INTERNATIONAL SOLAR ALLIANCE (ISA)
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an initiative led by India and France, launched during the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris in 2015.
- It aims to promote the use of solar energy globally, especially in solar-rich countries lying fully or partially between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. However, membership is now open to all UN member countries
- India, as a founding member, uses ISA as a platform to advance its renewable energy targets, including the ambitious goal of achieving 500 GW of renewable capacity by 2030.
- The ISA complements India's domestic initiatives, like the National Solar Mission
- In 2021, the United States joined the ISA, signaling global support for solar energy adoption.
- The One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG) initiative, also led by India, aligns with ISA’s objectives by advocating for a transnational solar grid that connects renewable energy sources globally.
-
The ISA was intended to act as a catalyst, helping countries tackle challenges like financial, technological, and regulatory barriers to adopt solar energy effectively.
-
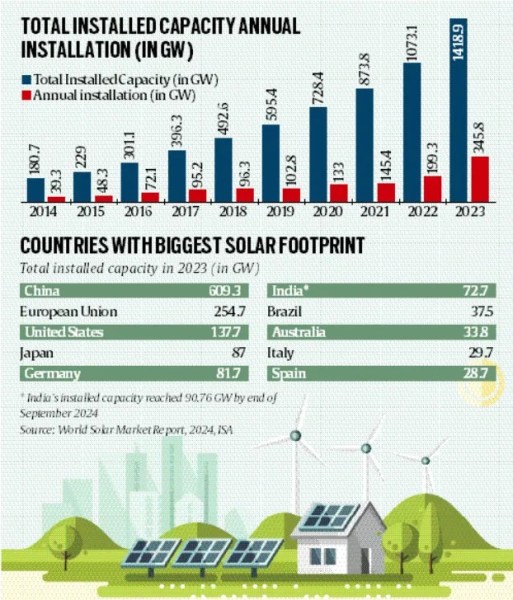
Despite significant advancements in solar energy deployment, ISA has had limited success in facilitating a large number of projects. Over the past five years, global solar power capacity has grown by over 20% annually, with a more than 30% increase reported last year, as indicated by ISA’s World Solar Market Report 2024.
-
Ajay Mathur, director general of ISA, noted that most of these new installations are concentrated in a few countries, with China leading the way. Of the 345 GW of solar capacity added in 2023, China alone contributed over 216 GW, representing more than 62% of the total.
-
More than 80% of global solar energy investments go to developed countries, China, and major emerging markets like India.
-
Many countries lack experience with large-scale energy projects, especially in solar, which is a relatively new technology. Local developers are often absent, meaning international companies are needed for investment. However, these investors typically look for policy stability and well-defined regulatory frameworks.
-
ISA has partnered with governments and local organizations to help establish regulatory frameworks, prepare power purchase agreements, and train local professionals
| India’s dedication to renewable energy and climate action was fundamental to the establishment of the ISA. With a goal of reaching 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy by 2030, India’s renewable energy targets align with the ISA’s mission to promote solar energy worldwide. This target is part of India’s broader Panchamrit Initiative, which focuses on reducing carbon emissions and advancing sustainable development. Additionally, India is instrumental in shaping ISA’s programs and promoting global cooperation. Its extensive experience in scaling solar energy projects and developing supportive policies serves as a model for other member nations, particularly those aiming to expand energy access. By sharing best practices and technical knowledge, India seeks to support other countries in advancing their solar energy initiatives. |
- Solar energy plays a pivotal role in the global shift to renewable energy, which is essential for addressing climate change. It is the fastest-growing renewable source, though it does face the challenge of intermittency.
-
In many parts of the world, solar is now the most cost-effective energy source when sunlight is available. Projections for solar energy capacity show it could expand by 3 to 15 times by 2050, depending on the pathway chosen to reach global net-zero emissions.
-
China leads in solar PV installations, accounting for about 43% of the world's total. The top ten markets together hold over 95% of installed capacity, while less than 2% of new solar installations are in Africa—a region where nearly 80% of the 745 million people without electricity reside.
-
The ISA was founded with a broader strategic vision for India, aiming to enhance its influence, especially among the Global South, with a particular focus on African nations
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) seeks to mobilize $1 trillion in solar investments by 2030 through its 'Towards 1000' strategy, which aims to lower both technology and financing costs.
- This ambitious plan targets energy access for 1 billion people and the installation of 1,000 GW of solar capacity. Achieving these objectives would reduce global carbon emissions by approximately 1,000 million tonnes of CO₂ per year.
- ISA’s programs focus on three core areas—Analytics & Advocacy, Capacity Building, and Programmatic Support—to establish a supportive environment for solar investments and share best practices among member nations.
- ISA also drives solar adoption across sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, transportation, and power generation. By promoting policies and facilitating the exchange of successful strategies, ISA enables member countries to encourage solar energy deployment.
- The alliance has introduced innovative business models, supported governments in developing solar-friendly policies via its Ease of Doing Solar analytics, and pooled demand to reduce costs of solar technologies.
- Additionally, ISA enhances financing access by lowering investment risks, making the solar sector more attractive to private investors and paving the way toward a sustainable energy future.
- India's solar sector is growing rapidly, placing the country fifth globally in terms of solar power capacity. As of September 2024, India’s installed solar capacity has reached around 90.76 GW, a 30-fold increase over the last nine years. According to the National Institute of Solar Energy, the country’s solar potential is estimated at 748 GW.
- India’s Panchamrit targets include: (i) achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy capacity by 2030, (ii) sourcing 50% of its energy from renewables by 2030, (iii) reducing projected carbon emissions by one billion tonnes by 2030, (iv) cutting carbon intensity by 45% by 2030, and (v) reaching Net Zero by 2070.
- India has made significant progress, with its non-fossil fuel capacity increasing by 396% over the past 8.5 years, and 46.3% of its total energy capacity now comes from non-fossil sources, underscoring its dedication to sustainable energy as highlighted in international climate forums.
- Government policies, including the 100% FDI allowance in renewable energy projects, have enhanced the sector's appeal to investors. Additionally, technological advancements and a strong regulatory framework are creating an enabling environment for the continued expansion of solar energy projects
The International Solar Alliance (ISA) represents a pivotal shift towards a sustainable energy future, with India at the forefront of this initiative. The ISA’s mission extends beyond improving energy access and security to making substantial global carbon emissions reductions. The upcoming assembly offers an essential platform for nations to collaborate and emphasize the urgent need to accelerate solar energy adoption.
As more countries align with ISA’s mission, solar energy is positioned to play a central role in the global energy landscape. The ISA’s efforts, coupled with India’s strong commitment to solar advancement, pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable world for future generations. Through international cooperation and innovative approaches, the ISA is well-positioned to contribute meaningfully to global climate objectives and universal energy access
|
For Prelims: General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity & climate change For Mains: GS-III: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment. |
|
Previous Year Questions
1.Consider the following statements: (2016)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only Answer (a)
|





