RULE OF LAW
1. Introduction
- The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders
- The notion behind the rule of law is to curb the exercise of arbitrary power by anyone
- But, formally defining the rule of law can be much more onerous and can often lead to rather serpentine definitions
- For the United Nations (UN), the rule of law “is a principle of governance in which all persons, institutions and entities, public and private, including the State itself, are accountable to laws that are publicly promulgated, equally enforced and independently adjudicated, and which are consistent with international human rights norms and standards”
2. Outcomes of Rule of Law
The World Justice Project (WJP), which is an independent, multidisciplinary organization working to advance the rule of law worldwide, lays out four broad outcomes, as it were, if the rule of law prevails in a country
These are:
- Accountability: Implying that the government as well as private actors are accountable under the law
- Just Law: Implying that the law is clear, publicised, and stable and is applied evenly. It ensures human rights as well as property, contract, and procedural rights
- Open Government: Implying that the processes by which the law is adopted, administered, adjudicated, and enforced are accessible, fair, and efficient
- Accessible and Impartial Justice: Implying that justice is delivered timely by competent, ethical, and independent representatives and neutrals who are accessible, have adequate resources, and reflect the makeup of the communities they serve
3. Calculation of Rule of Law
- The index measures people’s perceptions and experiences of the rule of law in 140 countries and jurisdictions
- The data featured in the 2022 report comes from global surveys completed by more than 154,000 households and 3,600 legal practitioners and experts
- To build this index, the WJP looks at eight factors, which are further sub-divided into 44 sub-factors.
The eight main factors are as follows:
- Constraints on government powers: This includes things like how effectively does the legislature or the judiciary deal with the government.
- Absence of corruption: This essentially ascertains if public offices are being used for private gains.
- Open Government: This includes things such as the right to information and laws and government data are well publicised.
- Fundamental rights: This also includes whether the due process was followed.
