PYROCUMULONIMBUS CLOUDS
1. Context
The wildfires currently raging in the United States and Canada are so intense that they have created ‘pyrocumulonimbus’ clouds, which have the potential to spit out thunder and spark more fires
2.What is a Pyrocumulonimbus cloud?
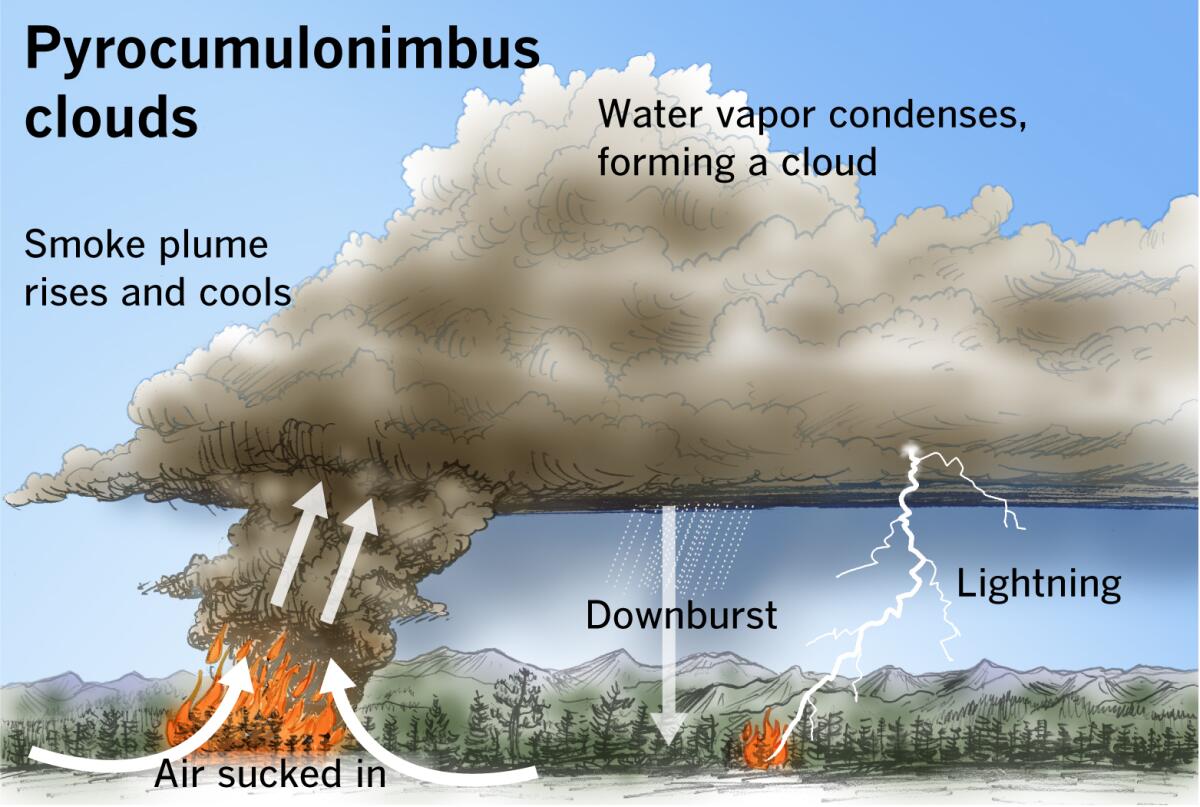
- A pyrocumulonimbus cloud is a type of cloud associated with intense wildfire activity. It forms when a wildfire generates enough heat to create a strong updraft, which can lift smoke and other particulates high into the atmosphere. As the rising air cools, it condenses to form a cloud
- Not all wildfires result in the formation of pyrocumulonimbus clouds. These clouds typically develop only during exceptionally intense wildfires, though volcanic eruptions can also cause their formation. For example, during the Australian bushfires of 2019-2020, pyrocumulonimbus clouds emerged when temperatures exceeded 800 degrees Celsius.
