
- SHAPE can be used to study the distribution of water vapor in Earth's atmosphere. Water vapor is an important greenhouse gas that plays a role in climate change. SHAPE can be used to map the distribution of water vapor in the atmosphere and to study how it changes over time.
- SHAPE can be used to study the presence of clouds and aerosols in Earth's atmosphere. Clouds and aerosols reflect sunlight, which can affect the amount of heat that is absorbed by Earth. SHAPE can be used to map the distribution of clouds and aerosols in the atmosphere and to study how they change over time.
- SHAPE can be used to study the structure of Earth's atmosphere. The atmosphere is made up of several layers, each with its own unique properties. SHAPE can be used to study the different layers of the atmosphere and to study how they interact with each other.
- SHAPE can be used to study the changes in Earth's atmosphere caused by human activity. Human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels, is releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases are causing the atmosphere to warm, which is leading to changes in the climate. SHAPE can be used to study these changes and to help us understand the impact of human activity on the atmosphere
|
For Prelims: Chandrayan-3, SHAPE, PSLV, GSLV
For Mains: 1.Critically assess the role of Chandrayaan missions in promoting scientific research and technological innovation in India. How have these missions inspired the nation's youth and bolstered India's reputation in the global space community?
2.Discuss the international collaborations and partnerships that ISRO has established for its Chandrayaan missions. How do such collaborations enhance the scientific outcomes of these missions and contribute to global space research?
|
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Chandrayan-1, India's first mission to the moonwas launched from----- (SSC CPO Tier-1 2019)
A. Srikalahasti
B.Srikakulam
C.Sriharikota
D.Srisailam
Answer- C
|