- Order and security: Whether crime is effectively controlled and civil conflict limited etc.
- Regulatory enforcement: Things like whether regulations are effectively enforced etc.
- Civil justice: Includes factors such as whether people can afford and access civil justice,
- Criminal justice: Includes factors such as whether due procedures are followed etc.
The index values range between 0 and 1 with 1 being the score for complete adherence to the rule of law.
4. Importance of Rule of Law
Research shows that a stricter adherence to the rule of law is positively correlated to higher economic growth, better educational attainment, improved health outcomes, and greater peace among other benefits
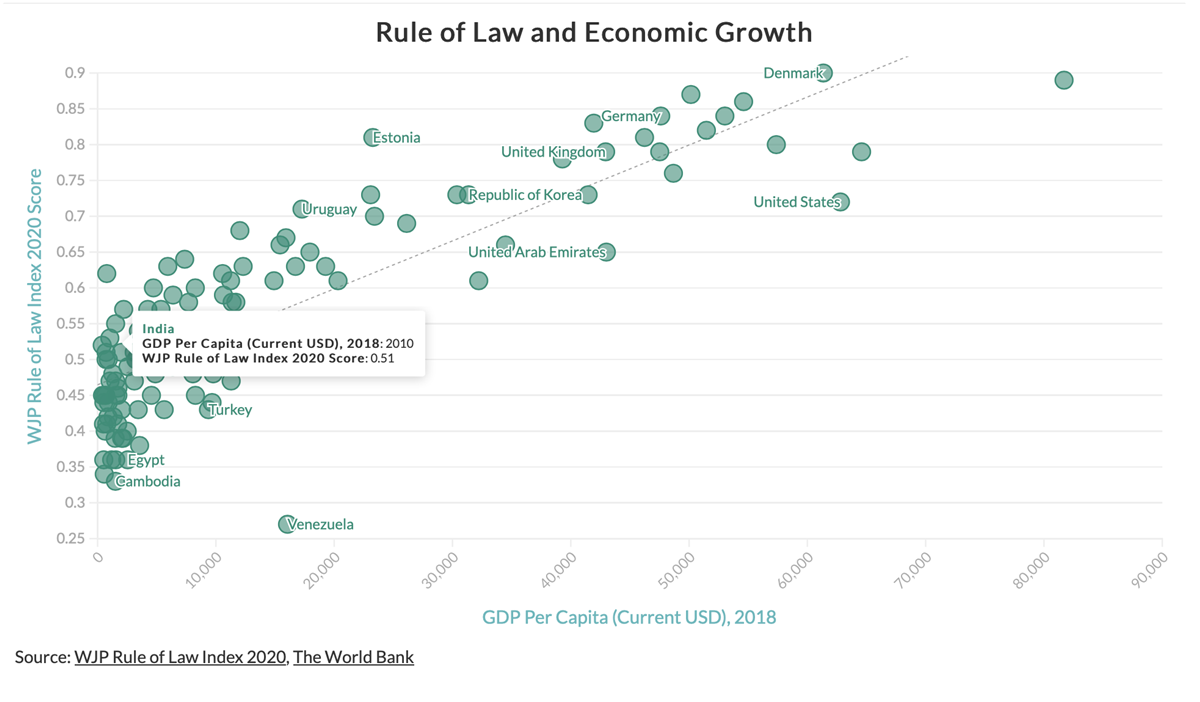
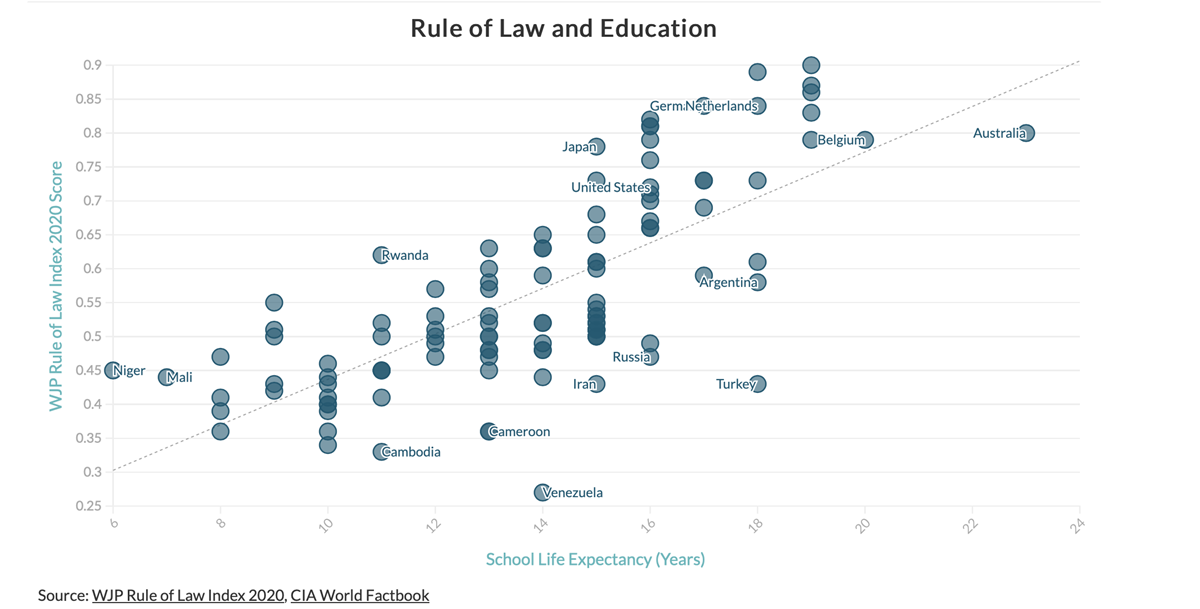
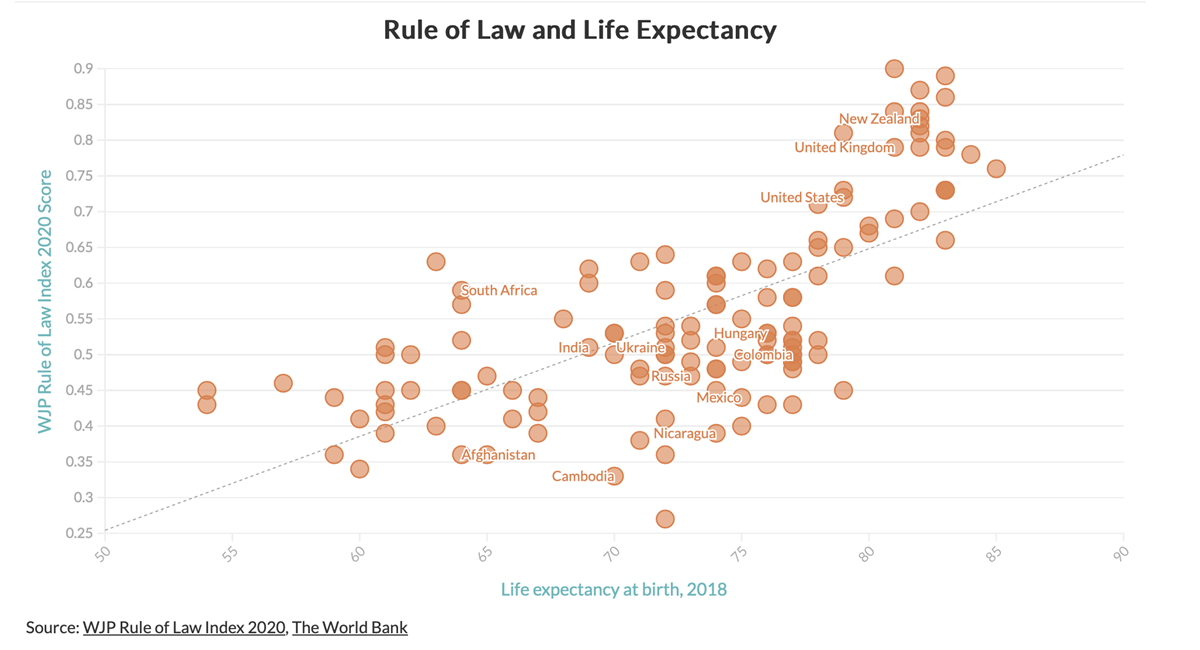
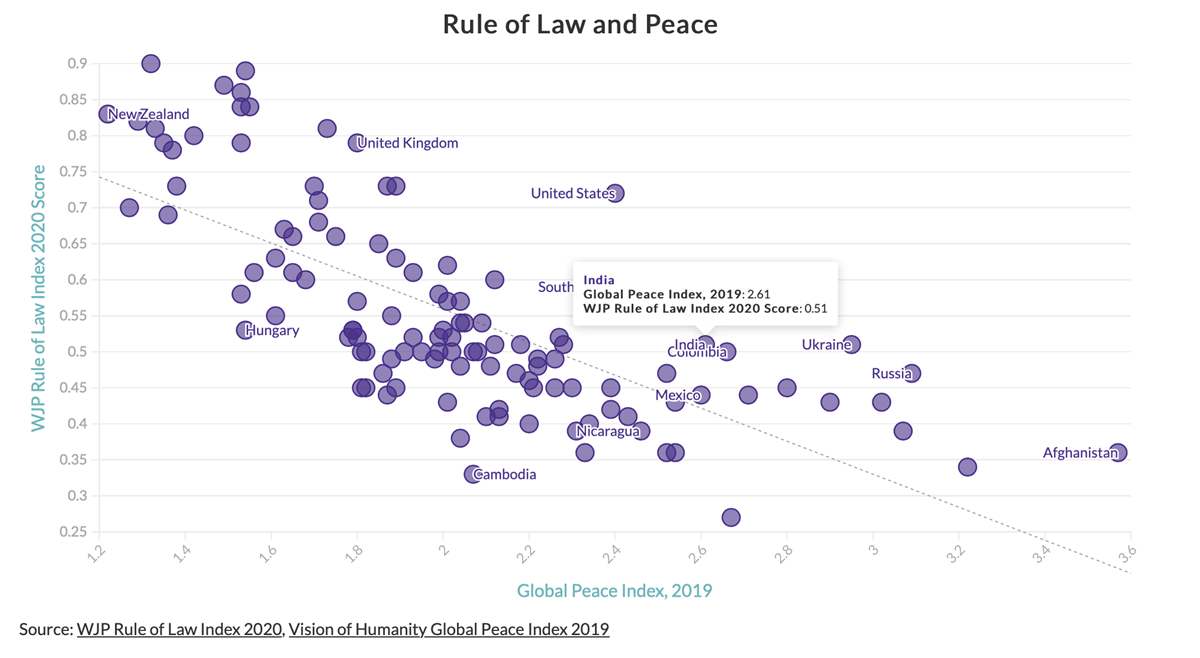
5. India's Stand on the Rule of Law
India’s overall score in the 2022 report is 0.5 and its global rank is 77 out of 140 countries
It is noteworthy that in 6 out of the 8 categories, India’s rank is lower than its overall rank
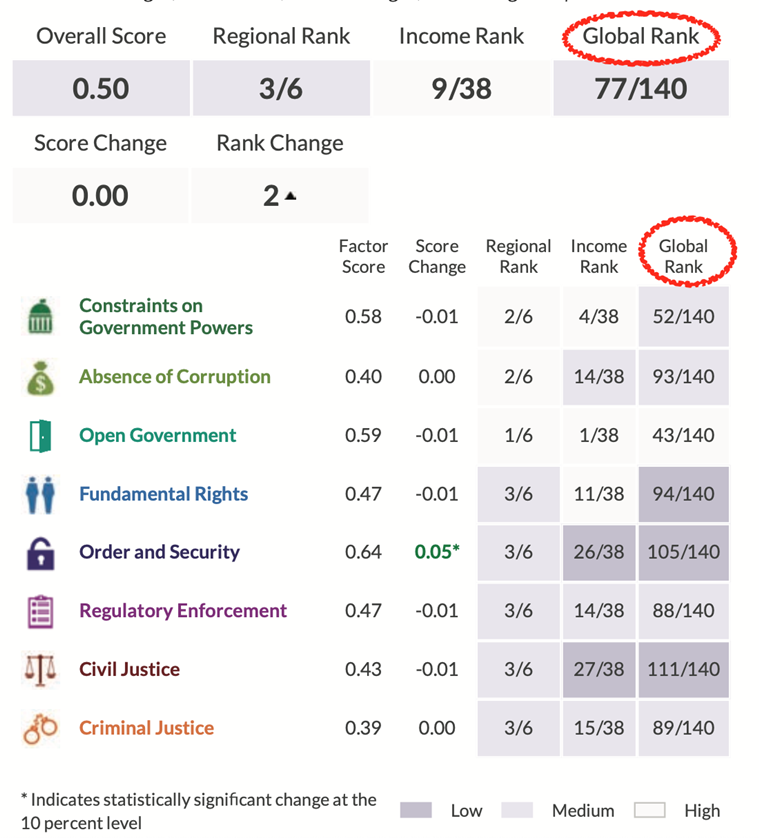