- The extreme heat from the fire warms the surrounding air, causing it to rise into the atmosphere. As this hot, buoyant air—laden with water vapor, smoke, and ash—ascends, it expands and cools.
- When it reaches a sufficiently low temperature, the water vapor condenses around the ash, creating a grey or brown cloud known as a pyrocumulus or 'fire cloud.'
- If enough water vapor is present and the upward air movement strengthens, these clouds can develop into pyrocumulonimbus clouds, which can reach altitudes of up to 50,000 feet and generate their own thunderstorm systems.
- While pyrocumulonimbus clouds can produce lightning, they usually do not produce significant rainfall. This can lead to new wildfires starting far from the original blaze and may also generate strong winds that accelerate and complicate the spread of the wildfire
3. Frequent events of forming pyrocumulonimbus cloud
Pyrocumulonimbus cloud events are occurring more frequently due to several interrelated factors:
- Rising global temperatures contribute to more frequent and intense wildfires. Higher temperatures lead to drier conditions and more flammable vegetation, which can fuel larger and more intense fires that generate the necessary heat to form pyrocumulonimbus clouds
- Climate change is driving more extreme weather patterns, including hotter and drier conditions. These conditions are conducive to larger and more severe wildfires, increasing the likelihood of pyrocumulonimbus cloud formation
- Warmer temperatures and prolonged droughts are extending the fire season, allowing for more opportunities for pyrocumulonimbus clouds to develop. In some regions, fires are now burning year-round, rather than just during traditional fire seasons
- The size and duration of wildfires have increased, creating more sustained heat sources. This sustained heat can produce the intense updrafts necessary for the formation of pyrocumulonimbus clouds
- Changes in land use, such as deforestation and the expansion of agricultural lands, can alter the natural vegetation cover, making areas more susceptible to intense wildfires
- Increased human activity and infrastructure development in wildfire-prone areas can lead to more frequent ignition sources and larger fires, which can contribute to the formation of pyrocumulonimbus clouds
4. Challenges with pyrocumulonimbus Clouds
Pyrocumulonimbus clouds pose several significant challenges, particularly in the context of wildfire management and environmental impact:
- Pyrocumulonimbus clouds can create their own weather systems, including strong winds and lightning, which can exacerbate existing wildfires and cause them to spread more rapidly and unpredictably
- The lightning generated by pyrocumulonimbus clouds can spark new wildfires many kilometers away from the original blaze, complicating firefighting efforts and increasing the area affected by fires
- These clouds can produce severe weather conditions, including intense winds and localized thunderstorms. This can lead to dangerous situations for both firefighters and nearby communities, as well as contribute to further fire spread
- Pyrocumulonimbus clouds contribute to the release of large amounts of particulate matter, smoke, and pollutants into the atmosphere. This can severely degrade air quality over large areas, affecting human health and the environment
- The complex interactions between the heat generated by the fire and atmospheric conditions can make the behavior of pyrocumulonimbus clouds highly unpredictable. This unpredictability complicates forecasting and planning for fire management
- The ash and smoke from these clouds can have a short-term cooling effect on the atmosphere but may contribute to longer-term climate changes. Additionally, the particles can affect weather patterns and precipitation
- The intense heat and high winds associated with pyrocumulonimbus clouds can cause significant damage to infrastructure, including power lines, buildings, and transportation networks
5. Way forward
The precise cause is still uncertain because, unlike other extreme weather events, research on pyrocumulonimbus clouds is relatively recent. Nonetheless, scientists suspect that climate change may be contributing to their increased frequency.
Research indicates that rising global temperatures are leading to more frequent and severe wildfires, which might be driving up the occurrence of pyrocumulonimbus clouds
|
For Prelims: Cumulonimbus clouds, pyrocumulonimbus clouds
For Mains: GS I - World Geography
|
Source: Indianexpress