- Even though India’s score hasn’t changed, it has moved up two places in the latest rankings. However, if one compares it to 2015, the score has fallen marginally from 0.51 to 0.50 while the rank has changed from being 59th out of the 102 countries ranked in 2015
- Within the South Asia region, India is placed third, behind Nepal and Sri Lanka, out of six countries; Bangladesh, Pakistan and Afghanistan being the other three
- Among the 38 countries that fall under the same income bracket — namely lower-middle income India is ranked 9th. Countries such as Senegal, Ghana, Indonesia and Ukraine were ahead of India as of the 2022 report
6. Uttar Pradesh's Ranking
The WJP Index does not provide sun-national ranks. However, the India Justice Report (IJR) a collaborative effort between DAKSH, Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative, Common Cause, Centre for Social Justice, Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy and TISS-Prayas for the year 2022 ranks UP at 18 among the 18 large and mid-sized states of India
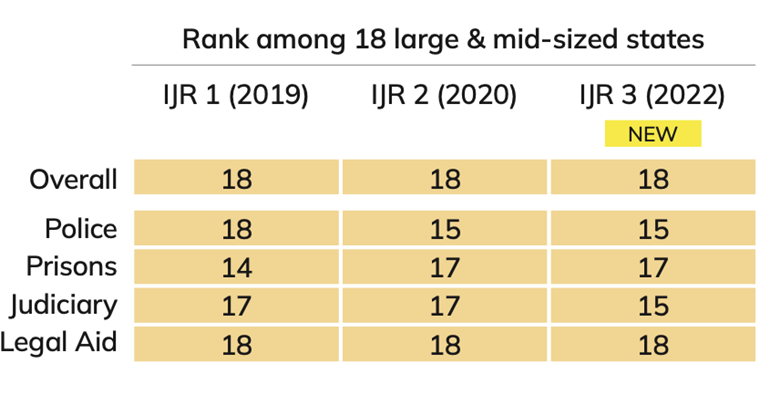
UP was never particularly known for upholding the rule of law. The ongoing approach to dealing with mafia in the state is attracting a lot of attention
Source: indianexpress




